diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 148f49d8..3dbf2c0d 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -4,11 +4,12 @@
> 1. **介绍**:本项目是一套完整的刷题计划,旨在帮助大家少走弯路,循序渐进学算法,[关注作者](#关于作者)
> 2. **PDF版本** : [「代码随想录」算法精讲 PDF 版本](https://programmercarl.com/other/algo_pdf.html) 。
-> 3. **最强八股文:**:[代码随想录知识星球精华PDF](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar_baguwen.html)
-> 4. **刷题顺序** : README已经将刷题顺序排好了,按照顺序一道一道刷就可以。
-> 5. **学习社区** : 一起学习打卡/面试技巧/如何选择offer/大厂内推/职场规则/简历修改/技术分享/程序人生。欢迎加入[「代码随想录」知识星球](https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html) 。
-> 6. **提交代码**:本项目统一使用C++语言进行讲解,但已经有Java、Python、Go、JavaScript等等多语言版本,感谢[这里的每一位贡献者](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors),如果你也想贡献代码点亮你的头像,[点击这里](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A)了解提交代码的方式。
-> 7. **转载须知** :以下所有文章皆为我([程序员Carl](https://github.com/youngyangyang04))的原创。引用本项目文章请注明出处,发现恶意抄袭或搬运,会动用法律武器维护自己的权益。让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境!
+> 3. **算法公开课** : [《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fA4y1o715) 。
+> 4. **最强八股文:**:[代码随想录知识星球精华PDF](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar_baguwen.html)
+> 5. **刷题顺序** : README已经将刷题顺序排好了,按照顺序一道一道刷就可以。
+> 6. **学习社区** : 一起学习打卡/面试技巧/如何选择offer/大厂内推/职场规则/简历修改/技术分享/程序人生。欢迎加入[「代码随想录」知识星球](https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html) 。
+> 7. **提交代码**:本项目统一使用C++语言进行讲解,但已经有Java、Python、Go、JavaScript等等多语言版本,感谢[这里的每一位贡献者](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors),如果你也想贡献代码点亮你的头像,[点击这里](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A)了解提交代码的方式。
+> 8. **转载须知** :以下所有文章皆为我([程序员Carl](https://github.com/youngyangyang04))的原创。引用本项目文章请注明出处,发现恶意抄袭或搬运,会动用法律武器维护自己的权益。让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境!
@@ -102,6 +103,7 @@
* [看了这么多代码,谈一谈代码风格!](./problems/前序/代码风格.md)
* [力扣上的代码想在本地编译运行?](./problems/前序/力扣上的代码想在本地编译运行?.md)
* [什么是核心代码模式,什么又是ACM模式?](./problems/前序/什么是核心代码模式,什么又是ACM模式?.md)
+ * [刷题要不要用库函数](./problems/前序/刷力扣用不用库函数.md)
* [ACM模式如何构造二叉树](./problems/前序/ACM模式如何构建二叉树.md)
* [解密互联网大厂研发流程](./problems/前序/互联网大厂研发流程.md)
@@ -129,45 +131,6 @@
* [递归算法的时间与空间复杂度分析!](./problems/前序/递归算法的时间与空间复杂度分析.md)
* [刷了这么多题,你了解自己代码的内存消耗么?](./problems/前序/刷了这么多题,你了解自己代码的内存消耗么?.md)
-## 知识星球精选
-
-* [秋招面试,心态很重要!](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结3.md)
-* [秋招倒霉透顶,触底反弹!](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结2.md)
-* [无竞赛,无实习,如何秋招?](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结1.md)
-* [offer总决赛,何去何从!](./problems/知识星球精选/offer总决赛,何去何从.md)
-* [入职后担心代码能力跟不上!](./problems/知识星球精选/入职后担心代码能力跟不上.md)
-* [秋招进入offer决赛圈!](./problems/知识星球精选/offer对比-决赛圈.md)
-* [非科班的困扰](./problems/知识星球精选/非科班的困扰.md)
-* [offer的选择-开奖](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招开奖.md)
-* [看到代码就抵触!怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/不喜欢写代码怎么办.md)
-* [遭遇逼签,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/逼签.md)
-* [HR特意刁难非科班!](./problems/知识星球精选/HR特意刁难非科班.md)
-* [offer的选择](./problems/知识星球精选/offer的选择.md)
-* [天下乌鸦一般黑,哪家没有PUA?](./problems/知识星球精选/天下乌鸦一般黑.md)
-* [初入大三,考研VS工作](./problems/知识星球精选/初入大三选择考研VS工作.md)
-* [非科班2021秋招总结](./problems/知识星球精选/非科班2021秋招总结.md)
-* [秋招下半场依然没offer,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招下半场依然没offer.md)
-* [合适自己的就是最好的](./problems/知识星球精选/合适自己的就是最好的.md)
-* [为什么都说客户端会消失](./problems/知识星球精选/客三消.md)
-* [博士转计算机如何找工作](./problems/知识星球精选/博士转行计算机.md)
-* [不一样的七夕](./problems/知识星球精选/不一样的七夕.md)
-* [HR面注意事项](./problems/知识星球精选/HR面注意事项.md)
-* [刷题攻略要刷两遍!](./problems/知识星球精选/刷题攻略要刷两遍.md)
-* [秋招进行中的迷茫与焦虑......](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招进行中的迷茫与焦虑.md)
-* [大厂新人培养体系应该是什么样的?](./problems/知识星球精选/大厂新人培养体系.md)
-* [你的简历里「专业技能」写的够专业么?](./problems/知识星球精选/专业技能可以这么写.md)
-* [Carl看了上百份简历,总结了这些!](./problems/知识星球精选/写简历的一些问题.md)
-* [备战2022届秋招](./problems/知识星球精选/备战2022届秋招.md)
-* [技术不太好,如果选择方向](./problems/知识星球精选/技术不好如何选择技术方向.md)
-* [刷题要不要使用库函数](./problems/知识星球精选/刷力扣用不用库函数.md)
-* [关于实习的几点问题](./problems/知识星球精选/关于实习大家的疑问.md)
-* [面试中遇到了发散性问题,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/面试中发散性问题.md)
-* [英语到底重不重要!](./problems/知识星球精选/英语到底重不重要.md)
-* [计算机专业要不要读研!](./problems/知识星球精选/要不要考研.md)
-* [关于提前批的一些建议](./problems/知识星球精选/关于提前批的一些建议.md)
-* [已经在实习的录友要如何准备秋招](./problems/知识星球精选/如何权衡实习与秋招复习.md)
-* [华为提前批已经开始了](./problems/知识星球精选/提前批已经开始了.md)
-
## 杂谈
* [「代码随想录」刷题网站上线](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-6rd_g7LrVD1fuKBYk2tXQ)。
@@ -179,77 +142,77 @@
## 数组
1. [数组过于简单,但你该了解这些!](./problems/数组理论基础.md)
-2. [数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
-3. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
-4. [数组:有序数组的平方,还有序么?](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
-5. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
-6. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
+2. [数组:二分查找](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
+3. [数组:移除元素](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
+4. [数组:序数组的平方](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
+5. [数组:长度最小的子数组](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
+6. [数组:螺旋矩阵II](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
7. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
## 链表
1. [关于链表,你该了解这些!](./problems/链表理论基础.md)
-2. [链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](./problems/0203.移除链表元素.md)
-3. [链表:一道题目考察了常见的五个操作!](./problems/0707.设计链表.md)
-4. [链表:听说过两天反转链表又写不出来了?](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
+2. [链表:移除链表元素](./problems/0203.移除链表元素.md)
+3. [链表:设计链表](./problems/0707.设计链表.md)
+4. [链表:翻转链表](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
5. [链表:两两交换链表中的节点](./problems/0024.两两交换链表中的节点.md)
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
-8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
