mirror of
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master.git
synced 2026-02-11 14:45:14 +08:00
Merge branch 'youngyangyang04:master' into master
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,6 +1,10 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 44. 开发商购买土地
|
||||
|
||||
> 本题为代码随想录后续扩充题目,还没有视频讲解,顺便让大家练习一下ACM输入输出模式(笔试面试必备)
|
||||
|
||||
[题目链接](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1044)
|
||||
|
||||
【题目描述】
|
||||
|
||||
在一个城市区域内,被划分成了n * m个连续的区块,每个区块都拥有不同的权值,代表着其土地价值。目前,有两家开发公司,A 公司和 B 公司,希望购买这个城市区域的土地。
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +61,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如果本题要求 任何两个行(或者列)之间的数值总和,大家在[0058.区间和](./0058.区间和.md) 的基础上 应该知道怎么求。
|
||||
|
||||
就是前缀和的思路,先统计好,前n行的和 q[n],如果要求矩阵 a 行到 b行 之间的总和,那么就 q[b] - q[a - 1]就好。
|
||||
就是前缀和的思路,先统计好,前n行的和 q[n],如果要求矩阵 a行 到 b行 之间的总和,那么就 q[b] - q[a - 1]就好。
|
||||
|
||||
至于为什么是 a - 1,大家去看 [0058.区间和](./0058.区间和.md) 的分析,使用 前缀和 要注意 区间左右边的开闭情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@
|
||||
5 6 2
|
||||
5 7 1
|
||||
6 7 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出示例:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ kruscal的思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
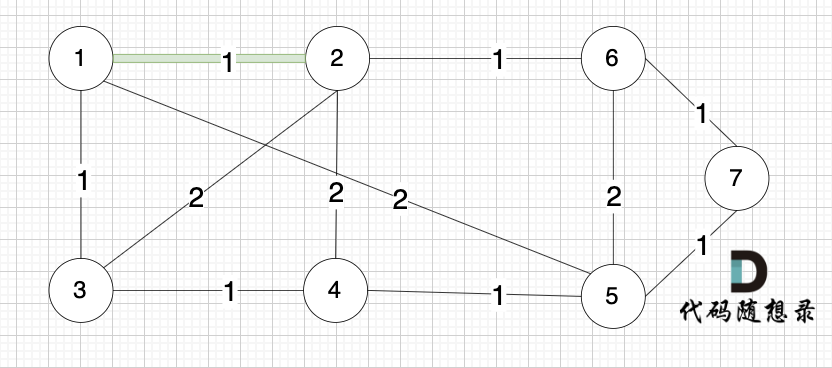
选边(4,5),节点4 和 节点 5 不在同一个集合,生成树可以添加边(4,5) ,并将节点4,节点5 放到同一个集合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ kruscal的思路:
|
||||
|
||||
**大家判断两个节点是否在同一个集合,就看图中两个节点是否有绿色的粗线连着就行**
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
(这里在强调一下,以下选边是按照上面排序好的边的数组来选择的)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,13 +95,13 @@ kruscal的思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---------
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
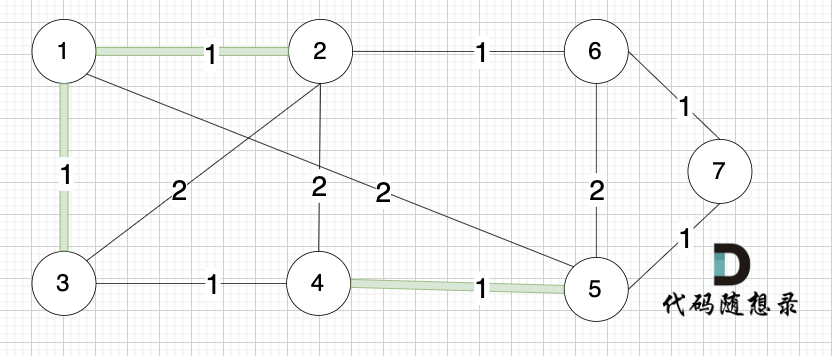
选边(2,6),节点2 和 节点6 不在同一个集合,生成树添加边(2,6),并将节点2,节点6 放到同一个集合。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
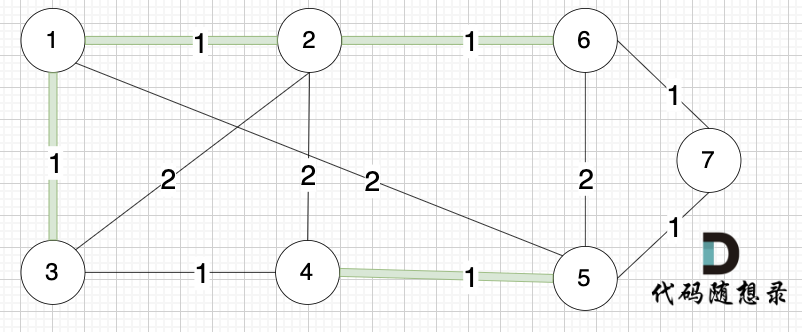
选边(3,4),节点3 和 节点4 不在同一个集合,生成树添加边(3,4),并将节点3,节点4 放到同一个集合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ kruscal的思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
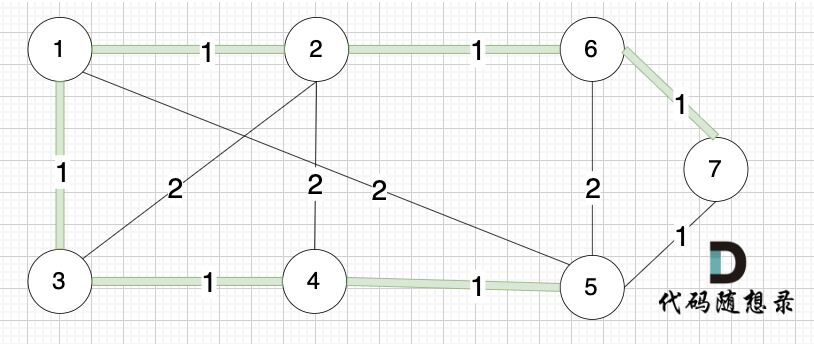
选边(5,7),节点5 和 节点7 在同一个集合,不做计算。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ kruscal的思路:
|
||||
后面遍历 边(3,2),(2,4),(5,6) 同理,都因两个节点已经在同一集合,不做计算。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
此时 我们就已经生成了一个最小生成树,即:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ int main() {
|
||||
|
||||
如果题目要求将最小生成树的边输出的话,应该怎么办呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Kruskal 算法 输出边的话,相对prim 要容易很多,因为 Kruskal 本来就是直接操作边,边的结构自然清晰,不用像 prim一样 需要再节点练成线输出边 (因为prim是对节点操作,而 Kruskal是对边操作,这是本质区别)
|
||||
Kruskal 算法 输出边的话,相对prim 要容易很多,因为 Kruskal 本来就是直接操作边,边的结构自然清晰,不用像 prim一样 需要再将节点连成线输出边 (因为prim是对节点操作,而 Kruskal是对边操作,这是本质区别)
|
||||
|
||||
本题中,边的结构为:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 58. 区间和
|
||||
|
||||
> 本题为代码随想录后续扩充题目,还没有视频讲解,顺便让大家练习一下ACM输入输出模式(笔试面试必备)
|
||||
|
||||
[题目链接](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1070)
|
||||
|
||||
题目描述
|
||||
@@ -97,11 +99,11 @@ int main() {
|
||||
|
||||
为什么呢?