+8. [链表:环形链表](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
9. [链表:总结篇!](./problems/链表总结篇.md)
## 哈希表
1. [关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](./problems/哈希表理论基础.md)
-2. [哈希表:可以拿数组当哈希表来用,但哈希值不要太大](./problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md)
+2. [哈希表:有效的字母异位词](./problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md)
3. [哈希表:查找常用字符](./problems/1002.查找常用字符.md)
-4. [哈希表:哈希值太大了,还是得用set](./problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md)
-5. [哈希表:用set来判断快乐数](./problems/0202.快乐数.md)
-6. [哈希表:map等候多时了](./problems/0001.两数之和.md)
-7. [哈希表:其实需要哈希的地方都能找到map的身影](./problems/0454.四数相加II.md)
-8. [哈希表:这道题目我做过?](./problems/0383.赎金信.md)
-9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
-10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
-11. [哈希表:总结篇!(每逢总结必经典)](./problems/哈希表总结.md)
+4. [哈希表:两个数组的交集](./problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md)
+5. [哈希表:快乐数](./problems/0202.快乐数.md)
+6. [哈希表:两数之和](./problems/0001.两数之和.md)
+7. [哈希表:四数相加II](./problems/0454.四数相加II.md)
+8. [哈希表:赎金信](./problems/0383.赎金信.md)
+9. [哈希表:三数之和](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
+10. [双指针法:四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
+11. [哈希表:总结篇!](./problems/哈希表总结.md)
## 字符串
-1. [字符串:这道题目,使用库函数一行代码搞定](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
-2. [字符串:简单的反转还不够!](./problems/0541.反转字符串II.md)
+1. [字符串:反转字符串](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
+2. [字符串:反转字符串II](./problems/0541.反转字符串II.md)
3. [字符串:替换空格](./problems/剑指Offer05.替换空格.md)
-4. [字符串:花式反转还不够!](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
-5. [字符串:反转个字符串还有这个用处?](./problems/剑指Offer58-II.左旋转字符串.md)
+4. [字符串:翻转字符串里的单词](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
+5. [字符串:左旋转字符串](./problems/剑指Offer58-II.左旋转字符串.md)
6. [帮你把KMP算法学个通透](./problems/0028.实现strStr.md)
-8. [字符串:KMP算法还能干这个!](./problems/0459.重复的子字符串.md)
+8. [字符串:重复的子字符串](./problems/0459.重复的子字符串.md)
9. [字符串:总结篇!](./problems/字符串总结.md)
## 双指针法
双指针法基本都是应用在数组,字符串与链表的题目上
-1. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
-2. [字符串:这道题目,使用库函数一行代码搞定](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
+1. [数组:移除元素](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
+2. [字符串:反转字符串](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
3. [字符串:替换空格](./problems/剑指Offer05.替换空格.md)
-4. [字符串:花式反转还不够!](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
-5. [链表:听说过两天反转链表又写不出来了?](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
+4. [字符串:翻转字符串里的单词](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
+5. [链表:翻转链表](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
-8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
-9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
-10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
-11. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
+8. [链表:环形链表](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
+9. [双指针:三数之和](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
+10. [双指针:四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
+11. [双指针:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
## 栈与队列
1. [栈与队列:来看看栈和队列不为人知的一面](./problems/栈与队列理论基础.md)
-2. [栈与队列:我用栈来实现队列怎么样?](./problems/0232.用栈实现队列.md)
-3. [栈与队列:用队列实现栈还有点别扭](./problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md)
-4. [栈与队列:系统中处处都是栈的应用](./problems/0020.有效的括号.md)
-5. [栈与队列:匹配问题都是栈的强项](./problems/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.md)
-6. [栈与队列:有没有想过计算机是如何处理表达式的?](./problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md)
-7. [栈与队列:滑动窗口里求最大值引出一个重要数据结构](./problems/0239.滑动窗口最大值.md)
-8. [栈与队列:求前 K 个高频元素和队列有啥关系?](./problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md)
+2. [栈与队列:用栈实现队列](./problems/0232.用栈实现队列.md)
+3. [栈与队列:用队列实现栈](./problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md)
+4. [栈与队列:有效的括号](./problems/0020.有效的括号.md)
+5. [栈与队列:删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](./problems/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.md)
+6. [栈与队列:逆波兰表达式求值](./problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md)
+7. [栈与队列:滑动窗口最大值](./problems/0239.滑动窗口最大值.md)
+8. [栈与队列:前K个高频元素](./problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md)
9. [栈与队列:总结篇!](./problems/栈与队列总结.md)
## 二叉树
@@ -258,41 +221,41 @@
 1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
-2. [二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
-3. [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
-4. [二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么?](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:层序遍历登场!](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:你真的会翻转二叉树么?](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
+3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
+4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
-8. [二叉树:我对称么?](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
-9. [二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
-10. [二叉树:看看这些树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
-11. [二叉树:我有多少个节点?](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
-12. [二叉树:我平衡么?](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
-13. [二叉树:找我的所有路径?](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
+8. [二叉树:对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
+9. [二叉树:二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
+10. [二叉树:二叉树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
+11. [二叉树:完全二叉树的节点个数](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
+12. [二叉树:平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
+13. [二叉树:二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!二叉树系列二](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:以为使用了递归,其实还隐藏着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
-16. [二叉树:做了这么多题目了,我的左叶子之和是多少?](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
-17. [二叉树:我的左下角的值是多少?](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
+15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
+16. [二叉树:左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
+17. [二叉树:找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
-19. [二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
-20. [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
+19. [二叉树:构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
+20. [二叉树:最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
21. [本周小结!(二叉树系列三)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
-24. [二叉树:我是不是一棵二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
+24. [二叉树:验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
25. [二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](./problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md)
-26. [二叉树:我的众数是多少?](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
+26. [二叉树:二叉搜索树中的众数](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
27. [二叉树:公共祖先问题](./problems/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.md)
28. [本周小结!(二叉树系列四)](./problems/周总结/20201017二叉树周末总结.md)
-29. [二叉树:搜索树的公共祖先问题](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
+29. [二叉树:搜索树的最近公共祖先](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
30. [二叉树:搜索树中的插入操作](./problems/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.md)
31. [二叉树:搜索树中的删除操作](./problems/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.md)
32. [二叉树:修剪一棵搜索树](./problems/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.md)
33. [二叉树:构造一棵搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:搜索树转成累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
-
+
## 回溯算法
题目分类大纲如下:
@@ -538,29 +501,14 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-
-
-# B站算法视频讲解
-
-以下为[B站「代码随想录」](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)算法讲解视频:
-
-* [KMP算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd)
-* [KMP算法(代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
-* [回溯算法理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM)
-* [回溯算法之组合问题(力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)
-* [组合问题的剪枝操作(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er)
-* [组合总和(对应力扣题目:39.组合总和)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
-* [分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6)
-* [二叉树理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Hy4y1t7ij)
-* [二叉树的递归遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wh411S7xt)
-* [二叉树的非递归遍历(一)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
# 贡献者
[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+# Star 趋势
+
+[](https://star-history.com/#youngyangyang04/leetcode-master&Date)
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -569,7 +517,8 @@
如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-
+
+
@@ -581,6 +530,7 @@
**来看看就知道了,你会发现相见恨晚!**
+
1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
-2. [二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
-3. [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
-4. [二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么?](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:层序遍历登场!](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:你真的会翻转二叉树么?](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
+3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
+4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
-8. [二叉树:我对称么?](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
-9. [二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
-10. [二叉树:看看这些树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
-11. [二叉树:我有多少个节点?](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
-12. [二叉树:我平衡么?](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
-13. [二叉树:找我的所有路径?](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
+8. [二叉树:对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
+9. [二叉树:二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
+10. [二叉树:二叉树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
+11. [二叉树:完全二叉树的节点个数](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
+12. [二叉树:平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
+13. [二叉树:二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!二叉树系列二](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:以为使用了递归,其实还隐藏着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
-16. [二叉树:做了这么多题目了,我的左叶子之和是多少?](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
-17. [二叉树:我的左下角的值是多少?](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
+15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
+16. [二叉树:左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
+17. [二叉树:找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
-19. [二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
-20. [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
+19. [二叉树:构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
+20. [二叉树:最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
21. [本周小结!(二叉树系列三)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
-24. [二叉树:我是不是一棵二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
+24. [二叉树:验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
25. [二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](./problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md)
-26. [二叉树:我的众数是多少?](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
+26. [二叉树:二叉搜索树中的众数](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
27. [二叉树:公共祖先问题](./problems/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.md)
28. [本周小结!(二叉树系列四)](./problems/周总结/20201017二叉树周末总结.md)