|
||||
|
||||
p[1] = vec[0] + vec[1];
|
||||
`p[1] = vec[0] + vec[1];`
|
||||
|
||||
p[5] = vec[0] + vec[1] + vec[2] + vec[3] + vec[4] + vec[5];
|
||||
`p[5] = vec[0] + vec[1] + vec[2] + vec[3] + vec[4] + vec[5];`
|
||||
|
||||
p[5] - p[1] = vec[2] + vec[3] + vec[4] + vec[5];
|
||||
`p[5] - p[1] = vec[2] + vec[3] + vec[4] + vec[5];`
|
||||
|
||||
这不就是我们要求的 下标 2 到下标 5 之间的累加和吗。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -109,15 +111,17 @@ p[5] - p[1] = vec[2] + vec[3] + vec[4] + vec[5];
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
p[5] - p[1] 就是 红色部分的区间和。
|
||||
`p[5] - p[1]` 就是 红色部分的区间和。
|
||||
|
||||
而 p 数组是我们之前就计算好的累加和,所以后面每次求区间和的之后 我们只需要 O(1)的操作。
|
||||
而 p 数组是我们之前就计算好的累加和,所以后面每次求区间和的之后 我们只需要 O(1) 的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
**特别注意**: 在使用前缀和求解的时候,要特别注意 求解区间。
|
||||
|
||||
如上图,如果我们要求 区间下标 [2, 5] 的区间和,那么应该是 p[5] - p[1],而不是 p[5] - p[2]。
|
||||
|
||||
很多录友在使用前缀和的时候,分不清前缀和的区间,建议画一画图,模拟一下 思路会更清晰。
|
||||
**很多录友在使用前缀和的时候,分不清前缀和的区间,建议画一画图,模拟一下 思路会更清晰**。
|
||||
|
||||
本题C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
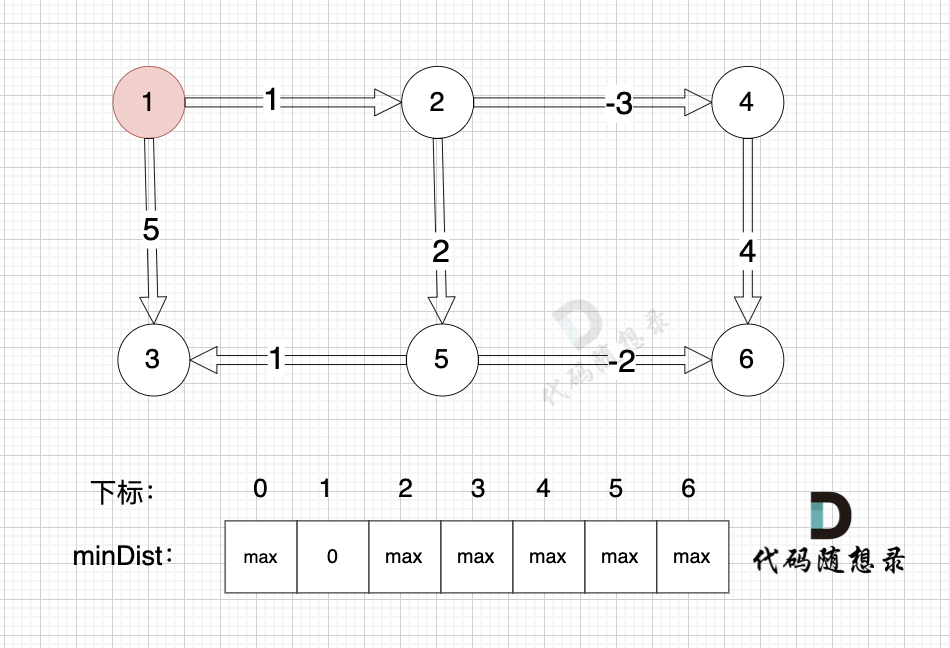
本图中,对所有边进行松弛,真正有效的松弛,只有松弛 边(节点1->节点2) 和 边(节点1->节点5) 。
|
||||
本图中,对所有边进行松弛,真正有效的松弛,只有松弛 边(节点1->节点2) 和 边(节点1->节点3) 。
|
||||
|
||||
而松弛 边(节点4->节点6) ,边(节点5->节点3)等等 都是无效的操作,因为 节点4 和 节点 5 都是没有被计算过的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -158,16 +158,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
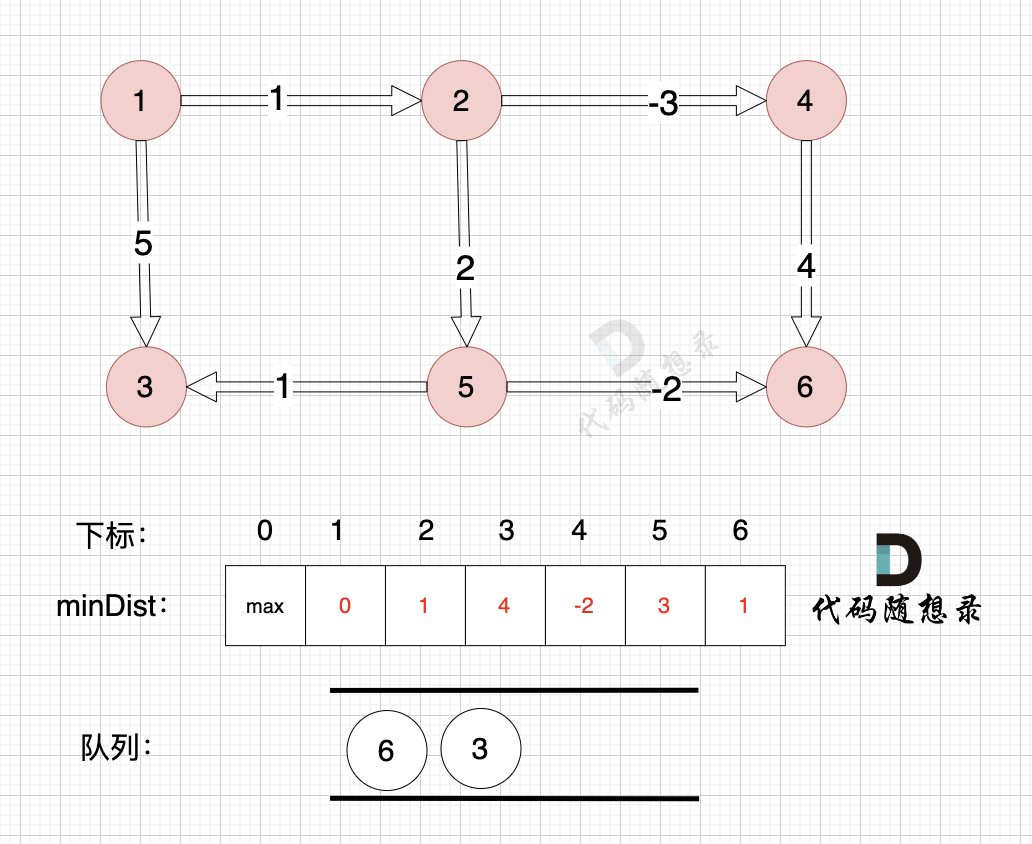
边:节点5 -> 节点6,权值为-2 ,minDist[6] > minDist[5] + (-2) ,更新 minDist[6] = minDist[5] + (-2) = 3 - 2 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
如图,将节点3加入队列,因为节点6已经在队列里,所以不用重复添加
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
因为节点3 和 节点6 都曾经加入过队列,不用重复加入,避免重复计算。
|
||||
|
||||
在代码中我们可以用一个数组 visited 来记录入过队列的元素,加入过队列的元素,不再重复入队列。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以我们在加入队列的过程可以有一个优化,**用visited数组记录已经在队列里的元素,已经在队列的元素不用重复加入**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -175,11 +170,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
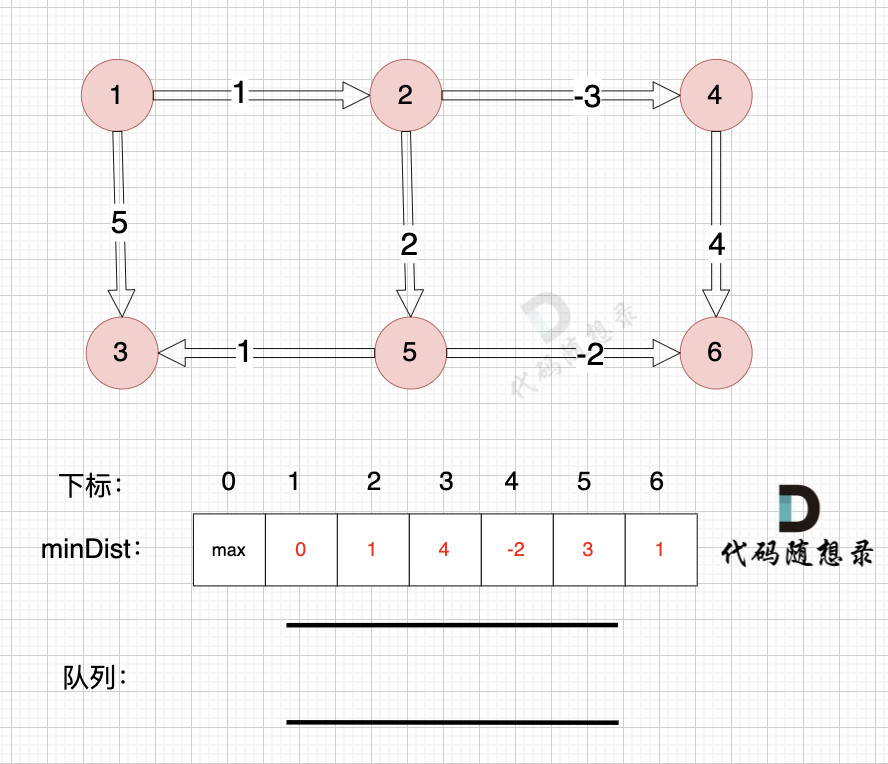
节点6作为终点,没有可以出发的边。
|
||||
|
||||
同理从队列中取出节点3,也没有可以出发的边
|
||||
|
||||
所以直接从队列中取出,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
这样我们就完成了基于队列优化的bellman_ford的算法模拟过程。
|
||||
@@ -190,12 +186,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在上面模拟过程中,我们每次都要知道 一个节点作为出发点连接了哪些节点。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想方便知道这些数据,就需要使用邻接表来存储这个图,如果对于邻接表不了解的话,可以看 [kama0047.参会dijkstra堆](./kama0047.参会dijkstra堆.md) 中 图的存储 部分。
|
||||
如果想方便知道这些数据,就需要使用邻接表来存储这个图,如果对于邻接表不了解的话,可以看 [kama0047.参会dijkstra堆](./0047.参会dijkstra堆.md) 中 图的存储 部分。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
整体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
```
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <queue>
|
||||
@@ -215,7 +211,9 @@ int main() {
|
||||
int n, m, p1, p2, val;
|
||||
cin >> n >> m;
|
||||
|
||||
vector<list<Edge>> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
|
||||
vector<list<Edge>> grid(n + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
vector<bool> isInQueue(n + 1); // 加入优化,已经在队里里的元素不用重复添加
|
||||
|
||||
// 将所有边保存起来
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
|
||||
@@ -230,24 +228,26 @@ int main() {
|
||||
minDist[start] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
queue<int> que;
|
||||
que.push(start); // 队列里放入起点
|
||||
que.push(start);
|
||||
|
||||
while (!que.empty()) {
|
||||
|
||||
int node = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
isInQueue[node] = false; // 从队列里取出的时候,要取消标记,我们只保证已经在队列里的元素不用重复加入
|
||||
for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
|
||||
int from = node;
|
||||
int to = edge.to;
|
||||
int value = edge.val;
|
||||
if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + value) { // 开始松弛
|
||||
minDist[to] = minDist[from] + value;
|
||||
que.push(to);
|
||||
minDist[to] = minDist[from] + value;
|
||||
if (isInQueue[to] == false) { // 已经在队列里的元素不用重复添加
|
||||
que.push(to);
|
||||
isInQueue[to] = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (minDist[end] == INT_MAX) cout << "unconnected" << endl; // 不能到达终点
|
||||
else cout << minDist[end] << endl; // 到达终点最短路径
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -422,7 +422,8 @@ int main() {
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
#### 邻接矩阵写法
|
||||
|
||||
邻接矩阵写法
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.util.ArrayList;
|
||||
import java.util.List;
|
||||
@@ -477,7 +478,7 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 邻接表写法
|
||||
邻接表写法
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.util.ArrayList;
|
||||
import java.util.LinkedList;
|
||||
@@ -533,7 +534,7 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
#### 邻接矩阵写法
|
||||
邻接矩阵写法
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
def dfs(graph, x, n, path, result):
|
||||
if x == n:
|
||||
@@ -566,7 +567,7 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 邻接表写法
|
||||
邻接表写法
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -604,6 +605,125 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
#### 邻接矩阵写法
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var result [][]int // 收集符合条件的路径
|
||||
var path []int // 1节点到终点的路径
|
||||
|
||||
func dfs(graph [][]int, x, n int) {
|
||||
// 当前遍历的节点x 到达节点n
|
||||
if x == n { // 找到符合条件的一条路径
|
||||
temp := make([]int, len(path))
|
||||
copy(temp, path)
|
||||
result = append(result, temp)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { // 遍历节点x链接的所有节点
|
||||
if graph[x][i] == 1 { // 找到 x链接的节点
|
||||
path = append(path, i) // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
|
||||
dfs(graph, i, n) // 进入下一层递归
|
||||
path = path[:len(path)-1] // 回溯,撤销本节点
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
var n, m int
|
||||
fmt.Scanf("%d %d", &n, &m)
|
||||
|
||||
// 节点编号从1到n,所以申请 n+1 这么大的数组
|
||||
graph := make([][]int, n+1)
|
||||
for i := range graph {
|
||||
graph[i] = make([]int, n+1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
var s, t int
|
||||
fmt.Scanf("%d %d", &s, &t)
|
||||
// 使用邻接矩阵表示无向图,1 表示 s 与 t 是相连的
|
||||
graph[s][t] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path = append(path, 1) // 无论什么路径已经是从1节点出发
|
||||
dfs(graph, 1, n) // 开始遍历
|
||||
|
||||
// 输出结果
|
||||
if len(result) == 0 {
|
||||
fmt.Println(-1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for _, pa := range result {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(pa)-1; i++ {
|
||||
fmt.Print(pa[i], " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(pa[len(pa)-1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 邻接表写法
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var result [][]int
|
||||
var path []int
|
||||
|
||||
func dfs(graph [][]int, x, n int) {
|
||||
if x == n {
|
||||
temp := make([]int, len(path))
|
||||
copy(temp, path)
|
||||
result = append(result, temp)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, i := range graph[x] {
|
||||
path = append(path, i)
|
||||
dfs(graph, i, n)
|
||||
path = path[:len(path)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
var n, m int
|
||||
fmt.Scanf("%d %d", &n, &m)
|
||||
|
||||
graph := make([][]int, n+1)
|
||||
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
|
||||
graph[i] = make([]int, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for m > 0 {
|
||||
var s, t int
|
||||
fmt.Scanf("%d %d", &s, &t)
|
||||
graph[s] = append(graph[s], t)
|
||||
m--
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path = append(path, 1)
|
||||
dfs(graph, 1, n)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(result) == 0 {
|
||||
fmt.Println(-1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for _, pa := range result {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(pa)-1; i++ {
|
||||
fmt.Print(pa[i], " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(pa[len(pa)-1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -322,6 +322,72 @@ print(result)
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
``` go
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var count int
|
||||
var dir = [][]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}} // 四个方向
|
||||
|
||||
func dfs(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y int) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
nextx := x + dir[i][0]
|
||||
nexty := y + dir[i][1]
|
||||
if nextx < 0 || nextx >= len(grid) || nexty < 0 || nexty >= len(grid[0]) {
|
||||
continue // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1 { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
|
||||
count++
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
var n, m int
|
||||
fmt.Scan(&n, &m)
|
||||
|
||||
grid := make([][]int, n)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
grid[i] = make([]int, m)
|
||||
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
|
||||
fmt.Scan(&grid[i][j])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
visited := make([][]bool, n)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
visited[i] = make([]bool, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
result := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
|
||||
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
|
||||
count = 1 // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
|
||||
visited[i][j] = true
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, i, j)
|
||||
if count > result {
|
||||
result = count
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(result)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
@@ -420,6 +486,65 @@ const bfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
|
||||
|
||||
### PhP
|
||||
|
||||
``` php
|
||||
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
|
||||
function dfs(&$grid, &$visited, $x, $y, &$count, &$dir) {
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < 4; $i++) {
|
||||
$nextx = $x + $dir[$i][0];
|
||||
$nexty = $y + $dir[$i][1];
|
||||
if ($nextx < 0 || $nextx >= count($grid) || $nexty < 0 || $nexty >= count($grid[0])) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (!$visited[$nextx][$nexty] && $grid[$nextx][$nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
|
||||
$visited[$nextx][$nexty] = true;
|
||||
$count++;
|
||||
dfs($grid, $visited, $nextx, $nexty, $count, $dir);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Main function
|
||||
function main() {
|
||||
$input = trim(fgets(STDIN));
|
||||
list($n, $m) = explode(' ', $input);
|
||||
|
||||
$grid = [];
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
|
||||
$input = trim(fgets(STDIN));
|
||||
$grid[] = array_map('intval', explode(' ', $input));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
$visited = [];