-29. [二叉树:搜索树的公共祖先问题](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
+29. [二叉树:搜索树的最近公共祖先](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
30. [二叉树:搜索树中的插入操作](./problems/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.md)
31. [二叉树:搜索树中的删除操作](./problems/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.md)
32. [二叉树:修剪一棵搜索树](./problems/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.md)
33. [二叉树:构造一棵搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:搜索树转成累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
-
+
## 回溯算法
题目分类大纲如下:
@@ -538,29 +501,14 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-
-
-# B站算法视频讲解
-
-以下为[B站「代码随想录」](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)算法讲解视频:
-
-* [KMP算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd)
-* [KMP算法(代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
-* [回溯算法理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM)
-* [回溯算法之组合问题(力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)
-* [组合问题的剪枝操作(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er)
-* [组合总和(对应力扣题目:39.组合总和)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
-* [分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6)
-* [二叉树理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Hy4y1t7ij)
-* [二叉树的递归遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wh411S7xt)
-* [二叉树的非递归遍历(一)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
# 贡献者
[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+# Star 趋势
+
+[](https://star-history.com/#youngyangyang04/leetcode-master&Date)
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -569,7 +517,8 @@
如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-
+
+
@@ -581,6 +530,7 @@
**来看看就知道了,你会发现相见恨晚!**
+







 diff --git a/problems/0028.实现strStr.md b/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
index 634d8535..271822dc 100644
--- a/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
+++ b/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
# 28. 实现 strStr()
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-strstr/)
实现 strStr() 函数。
@@ -685,7 +685,21 @@ class Solution {
```
Python3:
-
+```python
+//暴力解法:
+class Solution(object):
+ def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
+ """
+ :type haystack: str
+ :type needle: str
+ :rtype: int
+ """
+ m,n=len(haystack),len(needle)
+ for i in range(m):
+ if haystack[i:i+n]==needle:
+ return i
+ return -1
+```
```python
// 方法一
class Solution:
@@ -1059,5 +1073,231 @@ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
```
+> 前缀表右移
+
+```swift
+func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
+
+ let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
+ guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
+
+ var j = 0
+ var next = [Int].init(repeating: 0, count: p.count)
+ getNext(&next, p)
+
+ for i in 0 ..< s.count {
+
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
+ j = next[j]
+ }
+
+ if s[i] == p[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ if j == p.count {
+ return i - p.count + 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ // 前缀表后移一位,首位用 -1 填充
+ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], _ needle: [Character]) {
+
+ guard needle.count > 1 else { return }
+
+ var j = 0
+ next[0] = j
+
+ for i in 1 ..< needle.count-1 {
+
+ while j > 0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if needle[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ next[i] = j
+ }
+ next.removeLast()
+ next.insert(-1, at: 0)
+ }
+```
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```swift
+
+func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
+
+ let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
+ guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
+
+ var j = 0
+ var next = [Int](repeating: 0, count: needle.count)
+ // KMP
+ getNext(&next, needle: p)
+
+ for i in 0 ..< s.count {
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if s[i] == p[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ if j == p.count {
+ return i - p.count + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ //前缀表
+ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
+
+ var j = 0
+ next[0] = j
+
+ for i in 1 ..< needle.count {
+
+ while j>0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if needle[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ next[i] = j
+
+ }
+ }
+
+```
+
+PHP:
+
+> 前缀表统一减一
+```php
+function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
+ if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
+ $next= [];
+ $this->getNext($next,$needle);
+
+ $j = -1;
+ for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
+ while($j >= 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j + 1]) {
+ $j = $next[$j];
+ }
+ if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j + 1]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ if ($j == (strlen($needle) - 1) ) {
+ return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+function getNext(&$next, $s){
+ $j = -1;
+ $next[0] = $j;
+ for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
+ while ($j >= 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j + 1]) {
+ $j = $next[$j];
+ }
+ if ($s[$i] == $s[$j + 1]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ $next[$i] = $j;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```php
+function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
+ if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
+ $next= [];
+ $this->getNext($next,$needle);
+
+ $j = 0;
+ for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
+ while($j > 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j]) {
+ $j = $next[$j-1];
+ }
+ if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ if ($j == strlen($needle)) {
+ return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+function getNext(&$next, $s){
+ $j = 0;
+ $next[0] = $j;
+ for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
+ while ($j > 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j]) {
+ $j = $next[$j-1];
+ }
+ if ($s[$i] == $s[$j]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ $next[$i] = $j;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Rust:
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn get_next(next: &mut Vec, s: &Vec) {
+ let len = s.len();
+ let mut j = 0;
+ for i in 1..len {
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != s[j] {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ if s[i] == s[j] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+ next[i] = j;
+ }
+ }
+
+ pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
+ let (haystack_len, needle_len) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
+ if haystack_len == 0 { return 0; }
+ if haystack_len < needle_len { return -1;}
+ let (haystack, needle) = (haystack.chars().collect::>(), needle.chars().collect::>());
+ let mut next: Vec = vec![0; haystack_len];
+ Self::get_next(&mut next, &needle);
+ let mut j = 0;
+ for i in 0..haystack_len {
+ while j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+ if j == needle_len {
+ return (i - needle_len + 1) as i32;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0028.实现strStr.md b/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
index 634d8535..271822dc 100644
--- a/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
+++ b/problems/0028.实现strStr.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
# 28. 实现 strStr()
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-strstr/)
实现 strStr() 函数。
@@ -685,7 +685,21 @@ class Solution {
```
Python3:
-
+```python
+//暴力解法:
+class Solution(object):
+ def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
+ """
+ :type haystack: str
+ :type needle: str
+ :rtype: int
+ """
+ m,n=len(haystack),len(needle)
+ for i in range(m):
+ if haystack[i:i+n]==needle:
+ return i
+ return -1
+```
```python
// 方法一
class Solution:
@@ -1059,5 +1073,231 @@ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
```
+> 前缀表右移
+
+```swift
+func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
+
+ let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
+ guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
+
+ var j = 0
+ var next = [Int].init(repeating: 0, count: p.count)
+ getNext(&next, p)
+
+ for i in 0 ..< s.count {
+
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
+ j = next[j]
+ }
+
+ if s[i] == p[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ if j == p.count {
+ return i - p.count + 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ // 前缀表后移一位,首位用 -1 填充
+ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], _ needle: [Character]) {
+
+ guard needle.count > 1 else { return }
+
+ var j = 0
+ next[0] = j
+
+ for i in 1 ..< needle.count-1 {
+
+ while j > 0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if needle[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ next[i] = j
+ }
+ next.removeLast()
+ next.insert(-1, at: 0)
+ }
+```
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```swift
+
+func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
+
+ let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
+ guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
+
+ var j = 0
+ var next = [Int](repeating: 0, count: needle.count)
+ // KMP
+ getNext(&next, needle: p)
+
+ for i in 0 ..< s.count {
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if s[i] == p[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ if j == p.count {
+ return i - p.count + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ //前缀表
+ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
+
+ var j = 0
+ next[0] = j
+
+ for i in 1 ..< needle.count {
+
+ while j>0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j-1]
+ }
+
+ if needle[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1
+ }
+
+ next[i] = j
+
+ }
+ }
+
+```
+
+PHP:
+
+> 前缀表统一减一
+```php
+function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
+ if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
+ $next= [];
+ $this->getNext($next,$needle);
+
+ $j = -1;
+ for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
+ while($j >= 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j + 1]) {
+ $j = $next[$j];
+ }
+ if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j + 1]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ if ($j == (strlen($needle) - 1) ) {
+ return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+function getNext(&$next, $s){
+ $j = -1;
+ $next[0] = $j;
+ for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
+ while ($j >= 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j + 1]) {
+ $j = $next[$j];
+ }
+ if ($s[$i] == $s[$j + 1]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ $next[$i] = $j;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```php
+function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
+ if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
+ $next= [];
+ $this->getNext($next,$needle);
+
+ $j = 0;
+ for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
+ while($j > 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j]) {
+ $j = $next[$j-1];
+ }
+ if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ if ($j == strlen($needle)) {
+ return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+function getNext(&$next, $s){
+ $j = 0;
+ $next[0] = $j;
+ for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
+ while ($j > 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j]) {
+ $j = $next[$j-1];
+ }
+ if ($s[$i] == $s[$j]) {
+ $j++;
+ }