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
|
||||
$visited[] = array_fill(0, $m, false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
$result = 0;
|
||||
$count = 0;
|
||||
$dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]; // 四个方向
|
||||
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
|
||||
for ($j = 0; $j < $m; $j++) {
|
||||
if (!$visited[$i][$j] && $grid[$i][$j] == 1) {
|
||||
$count = 1; // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
|
||||
$visited[$i][$j] = true;
|
||||
dfs($grid, $visited, $i, $j, $count, $dir); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||||
$result = max($result, $count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
echo $result . "\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
main();
|
||||
|
||||
?>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -185,6 +185,77 @@ int main() {
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
``` java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
private static int count = 0;
|
||||
private static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
|
||||
|
||||
private static void bfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y) {
|
||||
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
que.add(new int[]{x, y});
|
||||
grid[x][y] = 0; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
|
||||
int[] cur = que.poll();
|
||||
int curx = cur[0];
|
||||
int cury = cur[1];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.length || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].length) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {
|
||||
que.add(new int[]{nextx, nexty});
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
grid[nextx][nexty] = 0; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int m = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取网格
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
grid[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 从左侧边,和右侧边向中间遍历
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
if (grid[i][0] == 1) bfs(grid, i, 0);
|
||||
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) bfs(grid, i, m - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 从上边和下边向中间遍历
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
if (grid[0][j] == 1) bfs(grid, 0, j);
|
||||
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) bfs(grid, n - 1, j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
count = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
if (grid[i][j] == 1) bfs(grid, i, j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
@@ -238,6 +309,97 @@ print(count)
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
``` go
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var count int
|
||||
var dir = [4][2]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}} // 四个方向
|
||||
|
||||
func bfs(grid [][]int, x, y int) {
|
||||
queue := [][2]int{{x, y}}
|
||||
grid[x][y] = 0 // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||||
count++
|
||||
|
||||
for len(queue) > 0 {
|
||||
cur := queue[0]
|
||||
queue = queue[1:]
|
||||
curx, cury := cur[0], cur[1]
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
nextx := curx + dir[i][0]
|
||||
nexty := cury + dir[i][1]
|
||||
|
||||
if nextx < 0 || nextx >= len(grid) || nexty < 0 || nexty >= len(grid[0]) {
|
||||
continue // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if grid[nextx][nexty] == 1 {
|
||||
queue = append(queue, [2]int{nextx, nexty})
|
||||
count++
|
||||
grid[nextx][nexty] = 0 // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
var n, m int
|
||||
fmt.Scan(&n, &m)
|
||||
|
||||
grid := make([][]int, n)
|
||||
for i := range grid {
|
||||
grid[i] = make([]int, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
|
||||
fmt.Scan(&grid[i][j])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 从左侧边,和右侧边向中间遍历
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if grid[i][0] == 1 {
|
||||
bfs(grid, i, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if grid[i][m-1] == 1 {
|
||||
bfs(grid, i, m-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 从上边和下边向中间遍历
|
||||
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
|
||||
if grid[0][j] == 1 {
|
||||
bfs(grid, 0, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if grid[n-1][j] == 1 {
|
||||
bfs(grid, n-1, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 清空之前的计数
|
||||
count = 0
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历所有位置
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
|
||||
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
|
||||
bfs(grid, i, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(count)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -355,6 +355,62 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
first = set()
|
||||
second = set()
|
||||
directions = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]]
|
||||
|
||||
def dfs(i, j, graph, visited, side):
|
||||
if visited[i][j]:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
visited[i][j] = True
|
||||
side.add((i, j))
|
||||
|
||||
for x, y in directions:
|
||||
new_x = i + x
|
||||
new_y = j + y
|
||||
if (
|
||||
0 <= new_x < len(graph)
|
||||
and 0 <= new_y < len(graph[0])
|
||||
and int(graph[new_x][new_y]) >= int(graph[i][j])
|
||||
):
|
||||
dfs(new_x, new_y, graph, visited, side)
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
global first
|
||||
global second
|
||||
|
||||
N, M = map(int, input().strip().split())
|
||||
graph = []
|
||||
for _ in range(N):
|
||||
row = input().strip().split()
|
||||
graph.append(row)
|
||||
|
||||
# 是否可到达第一边界
|
||||
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
|
||||
for i in range(M):
|
||||
dfs(0, i, graph, visited, first)
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
dfs(i, 0, graph, visited, first)
|
||||
|
||||
# 是否可到达第二边界
|
||||
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
|
||||
for i in range(M):
|
||||
dfs(N - 1, i, graph, visited, second)
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
dfs(i, M - 1, graph, visited, second)
|
||||
|
||||
# 可到达第一边界和第二边界
|
||||
res = first & second
|
||||
|
||||
for x, y in res:
|
||||
print(f"{x} {y}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -362,6 +418,350 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
#### 深搜
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||||
// 创建readline接口
|
||||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||||
|
||||
let graph // 地图
|
||||
let N, M // 地图大小
|
||||
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
const initGraph = async () => {
|
||||
let line = await readline();
|
||||
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
|
||||
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
line = await readline()
|
||||
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
graph[i][j] = line[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @description: 从(x,y)开始深度优先遍历地图
|
||||
* @param {*} graph 地图
|
||||
* @param {*} visited 可访问节点
|
||||
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @return {*}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
|
||||
if (visited[x][y]) return
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true // 标记为可访问
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
let nextx = x + dir[i][0]
|
||||
let nexty = y + dir[i][1]
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue //越界,跳过
|
||||
if (graph[x][y] < graph[nextx][nexty]) continue //不能流过.跳过
|
||||
dfs(graph, visited, nextx, nexty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @description: 判断地图上的(x, y)是否可以到达第一组边界和第二组边界
|
||||
* @param {*} x 坐标
|
||||
* @param {*} y 坐标
|
||||
* @return {*} true可以到达,false不可以到达
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const isResult = (x, y) => {
|
||||
let visited = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
|
||||
|
||||
let isFirst = false //是否可到达第一边界
|
||||
let isSecond = false //是否可到达第二边界
|
||||
|
||||
// 深搜,将(x, y)可到达的所有节点做标记
|
||||
dfs(graph, visited, x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第一边界左边
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
if (visited[i][0]) {
|
||||
isFirst = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第一边界上边
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (visited[0][j]) {
|
||||
isFirst = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第二边界右边
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
if (visited[i][M - 1]) {
|
||||
isSecond = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第二边界下边
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (visited[N - 1][j]) {
|
||||
isSecond = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return isFirst && isSecond
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async function () {
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
await initGraph()
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历地图,判断是否能到达第一组边界和第二组边界
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (isResult(i, j)) console.log(i + ' ' + j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
})()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 广搜-解法一
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||||
// 创建readline接口
|
||||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||||
|
||||
let graph // 地图
|
||||
let N, M // 地图大小
|
||||
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
const initGraph = async () => {
|
||||
let line = await readline();
|
||||
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
|
||||
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
line = await readline()
|
||||
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
graph[i][j] = line[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @description: 从(x,y)开始广度优先遍历地图
|
||||
* @param {*} graph 地图
|
||||
* @param {*} visited 可访问节点
|
||||
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @return {*}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const bfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
|
||||
let queue = []
|
||||
queue.push([x, y])
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true
|
||||
|
||||
while (queue.length) {
|
||||
const [xx, yy] = queue.shift()
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
let nextx = xx + dir[i][0]
|
||||
let nexty = yy + dir[i][1]
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue //越界, 跳过
|
||||
|
||||
// 可访问或者不能流过, 跳过 (注意这里是graph[xx][yy] < graph[nextx][nexty], 不是graph[x][y] < graph[nextx][nexty])
|
||||
if (visited[nextx][nexty] || graph[xx][yy] < graph[nextx][nexty]) continue
|
||||
|
||||
queue.push([nextx, nexty])
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @description: 判断地图上的(x, y)是否可以到达第一组边界和第二组边界