+ $next[$i] = $j;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Rust:
+
+> 前缀表统一不减一
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn get_next(next: &mut Vec, s: &Vec) {
+ let len = s.len();
+ let mut j = 0;
+ for i in 1..len {
+ while j > 0 && s[i] != s[j] {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ if s[i] == s[j] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+ next[i] = j;
+ }
+ }
+
+ pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
+ let (haystack_len, needle_len) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
+ if haystack_len == 0 { return 0; }
+ if haystack_len < needle_len { return -1;}
+ let (haystack, needle) = (haystack.chars().collect::>(), needle.chars().collect::>());
+ let mut next: Vec = vec![0; haystack_len];
+ Self::get_next(&mut next, &needle);
+ let mut j = 0;
+ for i in 0..haystack_len {
+ while j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j] {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j] {
+ j += 1;
+ }
+ if j == needle_len {
+ return (i - needle_len + 1) as i32;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-----------------------








参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 53. 最大子序和
+# 53. 最大子序和
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/)
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
@@ -187,6 +187,41 @@ const maxSubArray = nums => {
```
+Scala:
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def maxSubArray(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
+ var dp = new Array[Int](nums.length)
+ var result = nums(0)
+ dp(0) = nums(0)
+ for (i <- 1 until nums.length) {
+ dp(i) = math.max(nums(i), dp(i - 1) + nums(i))
+ result = math.max(result, dp(i)) // 更新最大值
+ }
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
+
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i]:以nums[i]结尾的最大和
+ */
+ const dp: number[] = []
+ dp[0] = nums[0];
+ let resMax: number = 0;
+ for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
+ resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
+ }
+ return resMax;
+};
+```
+
-----------------------






参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 70. 爬楼梯
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/)
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
@@ -308,7 +308,58 @@ var climbStairs = function(n) {
};
```
+TypeScript
+
+> 爬2阶
+
+```typescript
+function climbStairs(n: number): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i]: i阶楼梯的方法种数
+ dp[1]: 1;
+ dp[2]: 2;
+ ...
+ dp[i]: dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
+ */
+ const dp: number[] = [];
+ dp[1] = 1;
+ dp[2] = 2;
+ for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+};
+```
+
+> 爬m阶
+
+```typescript
+function climbStairs(n: number): number {
+ /**
+ 一次可以爬m阶
+ dp[i]: i阶楼梯的方法种数
+ dp[1]: 1;
+ dp[2]: 2;
+ dp[3]: dp[2] + dp[1];
+ ...
+ dp[i]: dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + ... + dp[max(i - m, 1)]; 从i-1加到max(i-m, 1)
+ */
+ const m: number = 2; // 本题m为2
+ const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ dp[1] = 1;
+ dp[2] = 2;
+ for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
+ const end: number = Math.max(i - m, 1);
+ for (let j = i - 1; j >= end; j--) {
+ dp[i] += dp[j];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+};
+```
+
### C
+
```c
int climbStairs(int n){
//若n<=2,返回n
@@ -350,6 +401,38 @@ int climbStairs(int n){
}
```
+### Scala
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def climbStairs(n: Int): Int = {
+ if (n <= 2) return n
+ var dp = new Array[Int](n + 1)
+ dp(1) = 1
+ dp(2) = 2
+ for (i <- 3 to n) {
+ dp(i) = dp(i - 1) + dp(i - 2)
+ }
+ dp(n)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+优化空间复杂度:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def climbStairs(n: Int): Int = {
+ if (n <= 2) return n
+ var (a, b) = (1, 2)
+ for (i <- 3 to n) {
+ var tmp = a + b
+ a = b
+ b = tmp
+ }
+ b // 最终返回b
+ }
+}
+```
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md b/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md
index 2286de2d..ec019e57 100644
--- a/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md
+++ b/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
## 70. 爬楼梯
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/)
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
@@ -199,6 +199,28 @@ var climbStairs = function(n) {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function climbStairs(n: number): number {
+ const m: number = 2; // 本题m为2
+ const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ // 遍历背包
+ for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ // 遍历物品
+ for (let j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
+ if (j <= i) {
+ dp[i] += dp[i - j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0072.编辑距离.md b/problems/0072.编辑距离.md
index 3802c228..e40461de 100644
--- a/problems/0072.编辑距离.md
+++ b/problems/0072.编辑距离.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 72. 编辑距离
+# 72. 编辑距离
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/edit-distance/)
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
@@ -327,5 +327,42 @@ const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i][j]: word1前i个字符,word2前j个字符,最少操作数
+ dp[0][0]=0:表示word1前0个字符为'', word2前0个字符为''
+ */
+ const length1: number = word1.length,
+ length2: number = word2.length;
+ const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
+ .map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
+ for (let i = 0; i <= length1; i++) {
+ dp[i][0] = i;
+ }
+ for (let i = 0; i <= length2; i++) {
+ dp[0][i] = i;
+ }
+ for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
+ for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
+ if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = Math.min(
+ dp[i - 1][j],