|
||||
* @param {*} x 坐标
|
||||
* @param {*} y 坐标
|
||||
* @return {*} true可以到达,false不可以到达
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const isResult = (x, y) => {
|
||||
let visited = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
|
||||
|
||||
let isFirst = false //是否可到达第一边界
|
||||
let isSecond = false //是否可到达第二边界
|
||||
|
||||
// 深搜,将(x, y)可到达的所有节点做标记
|
||||
bfs(graph, visited, x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
// console.log(visited);
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第一边界左边
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
if (visited[i][0]) {
|
||||
isFirst = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第一边界上边
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (visited[0][j]) {
|
||||
isFirst = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第二边界右边
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
if (visited[i][M - 1]) {
|
||||
isSecond = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断能否到第二边界下边
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (visited[N - 1][j]) {
|
||||
isSecond = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return isFirst && isSecond
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async function () {
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
await initGraph()
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历地图,判断是否能到达第一组边界和第二组边界
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (isResult(i, j)) console.log(i + ' ' + j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
})()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 广搜-解法二
|
||||
|
||||
从第一边界和第二边界开始向高处流, 标记可以流到的位置, 两个边界都能到达的位置就是所求结果
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||||
// 创建readline接口
|
||||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||||
|
||||
let graph // 地图
|
||||
let N, M // 地图大小
|
||||
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]] //方向
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
const initGraph = async () => {
|
||||
let line = await readline();
|
||||
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
|
||||
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
line = await readline()
|
||||
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
graph[i][j] = line[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @description: 从(x,y)开始广度优先遍历地图
|
||||
* @param {*} graph 地图
|
||||
* @param {*} visited 可访问节点
|
||||
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
|
||||
* @return {*}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const bfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
|
||||
if(visited[x][y]) return
|
||||
|
||||
let queue = []
|
||||
queue.push([x, y])
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true
|
||||
|
||||
while (queue.length) {
|
||||
const [xx, yy] = queue.shift()
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
let nextx = xx + dir[i][0]
|
||||
let nexty = yy + dir[i][1]
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue //越界, 跳过
|
||||
|
||||
// 可访问或者不能流过, 跳过 (注意因为是从边界往高处流, 所以这里是graph[xx][yy] >= graph[nextx][nexty], 还要注意不是graph[xx][yy] >= graph[nextx][nexty])
|
||||
if (visited[nextx][nexty] || graph[xx][yy] >= graph[nextx][nexty]) continue
|
||||
|
||||
queue.push([nextx, nexty])
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async function () {
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||||
await initGraph()
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录第一边界可到达的节点
|
||||
let firstBorder = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录第二边界可到达的节点
|
||||
let secondBorder = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
|
||||
|
||||
// 第一边界左边和第二边界右边
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
bfs(graph, firstBorder, i, 0)
|
||||
bfs(graph, secondBorder, i, M - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 第一边界上边和第二边界下边
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
bfs(graph, firstBorder, 0, j)
|
||||
bfs(graph, secondBorder, N - 1, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历地图,判断是否能到达第一组边界和第二组边界
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
|
||||
if (firstBorder[i][j] && secondBorder[i][j]) console.log(i + ' ' + j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
})()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
### PhP
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -366,6 +366,79 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import collections
|
||||
|
||||
directions = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0]]
|
||||
area = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def dfs(i, j, grid, visited, num):
|
||||
global area
|
||||
|
||||
if visited[i][j]:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
visited[i][j] = True
|
||||
grid[i][j] = num # 标记岛屿号码
|
||||
area += 1
|
||||
|
||||
for x, y in directions:
|
||||
new_x = i + x
|
||||
new_y = j + y
|
||||
if (
|
||||
0 <= new_x < len(grid)
|
||||
and 0 <= new_y < len(grid[0])
|
||||
and grid[new_x][new_y] == "1"
|
||||
):
|
||||
dfs(new_x, new_y, grid, visited, num)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
global area
|
||||
|
||||
N, M = map(int, input().strip().split())
|
||||
grid = []
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
grid.append(input().strip().split())
|
||||
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
|
||||
rec = collections.defaultdict(int)
|
||||
|
||||
cnt = 2
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
for j in range(M):
|
||||
if grid[i][j] == "1":
|
||||
area = 0
|
||||
dfs(i, j, grid, visited, cnt)
|
||||
rec[cnt] = area # 纪录岛屿面积
|
||||
cnt += 1
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0
|
||||
for i in range(N):
|
||||
for j in range(M):
|
||||
if grid[i][j] == "0":
|
||||
max_island = 1 # 将水变为陆地,故从1开始计数
|
||||
v = set()
|
||||
for x, y in directions:
|
||||
new_x = i + x
|
||||
new_y = j + y
|
||||
if (
|
||||
0 <= new_x < len(grid)
|
||||
and 0 <= new_y < len(grid[0])
|
||||
and grid[new_x][new_y] != "0"
|
||||
and grid[new_x][new_y] not in v # 岛屿不可重复
|
||||
):
|
||||
max_island += rec[grid[new_x][new_y]]
|
||||
v.add(grid[new_x][new_y])
|
||||
res = max(res, max_island)
|
||||
|
||||
if res == 0:
|
||||
return max(rec.values()) # 无水的情况
|
||||
return res
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
print(main())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -158,7 +158,62 @@ int main() {
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main{
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
int N, M;
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
N = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
M = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
DisJoint disJoint = new DisJoint(N + 1);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
|
||||
disJoint.join(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(disJoint.isSame(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt())) {
|
||||
System.out.println("1");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
System.out.println("0");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//并查集模板
|
||||
class DisJoint{
|
||||
private int[] father;
|
||||
|
||||
public DisJoint(int N) {
|
||||
father = new int[N];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
|
||||
father[i] = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int find(int n) {
|
||||
return n == father[n] ? n : (father[n] = find(father[n]));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void join (int n, int m) {
|
||||
n = find(n);
|
||||
m = find(m);
|
||||
if (n == m) return;
|
||||
father[m] = n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public boolean isSame(int n, int m){
|
||||
n = find(n);
|
||||
m = find(m);
|
||||
return n == m;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -141,6 +141,70 @@ int main() {
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||||
// 创建readline接口
|
||||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
let N // 节点数和边数
|
||||
let father = [] // 并查集
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 并查集初始化
|
||||
const init = () => {
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) father[i] = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 并查集里寻根的过程
|
||||
const find = (u) => {
|
||||
return u == father[u] ? u : father[u] = find(father[u])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 将v->u 这条边加入并查集
|
||||
const join = (u, v) => {
|
||||
u = find(u)
|
||||
v = find(v)
|
||||
if (u == v) return // 如果发现根相同,则说明在一个集合,不用两个节点相连直接返回
|
||||
father[v] = u
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断 u 和 v是否找到同一个根
|
||||
const isSame = (u, v) => {
|
||||
u = find(u)
|
||||
v = find(v)
|
||||
return u == v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(async function () {
|
||||
// 读取第一行输入
|
||||
let line = await readline();
|
||||
N = Number(line);
|
||||
|
||||
// 初始化并查集
|
||||
father = new Array(N)
|
||||
init()
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取边信息, 加入并查集
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
line = await readline()
|
||||
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isSame(line[0], line[1])) {
|
||||
join(line[0], line[1])
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
console.log(line[0], line[1]);
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
})()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
### PhP
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -78,7 +78,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
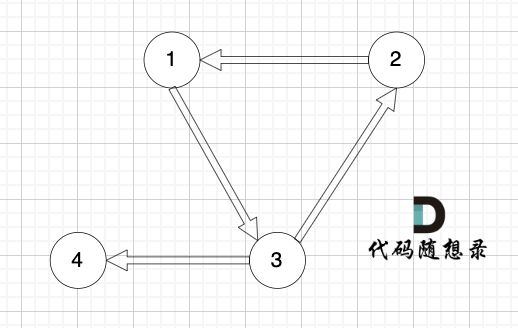
对于情况二,删掉构成环的边就可以了。
|
||||
对于情况三,删掉构成环的边就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 写代码
|
||||
@@ -225,6 +225,7 @@ int main() {
|
||||
vec.push_back(i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 情况一、情况二
|
||||
if (vec.size() > 0) {
|
||||
// 放在vec里的边已经按照倒叙放的,所以这里就优先删vec[0]这条边
|
||||
if (isTreeAfterRemoveEdge(edges, vec[0])) {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -217,6 +217,38 @@ public class Main {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
def judge(s1,s2):
|
||||
count=0
|
||||
for i in range(len(s1)):
|
||||
if s1[i]!=s2[i]:
|
||||
count+=1
|
||||
return count==1
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__=='__main__':
|
||||
n=int(input())
|
||||
beginstr,endstr=map(str,input().split())
|
||||
if beginstr==endstr:
|
||||
print(0)
|
||||
exit()
|
||||
strlist=[]
|
||||
for i in range(n):
|
||||
strlist.append(input())
|
||||
|
||||
# use bfs
|
||||
visit=[False for i in range(n)]
|
||||
queue=[[beginstr,1]]
|
||||
while queue:
|
||||
str,step=queue.pop(0)
|
||||
if judge(str,endstr):
|
||||
print(step+1)
|
||||
exit()
|
||||
for i in range(n):
|
||||
if visit[i]==False and judge(strlist[i],str):
|
||||
visit[i]=True
|
||||
queue.append([strlist[i],step+1])
|
||||
print(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
59
problems/kamacoder/0113.国际象棋.md
Normal file
59
problems/kamacoder/0113.国际象棋.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 113.国际象棋
|
||||
|
||||
广搜,但本题如果广搜枚举马和象的话会超时。
|
||||
|
||||
广搜要只枚举马的走位,同时判断是否在对角巷直接走象
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
const int N = 100005, mod = 1000000007;
|
||||
using ll = long long;
|
||||
int n, ans;
|
||||
int dir[][2] = {{1, 2}, {1, -2}, {-1, 2}, {-1, -2}, {2, 1}, {2, -1}, {-2, -1}, {-2, 1}};
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
while (n--) {
|
||||
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
|
||||
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
|
||||
cout << 0 << endl;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 判断象走一步到达
|
||||
int d = abs(x1 - x2) - abs(y1 - y2);
|
||||
if (!d) {cout << 1 << endl; continue;}
|
||||
// 判断马走一步到达
|
||||
bool one = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
|
||||
int dx = x1 + dir[i][0], dy = y1 + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (dx == x2 && dy == y2) {
|
||||
cout << 1 << endl;
|
||||
one = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (one) continue;
|
||||
// 接下来为两步的逻辑, 象走两步或者马走一步,象走一步
|
||||
// 象直接两步可以到达,这个计算是不是同颜色的格子,象可以在两步到达所有同颜色的格子
|
||||
int d2 = abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2);
|
||||
if (d2 % 2 == 0) {
|
||||
cout << 2 << endl;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 接下来判断马 + 象的组合
|
||||
bool two = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
|
||||
int dx = x1 + dir[i][0], dy = y1 + dir[i][1];
|
||||
int d = abs(dx - x2) - abs(dy - y2);
|
||||
if (!d) {cout << 2 << endl; two = true; break;}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (two) continue;
|
||||
// 剩下的格子全都是三步到达的
|
||||
cout << 3 << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -193,7 +193,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
理解思想后,确实不难,但代码写起来也不容易。
|
||||
|
||||
为了每次可以找到所有节点的入度信息,我们要在初始话的时候,就把每个节点的入度 和 每个节点的依赖关系做统计。
|
||||
为了每次可以找到所有节点的入度信息,我们要在初始化的时候,就把每个节点的入度 和 每个节点的依赖关系做统计。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -451,6 +451,80 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||||
// 创建readline接口
|
||||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
let N, M // 节点数和边数
|
||||
let inDegrees = [] // 入度
|
||||
let umap = new Map() // 记录文件依赖关系
|
||||
let result = [] // 结果
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据输入, 初始化数据
|
||||
const init = async () => {
|
||||
// 读取第一行输入
|
||||
let line = await readline();
|
||||
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
|
||||
inDegrees = new Array(N).fill(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// 读取边集
|
||||
while (M--) {
|
||||
line = await readline();
|
||||
let [x, y] = line.split(' ').map(Number)
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录入度
|
||||
inDegrees[y]++
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录x指向哪些文件
|
||||
if (!umap.has(x)) {
|
||||
umap.set(x, [y])
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
umap.get(x).push(y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
(async function () {
|
||||
// 根据输入, 初始化数据
|
||||
await init()
|
||||
|
||||
let queue = [] // 入度为0的节点
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||||
if (inDegrees[i] == 0) {
|
||||
queue.push(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (queue.length) {
|
||||
let cur = queue.shift() //当前文件
|
||||
|
||||
result.push(cur)
|
||||
|
||||
let files = umap.get(cur) // 当前文件指向的文件
|
||||
|
||||
// 当前文件指向的文件入度减1
|
||||
if (files && files.length) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
|
||||
inDegrees[files[i]]--
|
||||
if (inDegrees[files[i]] == 0) queue.push(files[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 这里result.length == N 一定要判断, 因为可能存在环
|
||||
if (result.length == N) return console.log(result.join(' '))
|
||||
console.log(-1)
|
||||
})()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
### PhP
|
||||
|
||||
132
problems/kamacoder/0121.小红的区间翻转.md
Normal file
132
problems/kamacoder/0121.小红的区间翻转.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 121. 小红的区间翻转
|
||||
|
||||
比较暴力的方式,就是直接模拟, 枚举所有 区间,然后检查其翻转的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
在检查翻转的时候,需要一些代码优化,否则容易超时。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
bool canTransform(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b, int left, int right) {
|
||||
// 提前检查翻转区间的值是否可以匹配
|
||||
for (int i = left, j = right; i <= right; i++, j--) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[j]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 检查翻转区间外的值是否匹配
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < left; i++) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = right + 1; i < a.size(); i++) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
|
||||
vector<int> a(n);
|
||||
vector<int> b(n);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cin >> a[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cin >> b[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历所有可能的区间
|
||||
for (int left = 0; left < n; left++) {
|
||||
for (int right = left; right < n; right++) {
|
||||
// 检查翻转区间 [left, right] 后,a 是否可以变成 b
|
||||
if (canTransform(a, b, left, right)) {
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << count << endl;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
也可以事先计算好,最长公共前缀,和最长公共后缀。
|
||||
|
||||
在公共前缀和公共后缀之间的部分进行翻转操作,这样我们可以减少很多不必要的翻转尝试。
|
||||
|
||||
通过在公共前缀和后缀之间的部分,找到可以通过翻转使得 a 和 b 相等的区间。
|
||||
|
||||
以下 为评论区 卡码网用户:码鬼的C++代码
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
vector<int> a(n), b(n);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cin >> a[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cin >> b[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
vector<int> prefix(n, 0), suffix(n, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算前缀相等的位置
|
||||
int p = 0;
|
||||
while (p < n && a[p] == b[p]) {
|
||||
prefix[p] = 1;
|
||||
p++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算后缀相等的位置
|
||||
int s = n - 1;
|
||||
while (s >= 0 && a[s] == b[s]) {
|
||||
suffix[s] = 1;
|
||||
s--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历所有可能的区间
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
// 判断前缀和后缀是否相等
|
||||
if ((i == 0 || prefix[i - 1] == 1) && (j == n - 1 || suffix[j + 1] == 1)) {
|
||||
// 判断翻转后的子数组是否和目标数组相同
|
||||
bool is_palindrome = true;
|
||||
for (int k = 0; k <= (j - i) / 2; k++) {
|
||||
if (a[i + k] != b[j - k]) {
|
||||
is_palindrome = false;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (is_palindrome) {
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cout << count << endl;
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
108
problems/kamacoder/0142.两个字符串的最小ASCII删除总和.md
Normal file
108
problems/kamacoder/0142.两个字符串的最小ASCII删除总和.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 142. 两个字符串的最小 ASCII 删除总和
|
||||
|
||||
本题和[代码随想录:两个字符串的删除操作](https://www.programmercarl.com/0583.%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%B8%B2%E7%9A%84%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.html) 思路基本是一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
属于编辑距离问题,如果想彻底了解,建议看看「代码随想录」的编辑距离总结篇。
|
||||
|
||||
本题dp数组含义:
|
||||
|
||||
dp[i][j] 表示 以i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以j-1位结尾的字符串word2,想要达到相等,所需要删除元素的最小ASCII 删除总和。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 s1[i - 1] 与 s2[j - 1] 相同,则不用删:`dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]`
|
||||
|
||||
如果 s1[i - 1] 与 s2[j - 1] 不相同,删word1 的 最小删除和: `dp[i - 1][j] + s1[i - 1]` ,删word2的最小删除和: `dp[i][j - 1] + s2[j - 1]`
|
||||
|
||||
取最小值: `dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + s1[i - 1], dp[i][j - 1] + s2[j - 1])`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
string s1, s2;
|
||||
cin >> s1 >> s2;
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> dp(s1.size() + 1, vector<int>(s2.size() + 1, 0));
|
||||
|
||||
// s1 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCLL值综合
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.size(); i++) dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + s1[i - 1];
|
||||
// s2 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCLL值综合
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + s2[j - 1];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.size(); i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.size(); j++) {
|
||||
if (s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
|
||||
else dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + s1[i - 1], dp[i][j - 1] + s2[j - 1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << dp[s1.size()][s2.size()] << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
String s1 = scanner.nextLine();
|
||||
String s2 = scanner.nextLine();
|
||||
int[][] dp = new int[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
|
||||
|
||||
// s1 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCII值综合
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.length(); i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + s1.charAt(i - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// s2 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCII值综合
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.length(); j++) {
|
||||
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + s2.charAt(j - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.length(); i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.length(); j++) {
|
||||
if (s1.charAt(i - 1) == s2.charAt(j - 1)) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j] + s1.charAt(i - 1), dp[i][j - 1] + s2.charAt(j - 1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.out.println(dp[s1.length()][s2.length()]);
|
||||
scanner.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def min_delete_sum(s1: str, s2: str) -> int:
|
||||
dp = [[0] * (len(s2) + 1) for _ in range(len(s1) + 1)]
|
||||
|
||||
# s1 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCII值综合
|
||||
for i in range(1, len(s1) + 1):
|
||||
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + ord(s1[i - 1])
|
||||
# s2 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCII值综合
|
||||
for j in range(1, len(s2) + 1):
|
||||
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + ord(s2[j - 1])
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, len(s1) + 1):
|
||||
for j in range(1, len(s2) + 1):
|
||||
if s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]:
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + ord(s1[i - 1]), dp[i][j - 1] + ord(s2[j - 1]))
|
||||
|
||||
return dp[len(s1)][len(s2)]
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
s1 = input().strip()
|
||||
s2 = input().strip()
|
||||
print(min_delete_sum(s1, s2))
|
||||
```
|
||||
237
problems/kamacoder/0143.最长同值路径.md
Normal file
237
problems/kamacoder/0143.最长同值路径.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 143. 最长同值路径
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本题两个考点:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 层序遍历构造二叉树
|
||||
2. 树形dp,找出最长路径
|
||||
|
||||
对于写代码不多,或者动手能力比较差的录友,第一个 构造二叉树 基本就被卡主了。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <queue>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义二叉树节点结构
|
||||
struct TreeNode {
|
||||
int val;
|
||||
TreeNode* left;
|
||||
TreeNode* right;
|
||||
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据层序遍历数组构建二叉树
|
||||
TreeNode* constructBinaryTree(const vector<string>& levelOrder) {
|
||||
if (levelOrder.empty()) return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[0]));
|
||||
queue<TreeNode*> q;
|
||||
q.push(root);
|
||||
int i = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (!q.empty() && i < levelOrder.size()) {
|
||||
TreeNode* current = q.front();
|
||||
q.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && levelOrder[i] != "null") {
|
||||
current->left = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[i]));
|
||||
q.push(current->left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && levelOrder[i] != "null") {
|
||||
current->right = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[i]));
|
||||
q.push(current->right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 树形DP
|
||||
int dfs(TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
if (node == NULL) return 0;
|
||||
int leftPath = dfs(node->left);
|
||||
int rightPath = dfs(node->right);
|
||||
|
||||
int leftNum = 0, rightNum = 0;
|
||||
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->val == node->val) {
|
||||
leftNum = leftPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node->right != NULL && node->right->val == node->val) {
|
||||
rightNum = rightPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = max(result, leftNum + rightNum);
|
||||
return max(leftNum, rightNum);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
vector<string> levelOrder(n);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) cin >> levelOrder[i];
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* root = constructBinaryTree(levelOrder);
|
||||
dfs(root);
|
||||
cout << result << endl;
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
class TreeNode {
|
||||
int val;
|
||||
TreeNode left, right;
|
||||
TreeNode(int x) {
|
||||
val = x;
|
||||
left = null;
|
||||
right = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static int result = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
public static TreeNode constructBinaryTree(List<String> levelOrder) {
|
||||
if (levelOrder.isEmpty()) return null;
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(levelOrder.get(0)));
|
||||
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
queue.add(root);
|
||||
int i = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty() && i < levelOrder.size()) {
|
||||
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && !levelOrder.get(i).equals("null")) {
|
||||
current.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(levelOrder.get(i)));
|
||||
queue.add(current.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && !levelOrder.get(i).equals("null")) {
|
||||
current.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(levelOrder.get(i)));
|
||||
queue.add(current.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static int dfs(TreeNode node) {
|
||||
if (node == null) return 0;
|
||||
int leftPath = dfs(node.left);
|
||||
int rightPath = dfs(node.right);
|
||||
|
||||
int leftNum = 0, rightNum = 0;
|
||||
if (node.left != null && node.left.val == node.val) {
|
||||
leftNum = leftPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node.right != null && node.right.val == node.val) {
|
||||
rightNum = rightPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = Math.max(result, leftNum + rightNum);
|
||||
return Math.max(leftNum, rightNum);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
sc.nextLine(); // consume the newline character
|
||||
List<String> levelOrder = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
levelOrder.add(sc.next());
|
||||
}
|
||||
TreeNode root = constructBinaryTree(levelOrder);
|
||||
dfs(root);
|
||||
System.out.println(result);
|
||||
sc.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
class TreeNode:
|
||||
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'TreeNode' = None, right: 'TreeNode' = None):
|
||||
self.val = val
|
||||
self.left = left
|
||||
self.right = right
|
||||
|
||||
def construct_binary_tree(level_order: List[str]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||||
if not level_order:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
root = TreeNode(int(level_order[0]))
|
||||
queue = deque([root])
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
|
||||
while queue and i < len(level_order):
|
||||
current = queue.popleft()
|
||||
|
||||
if i < len(level_order) and level_order[i] != "null":
|
||||
current.left = TreeNode(int(level_order[i]))
|
||||
queue.append(current.left)
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
|
||||
if i < len(level_order) and level_order[i] != "null":
|
||||
current.right = TreeNode(int(level_order[i]))
|
||||
queue.append(current.right)
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
|
||||
return root
|
||||
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def dfs(node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
|
||||
global result
|
||||
if node is None:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
left_path = dfs(node.left)
|
||||
right_path = dfs(node.right)
|
||||
|
||||
left_num = right_num = 0
|
||||
if node.left is not None and node.left.val == node.val:
|
||||
left_num = left_path + 1
|
||||
if node.right is not None and node.right.val == node.val:
|
||||
right_num = right_path + 1
|
||||
|
||||
result = max(result, left_num + right_num)
|
||||
return max(left_num, right_num)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
input = sys.stdin.read
|
||||
data = input().strip().split()
|
||||
|
||||
n = int(data[0])
|
||||
level_order = data[1:]
|
||||
|
||||
root = construct_binary_tree(level_order)
|
||||
dfs(root)
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
66
problems/kamacoder/0144.字典序最小的01字符串.md
Normal file
66
problems/kamacoder/0144.字典序最小的01字符串.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 0144.字典序最小的01字符串
|
||||
|
||||
贪心思路:移动尽可能 移动前面的1 ,这样可以是 字典序最小
|
||||
|
||||
从前到后遍历,遇到 0 ,就用前面的 1 来交换
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n,k;
|
||||
cin >> n >> k;
|
||||
string s;
|
||||
cin >> s;
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < n && k > 0; i++) {
|
||||
if(s[i] == '0') {
|
||||
// 开始用前面的 1 来交换
|
||||
int j = i;
|
||||
while(j > 0 && s[j - 1] == '1' && k > 0) {
|
||||
swap(s[j], s[j - 1]);
|
||||
--j;
|
||||
--k;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << s << endl;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int k = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗掉换行符
|
||||
String s = scanner.nextLine();
|
||||
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n && k > 0; i++) {
|
||||
if (ch[i] == '0') {
|
||||
// 开始用前面的 1 来交换
|
||||
int j = i;
|
||||
while (j > 0 && ch[j - 1] == '1' && k > 0) {
|
||||
char tmp = ch[j];
|
||||
ch[j] = ch[j - 1];
|
||||
ch[j - 1] = tmp;
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
k--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(new String(ch));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
98
problems/kamacoder/0145.数组子序列的排列.md
Normal file
98
problems/kamacoder/0145.数组子序列的排列.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 145. 数组子序列的排列
|
||||
|
||||
每个元素出现的次数相乘就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
注意 “长度为 m 的数组,1 到 m 每个元素都出现过,且恰好出现 1 次。” ,题目中有n个元素,所以我们要统计的就是 1 到 n 元素出现的个数。
|
||||
|
||||
因为如果有一个元素x 大于n了, 那不可能出现 长度为x的数组 且 1 到 x 每个元素都出现过。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
int main(){
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
int x;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
unordered_map<int, int> umap;
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
|
||||
cin >> x;
|
||||
if(umap.find(x) != umap.end()) umap[x]++;
|
||||
else umap[x] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
long long res = 0;
|
||||
long long num = 1;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
if (umap.find(i) == umap.end()) break; // 如果i都没出现,后面得数也不能 1 到 m 每个元素都出现过
|
||||
num = (num * umap[i]) % 1000000007;
|
||||
res += num;
|
||||
res %= 1000000007;
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << res << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.HashMap;
|
||||
import java.util.Map;
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
int x = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
map.put(x, map.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
long res = 0;
|
||||
long num = 1;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
if (!map.containsKey(i)) break; // 如果i都没出现,后面得数也不能1到m每个元素都出现过
|
||||
num = (num * map.get(i)) % 1000000007;
|
||||
res += num;
|
||||
res %= 1000000007;
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.out.println(res);
|
||||
sc.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
input = sys.stdin.read
|
||||
data = input().split()
|
||||
|
||||
n = int(data[0])
|
||||
umap = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, n + 1):
|
||||
x = int(data[i])
|
||||
if x in umap:
|
||||
umap[x] += 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
umap[x] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0
|
||||
num = 1
|
||||
MOD = 1000000007
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, n + 1):
|
||||
if i not in umap:
|
||||
break # 如果i都没出现,后面得数也不能1到m每个元素都出现过
|
||||
num = (num * umap[i]) % MOD
|
||||
res = (res + num) % MOD
|
||||
|
||||
print(res)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
65
problems/kamacoder/0146.传送树.md
Normal file
65
problems/kamacoder/0146.传送树.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 146. 传送树
|
||||
|
||||
本题题意是比较绕的,我后面给补上了 【提示信息】对 题目输出样例讲解一下,相对会容易理解的多。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> edge; // 邻接表来存图
|
||||
vector<int> nxt;