+ dp[i][j - 1],
+ dp[i - 1][j - 1]
+ ) + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[length1][length2];
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------















参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 115.不同的子序列
+# 115.不同的子序列
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/distinct-subsequences/)
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串 t ,计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。
@@ -267,6 +267,36 @@ const numDistinct = (s, t) => {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function numDistinct(s: string, t: string): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i][j]: s前i个字符,t前j个字符,s子序列中t出现的个数
+ dp[0][0]=1, 表示s前0个字符为'',t前0个字符为''
+ */
+ const sLen: number = s.length,
+ tLen: number = t.length;
+ const dp: number[][] = new Array(sLen + 1).fill(0)
+ .map(_ => new Array(tLen + 1).fill(0));
+ for (let m = 0; m < sLen; m++) {
+ dp[m][0] = 1;
+ }
+ for (let i = 1; i <= sLen; i++) {
+ for (let j = 1; j <= tLen; j++) {
+ if (s[i - 1] === t[j - 1]) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[sLen][tLen];
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针.md b/problems/0116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针.md
index 2c443de5..303108be 100644
--- a/problems/0116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针.md
+++ b/problems/0116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
# 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
@@ -287,6 +287,79 @@ const connect = root => {
};
```
+## TypeScript
+
+(注:命名空间‘Node’与typescript中内置类型冲突,这里改成了‘NodePro’)
+
+> 递归法:
+
+```typescript
+class NodePro {
+ val: number
+ left: NodePro | null
+ right: NodePro | null
+ next: NodePro | null
+ constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
+ this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
+ this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
+ this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
+ this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
+ }
+}
+
+function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
+ if (root === null) return null;
+ root.next = null;
+ recur(root);
+ return root;
+};
+function recur(node: NodePro): void {
+ if (node.left === null || node.right === null) return;
+ node.left.next = node.right;
+ node.right.next = node.next && node.next.left;
+ recur(node.left);
+ recur(node.right);
+}
+```
+
+> 迭代法:
+
+```typescript
+class NodePro {
+ val: number
+ left: NodePro | null
+ right: NodePro | null
+ next: NodePro | null
+ constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
+ this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
+ this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
+ this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
+ this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
+ }
+}
+
+function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
+ if (root === null) return null;
+ const queue: NodePro[] = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ while (queue.length > 0) {
+ for (let i = 0, length = queue.length; i < length; i++) {
+ const curNode: NodePro = queue.shift()!;
+ if (i === length - 1) {
+ curNode.next = null;
+ } else {
+ curNode.next = queue[0];
+ }
+ if (curNode.left !== null) queue.push(curNode.left);
+ if (curNode.right !== null) queue.push(curNode.right);
+ }
+ }
+ return root;
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md b/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md
index e7c0ac65..868c0e3e 100644
--- a/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md
+++ b/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
+# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
@@ -311,7 +311,36 @@ class Solution:
```
Go:
+> 贪心法:
+```Go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ low := math.MaxInt32
+ rlt := 0
+ for i := range prices{
+ low = min(low, prices[i])
+ rlt = max(rlt, prices[i]-low)
+ }
+ return rlt
+}
+func min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b{
+ return a
+ }
+
+ return b
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b{
+ return a
+ }
+
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+> 动态规划:版本一
```Go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
length:=len(prices)
@@ -338,6 +367,29 @@ func max(a,b int)int {
}
```
+> 动态规划:版本二
+```Go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ dp := [2][2]int{}
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
+ dp[0][1] = 0
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++{
+ dp[i%2][0] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][0], -prices[i])
+ dp[i%2][1] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][1], dp[(i-1)%2][0]+prices[i])
+ }
+
+ return dp[(len(prices)-1)%2][1]
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b{
+ return a
+ }
+
+ return b
+}
+```
+
JavaScript:
> 动态规划
@@ -374,6 +426,46 @@ var maxProfit = function(prices) {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+> 贪心法
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ if (prices.length === 0) return 0;
+ let buy: number = prices[0];
+ let profitMax: number = 0;
+ for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
+ profitMax = Math.max(profitMax, prices[i] - buy);
+ buy = Math.min(prices[i], buy);
+ }
+ return profitMax;
+};
+```
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i][0]: 第i天持有股票的最大现金
+ dp[i][1]: 第i天不持有股票的最大现金
+ */
+ const length = prices.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ const dp: number[][] = [];
+ dp[0] = [-prices[0], 0];
+ for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ dp[i] = [];
+ dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], -prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]);
+ }