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* 递归函数,用于找到每个节点的下一个传送门节点,并记录在nxt数组中。
|
||||
* 遍历当前节点的所有子节点,递归调用findNext以确保子节点的nxt值已经计算出来。
|
||||
* 更新当前节点的nxt值为其子节点中编号最小的节点。
|
||||
* 如果当前节点是叶子节点(即没有子节点),则将其nxt值设置为自身。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void findNext(int node) {
|
||||
for (int v : edge[node]) {
|
||||
findNext(v);
|
||||
if (nxt[node] == -1 || nxt[node] > min(v, nxt[v])) {
|
||||
nxt[node] = min(v, nxt[v]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 叶子节点
|
||||
if (nxt[node] == -1) {
|
||||
nxt[node] = node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算从节点u出发经过若干次传送门到达叶子节点所需的步数。
|
||||
// 通过不断访问nxt节点,直到到达叶子节点,记录访问的节点数。
|
||||
int get(int u) {
|
||||
int cnt = 1;
|
||||
while (nxt[u] != u) {
|
||||
cnt++;
|
||||
u = nxt[u];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cnt;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
edge.resize(n + 1);
|
||||
nxt.resize(n + 1, -1);
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
|
||||
int a, b;
|
||||
cin >> a >> b;
|
||||
edge[a].push_back(b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
findNext(1);
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
|
||||
cout << get(i) << ' ';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
78
problems/kamacoder/0147.三珠互斥.md
Normal file
78
problems/kamacoder/0147.三珠互斥.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 三珠互斥
|
||||
|
||||
1. 如果k * 3 大于 n 了,那说明一定没结果,如果没想明白,大家举个例子试试看
|
||||
2. 分别求出三个红珠子之间的距离
|
||||
3. 对这三段距离从小到大排序 y1, y2, y3
|
||||
4. 如果第一段距离y1 小于k,说明需要交换 k - y 次, 同理 第二段距离y2 小于k,说明需要交换 k - y2 次
|
||||
5. y1 y2 都调整好了,不用计算y3,因为 y3是距离最大
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main(){
|
||||
int t;
|
||||
cin >> t;
|
||||
int n, k, a1, a2, a3;
|
||||
vector<int> dis(3);
|
||||
|
||||
while (t--) {
|
||||
cin >> n >> k >> a1 >> a2 >> a3;
|
||||
if(k * 3 > n){
|
||||
cout << -1 << endl;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
dis[0] = min(abs(a1 - a2), n - abs(a1 - a2));
|
||||
dis[1] = min(abs(a1 - a3), n - abs(a1 - a3));
|
||||
dis[2] = min(abs(a3 - a2), n - abs(a3 - a2));
|
||||
|
||||
sort(dis.begin(), dis.end());
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
if (dis[0] < k) result += (k - dis[0]);
|
||||
if (dis[1] < k) result += (k - dis[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
cout << result << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int t = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
|
||||
while (t-- > 0) {
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int k = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int a1 = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int a2 = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
int a3 = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
if (k * 3 > n) {
|
||||
System.out.println(-1);
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
List<Integer> dis = new ArrayList<>(3);
|
||||
dis.add(Math.min(Math.abs(a1 - a2), n - Math.abs(a1 - a2)));
|
||||
dis.add(Math.min(Math.abs(a1 - a3), n - Math.abs(a1 - a3)));
|
||||
dis.add(Math.min(Math.abs(a3 - a2), n - Math.abs(a3 - a2)));
|
||||
|
||||
Collections.sort(dis);
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
if (dis.get(0) < k) result += (k - dis.get(0));
|
||||
if (dis.get(1) < k) result += (k - dis.get(1));
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
122
problems/kamacoder/0148.扑克牌同花顺.md
Normal file
122
problems/kamacoder/0148.扑克牌同花顺.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 扑克牌同花顺
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们要定义一个结构体,来存放我们的数据
|
||||
|
||||
`map<花色,{同一花色牌集合,同一花色的牌对应的牌数量}>`
|
||||
|
||||
再遍历 每一个花色下,每一个牌 的数量
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下详细注释:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
string cards[] = {"H","S","D","C"};
|
||||
typedef long long ll;
|
||||
struct color
|
||||
{
|
||||
set<int> st; // 同一花色 牌的集合
|
||||
map<int, ll> cnt; // 同一花色 牌对应的数量
|
||||
};
|
||||
unordered_map<string, color> umap;
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
int x, y;
|
||||
string card;
|
||||
cin >> x >> y >> card;
|
||||
umap[card].st.insert(x);
|
||||
umap[card].cnt[x] += y;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ll sum = 0;
|
||||
// 遍历每一个花色
|
||||
for (string cardOne : cards) {
|
||||
color colorOne = umap[cardOne];
|
||||
// 遍历 同花色 每一个牌
|
||||
for (int number : colorOne.st) {
|
||||
ll numberCount = colorOne.cnt[number]; // 获取牌为number的数量是 numberCount
|
||||
|
||||
// 统计 number 到 number + 4 都是否有牌,用cal 把 number 到number+4 的数量记下来
|
||||
ll cal = numberCount;
|
||||
for (int j = number + 1; j <= number + 4; j++) cal = min(cal, colorOne.cnt[j]);
|
||||
// 统计结果
|
||||
sum += cal;
|
||||
// 把统计过的同花顺数量减下去
|
||||
for (int j = number + 1; j <= number + 4; j++) colorOne.cnt[j] -= cal;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << sum << endl;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
static String[] cards = {"H", "S", "D", "C"}; // 花色数组
|
||||
|
||||
static class Color {
|
||||
Set<Integer> st; // 同一花色牌的集合
|
||||
Map<Integer, Long> cnt; // 同一花色牌对应的数量
|
||||
|
||||
Color() {
|
||||
st = new HashSet<>(); // 初始化集合
|
||||
cnt = new HashMap<>(); // 初始化映射
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static Map<String, Color> umap = new HashMap<>(); // 用于存储每种花色对应的Color对象
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 读取牌的数量
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
int x = scanner.nextInt(); // 读取牌的值
|
||||
int y = scanner.nextInt(); // 读取牌的数量
|
||||
String card = scanner.next(); // 读取牌的花色
|
||||
|
||||
umap.putIfAbsent(card, new Color()); // 如果不存在该花色,则创建一个新的Color对象
|
||||
umap.get(card).st.add(x); // 将牌的值加入集合
|
||||
umap.get(card).cnt.put(x, umap.get(card).cnt.getOrDefault(x, 0L) + y); // 更新牌的数量
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
long sum = 0; // 结果累加器
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历每一种花色
|
||||
for (String cardOne : cards) {
|
||||
Color colorOne = umap.getOrDefault(cardOne, new Color()); // 获取对应花色的Color对象
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历同花色的每一张牌
|
||||
for (int number : colorOne.st) {
|
||||
long numberCount = colorOne.cnt.get(number); // 获取当前牌的数量
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算从当前牌到number+4的最小数量
|
||||
long cal = numberCount;
|
||||
for (int j = number + 1; j <= number + 4; j++) {
|
||||
cal = Math.min(cal, colorOne.cnt.getOrDefault(j, 0L)); // 更新cal为最小值
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 将结果累加到sum
|
||||
sum += cal;
|
||||
|
||||
// 将统计过的同花顺数量减去
|
||||
for (int j = number + 1; j <= number + 4; j++) {
|
||||
colorOne.cnt.put(j, colorOne.cnt.getOrDefault(j, 0L) - cal);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(sum); // 输出结果
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
102
problems/kamacoder/0149.好数组.md
Normal file
102
problems/kamacoder/0149.好数组.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 149. 好数组
|
||||
|
||||
贪心思路:
|
||||
|
||||
整体思路是移动到中间位置(中位数),一定是 移动次数最小的。
|
||||
|
||||
有一个数可以不改变,对数组排序之后, 最小数 和 最大数 一定是移动次数最多的,所以分别保留最小 和 最大的不变。
|
||||
|
||||
中间可能有两个位置,所以要计算中间偏前 和 中间偏后的
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
vector<long> arr(n);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
cin >> arr[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[0] == arr[n - 1]) {
|
||||
cout << 1 << endl;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
long cnt = 0L;
|
||||
long cnt1 = 0L;
|
||||
|
||||
// 如果要保留一个不改变,要不不改最小的,要不不改最大的。
|
||||
|
||||
// 取中间偏前的位置
|
||||
long mid = arr[(n - 2) / 2];
|
||||
|
||||
// 不改最大的
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
|
||||
cnt += abs(arr[i] - mid);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 取中间偏后的位置
|
||||
mid = arr[n / 2];
|
||||
|
||||
// 不改最小的
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cnt1 += abs(arr[i] - mid);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cout << min(cnt, cnt1) << endl;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
long[] arr = new long[n];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
arr[i] = scanner.nextLong();
|
||||
}
|
||||
Arrays.sort(arr);
|
||||
|
||||
if (arr[0] == arr[n - 1]) {
|
||||
System.out.println(1);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
long cnt = 0L;
|
||||
long cnt1 = 0L;
|
||||
|
||||
// 如果要保留一个不改变,要不不改最小的,要不不改最大的。
|
||||
|
||||
// 取中间偏前的位置
|
||||
long mid = arr[(n - 2) / 2];
|
||||
|
||||
// 不改最大的
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
|
||||
cnt += Math.abs(arr[i] - mid);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 取中间偏后的位置
|
||||
mid = arr[n / 2];
|
||||
|
||||
// 不改最小的
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
cnt1 += Math.abs(arr[i] - mid);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(Math.min(cnt, cnt1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
66
problems/kamacoder/0150.极长连续段的权值.md
Normal file
66
problems/kamacoder/0150.极长连续段的权值.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 150. 极长连续段的权值
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划,枚举最后边节点的情况:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
string s;
|
||||
cin >> s;
|
||||
|
||||
long long result = 1;
|
||||
long long a = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
// 加上本身长度为1的子串
|
||||
if (s[i] == s[i - 1]) {
|
||||
a += 1;
|
||||
result += a;
|
||||
// 以最右节点为终点,每个子串的级长连续段都+1,再加本身长度为1的子串
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
a = a + i + 1;
|
||||
result += a;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << result << endl;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = scanner.nextInt();
|
||||
String s = scanner.next();
|
||||
|
||||
long result = 1;
|
||||
long a = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
// 加上本身长度为1的子串
|
||||
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i - 1)) {
|
||||
a += 1;
|
||||
result += a;
|
||||
// 以最右节点为终点,每个子串的级长连续段都+1,再加本身长度为1的子串
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
a = a + i + 1;
|
||||
result += a;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
127
problems/kamacoder/0151.手机流畅运行的秘密.md
Normal file
127
problems/kamacoder/0151.手机流畅运行的秘密.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
# 151. 手机流畅运行的秘密
|
||||
|
||||
[题目链接](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1229)
|
||||
|
||||
先运行 能留下电量多的 任务,才能有余电运行其他任务。
|
||||
|
||||
任务1,1:10 ,运行完 能留下 9个电
|
||||
|
||||
任务2,2:12,运行完 能留下 10个电
|
||||
|
||||
任务3,3:10,运行完 能留下 7个电。
|
||||
|
||||
运行顺序: 任务2 -> 任务1 -> 任务3
|
||||
|
||||
按照 最低初始电量 - 耗电量,从大到小排序。
|
||||
|
||||
计算总电量,需要 从小到大 遍历, 不断取 总电量 + 任务耗电量 与 任务最低初始电量 的最大值。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
bool cmp(const pair<int,int>& taskA, const pair<int,int>& taskB) {
|
||||
return (taskA.second - taskA.first) < (taskB.second - taskB.first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
string str, tmp;
|
||||
vector<pair<int,int>> tasks;
|
||||
|
||||
//处理输入
|
||||
getline(cin, str);
|
||||
stringstream ss(str);
|
||||
while (getline(ss, tmp, ',')) {
|
||||
int p = tmp.find(":");
|
||||
string a = tmp.substr(0, p);
|
||||
string b = tmp.substr(p + 1);
|
||||
tasks.push_back({stoi(a), stoi(b)});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 按照差值从小到大排序
|
||||
sort(tasks.begin(), tasks.end(), cmp);
|
||||
|
||||
// 收集结果
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0 ; i < tasks.size(); i++) {
|
||||
result = max(result + tasks[i].first, tasks[i].second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
result = result <= 4800 ? result : -1;
|
||||
cout << result << endl;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
String str = sc.nextLine();
|
||||
String[] tasksArray = str.split(",");
|
||||
List<Pair> tasks = Arrays.stream(tasksArray)
|
||||
.map(task -> {
|
||||
String[] parts = task.split(":");
|
||||
return new Pair(Integer.parseInt(parts[0]), Integer.parseInt(parts[1]));
|
||||
})
|
||||
.collect(Collectors.toList());
|
||||
|
||||
// 按照差值从小到大排序
|
||||
Collections.sort(tasks, (taskA, taskB) ->
|
||||
(taskA.second - taskA.first) - (taskB.second - taskB.first)
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// 收集结果
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for (Pair task : tasks) {
|
||||
result = Math.max(result + task.first, task.second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
result = result <= 4800 ? result : -1;
|
||||
System.out.println(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class Pair {
|
||||
int first;
|
||||
int second;
|
||||
|
||||
Pair(int first, int second) {
|
||||
this.first = first;
|
||||
this.second = second;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
input = sys.stdin.read
|
||||
|
||||
str = input().strip()
|
||||
tasks = []
|
||||
for tmp in str.split(','):
|
||||
a, b = map(int, tmp.split(':'))
|
||||
tasks.append((a, b))
|
||||
|
||||
# 按照差值从小到大排序
|
||||
tasks.sort(key=lambda task: task[1] - task[0])
|
||||
|
||||
# 收集结果
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
for task in tasks:
|
||||
result = max(result + task[0], task[1])
|
||||
|
||||
result = result if result <= 4800 else -1
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
121
problems/kamacoder/0152.小米手机通信校准.md
Normal file
121
problems/kamacoder/0152.小米手机通信校准.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 152. 小米手机通信校准
|
||||
|
||||
[题目链接](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1230)
|
||||
|
||||
一道模拟题,但比较考察 代码能力。
|
||||
|
||||
遍历去找 里 freq 最近的 freg就好, 需要记录刚遍历过的的freg和 loss,因为可能有 相邻一样的 freg。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int freq;
|
||||
cin >> freq;
|
||||
string data;
|
||||
double result = 0;
|
||||
int last_freg = 0; // 记录上一个 freg
|
||||
int last_loss = 0; // 记录上一个loss
|
||||
while(cin >> data) {
|
||||
int index = data.find(':');
|
||||
int freg = stoi(data.substr(0, index)); // 获取 freg 和 loss
|
||||
int loss = stoi(data.substr(index + 1));
|
||||
// 两遍一样
|
||||
if(abs(freg - freq) == abs(last_freg - freq)) {
|
||||
result = (double)(last_loss + loss)/2.0;
|
||||
} // 否则更新最新的result
|
||||
else if(abs(freg - freq) < abs(last_freg - freq)){
|
||||
result = (double)loss;
|
||||
}
|
||||
last_freg = freg;
|
||||
last_loss = loss;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("%.1lf\n", result);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java 版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int freq = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
sc.nextLine(); // 读取换行符
|
||||
|
||||
String inputLine = sc.nextLine(); // 读取包含所有后续输入的行
|
||||
String[] data = inputLine.split(" "); // 根据空格分割输入
|
||||
|
||||
double result = 0;
|
||||
int lastFreq = 0; // 记录上一个 freg
|
||||
int lastLoss = 0; // 记录上一个 loss
|
||||
|
||||
for (String entry : data) {
|
||||
int index = entry.indexOf(':');
|
||||
int freg = Integer.parseInt(entry.substring(0, index)); // 获取 freg 和 loss
|
||||
int loss = Integer.parseInt(entry.substring(index + 1));
|
||||
|
||||
// 两遍一样
|
||||
if (Math.abs(freg - freq) == Math.abs(lastFreq - freq)) {
|
||||
result = (double) (lastLoss + loss) / 2.0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 否则更新最新的 result
|
||||
else if (Math.abs(freg - freq) < Math.abs(lastFreq - freq)) {
|
||||
result = (double) loss;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lastFreq = freg;
|
||||
lastLoss = loss;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.printf("%.1f\n", result);
|
||||
sc.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
input = sys.stdin.read
|
||||
data = input().split()
|
||||
|
||||
freq = int(data[0])
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
last_freg = 0 # 记录上一个 freg
|
||||
last_loss = 0 # 记录上一个 loss
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, len(data)):
|
||||
item = data[i]
|
||||
index = item.find(':')
|
||||
freg = int(item[:index]) # 获取 freg 和 loss
|
||||
loss = int(item[index + 1:])
|
||||
|
||||
# 两遍一样
|
||||
if abs(freg - freq) == abs(last_freg - freq):
|
||||
result = (last_loss + loss) / 2.0
|
||||
# 否则更新最新的 result
|
||||
elif abs(freg - freq) < abs(last_freg - freq):
|
||||
result = loss
|
||||
|
||||
last_freg = freg
|
||||
last_loss = loss
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"{result:.1f}")
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本题和[代码随想录:两个字符串的删除操作](https://www.programmercarl.com/0583.%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%B8%B2%E7%9A%84%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.html) 思路基本是一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
string s1, s2;
|
||||
cin >> s1 >> s2;
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> dp(s1.size() + 1, vector<int>(s2.size() + 1, 0));
|
||||
|
||||
// s1 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCLL值综合
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.size(); i++) dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + s1[i - 1];
|
||||
// s2 如果变成空串的最小删除ASCLL值综合
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + s2[j - 1];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.size(); i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.size(); j++) {
|
||||
if (s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
|
||||
else dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + s1[i - 1], dp[i][j - 1] + s2[j - 1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cout << dp[s1.size()][s2.size()] << endl;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
int[] a = new int[n];
|
||||
int[] b = new int[n];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int p = -1, s = -1;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
if (a[i] == b[i]) p = i;
|
||||
else break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) {
|
||||
if (a[j] == b[j]) s = j;
|
||||
else break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
|
||||
int res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
for (int i = j ; i >= 0 ; i--) {
|
||||
if (i == j) dp[i][j] = a[i] == b[i];
|
||||
else if (i + 1 == j) dp[i][j] = (a[i] == b[j] && a[j] == b[i]);
|
||||
else {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] && (a[i] == b[j] && a[j] == b[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (dp[i][j] && (i == 0 || p >= i-1) && (j == n - 1 || j+1 >= s)) res++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
System.out.println(res);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.Scanner;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||||
int n = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
|
||||
int[] a = new int[n];
|
||||
int[] b = new int[n];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历所有可能的区间
|
||||
for (int left = 0; left < n; left++) {
|
||||
for (int right = left; right < n; right++) {
|
||||
// 检查翻转区间 [left, right] 后,a 是否可以变成 b
|
||||
if (canTransform(a, b, left, right)) {
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println(count);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static boolean canTransform(int[] a, int[] b, int left, int right) {
|
||||
// 提前检查翻转区间的值是否可以匹配
|
||||
for (int i = left, j = right; i <= right; i++, j--) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[j]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 检查翻转区间外的值是否匹配
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < left; i++) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = right + 1; i < a.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <queue>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义二叉树节点结构
|
||||
struct TreeNode {
|
||||
int val;
|
||||
TreeNode* left;
|
||||
TreeNode* right;
|
||||
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据层序遍历数组构建二叉树
|
||||
TreeNode* constructBinaryTree(const vector<string>& levelOrder) {
|
||||
if (levelOrder.empty()) return NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[0]));
|
||||
queue<TreeNode*> q;
|
||||
q.push(root);
|
||||
int i = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (!q.empty() && i < levelOrder.size()) {
|
||||
TreeNode* current = q.front();
|
||||
q.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && levelOrder[i] != "null") {
|
||||
current->left = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[i]));
|
||||
q.push(current->left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
|
||||
if (i < levelOrder.size() && levelOrder[i] != "null") {
|
||||
current->right = new TreeNode(stoi(levelOrder[i]));
|
||||
q.push(current->right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
int dfs(TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
if (node == NULL) return 0;
|
||||
int leftPath = dfs(node->left);
|
||||
int rightPath = dfs(node->right);
|
||||
|
||||
int leftNum = 0, rightNum = 0;
|
||||
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->val == node->val) {
|
||||
leftNum = leftPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node->right != NULL && node->right->val == node->val) {
|
||||
rightNum = rightPath + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = max(result, leftNum + rightNum);
|
||||
return max(leftNum, rightNum);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
cin >> n;
|
||||
vector<string> levelOrder(n);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) cin >> levelOrder[i];
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode* root = constructBinaryTree(levelOrder);
|
||||
dfs(root);
|
||||
cout << result << endl;
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user