+ return dp[length - 1][1];
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------

参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
+# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]);
}
- return dp[prices.length -1][0];
+ return dp[prices.length -1][1];
};
// 方法二:动态规划(滚动数组)
@@ -295,6 +295,42 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
}
```
+TypeScript:
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i][0]: 第i天持有股票
+ dp[i][1]: 第i天不持有股票
+ */
+ const length: number = prices.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0).map(_ => []);
+ dp[0] = [-prices[0], 0];
+ for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[length - 1][1];
+};
+```
+
+> 贪心法
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ let resProfit: number = 0;
+ for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
+ if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
+ resProfit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ return resProfit;
+};
+```
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md b/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md
index fc81c3e9..947e6947 100644
--- a/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md
+++ b/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
+# 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/)
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
@@ -148,8 +148,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(n × 5)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n × 5)
当然,大家可以看到力扣官方题解里的一种优化空间写法,我这里给出对应的C++版本:
@@ -173,8 +173,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
大家会发现dp[2]利用的是当天的dp[1]。 但结果也是对的。
@@ -352,6 +352,36 @@ const maxProfit = prices => {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+> 版本一
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i][0]: 无操作;
+ dp[i][1]: 第一次买入;
+ dp[i][2]: 第一次卖出;
+ dp[i][3]: 第二次买入;
+ dp[i][4]: 第二次卖出;
+ */
+ const length: number = prices.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0)
+ .map(_ => new Array(5).fill(0));
+ dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
+ for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
+ dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
+ dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
+ dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return Math.max(dp[length - 1][2], dp[length - 1][4]);
+};
+```
+
Go:
> 版本一:
diff --git a/problems/0127.单词接龙.md b/problems/0127.单词接龙.md
index 407596c0..f1c6f182 100644
--- a/problems/0127.单词接龙.md
+++ b/problems/0127.单词接龙.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
# 127. 单词接龙
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-ladder/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder/)
字典 wordList 中从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
* 序列中第一个单词是 beginWord 。
@@ -134,7 +134,29 @@ public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList)
```
## Python
-
+```
+class Solution:
+ def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
+ wordSet = set(wordList)
+ if len(wordSet)== 0 or endWord not in wordSet:
+ return 0
+ mapping = {beginWord:1}
+ queue = deque([beginWord])
+ while queue:
+ word = queue.popleft()
+ path = mapping[word]
+ for i in range(len(word)):
+ word_list = list(word)
+ for j in range(26):
+ word_list[i] = chr(ord('a')+j)
+ newWord = "".join(word_list)
+ if newWord == endWord:
+ return path+1
+ if newWord in wordSet and newWord not in mapping:
+ mapping[newWord] = path+1
+ queue.append(newWord)
+ return 0
+```
## Go
## JavaScript
diff --git a/problems/0129.求根到叶子节点数字之和.md b/problems/0129.求根到叶子节点数字之和.md
index b271ca7d..92a72fe3 100644
--- a/problems/0129.求根到叶子节点数字之和.md
+++ b/problems/0129.求根到叶子节点数字之和.md
@@ -3,9 +3,12 @@

参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+
+
+
# 129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
# 思路
@@ -245,6 +248,29 @@ class Solution:
```
Go:
+```go
+func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
+ sum = 0
+ travel(root, root.Val)
+ return sum
+}
+
+func travel(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int) {
+ if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
+ sum += tmpSum
+ } else {
+ if root.Left != nil {
+ travel(root.Left, tmpSum*10+root.Left.Val)
+ }
+ if root.Right != nil {
+ travel(root.Right, tmpSum*10+root.Right.Val)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
JavaScript:
```javascript
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
@@ -289,7 +315,40 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
+ if (root === null) return 0;
+ let resTotal: number = 0;
+ const route: number[] = [];
+ route.push(root.val);
+ recur(root, route);
+ return resTotal;
+ function recur(node: TreeNode, route: number[]): void {
+ if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
+ resTotal += listToSum(route);
+ return;
+ }
+ if (node.left !== null) {
+ route.push(node.left.val);
+ recur(node.left, route);
+ route.pop();
+ };
+ if (node.right !== null) {
+ route.push(node.right.val);
+ recur(node.right, route);
+ route.pop();
+ };
+ }
+ function listToSum(nums: number[]): number {
+ return Number(nums.join(''));
+ }
+};
+```
+
C:
+
```c
//sum记录总和
int sum;
diff --git a/problems/0131.分割回文串.md b/problems/0131.分割回文串.md
index f50f1c1d..37132503 100644
--- a/problems/0131.分割回文串.md
+++ b/problems/0131.分割回文串.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
# 131.分割回文串
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/)
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
@@ -206,6 +206,65 @@ public:
return result;
}
};
+```
+# 优化
+
+上面的代码还存在一定的优化空间, 在于如何更高效的计算一个子字符串是否是回文字串。上述代码```isPalindrome```函数运用双指针的方法来判定对于一个字符串```s```, 给定起始下标和终止下标, 截取出的子字符串是否是回文字串。但是其中有一定的重复计算存在:
+
+例如给定字符串```"abcde"```, 在已知```"bcd"```不是回文字串时, 不再需要去双指针操作```"abcde"```而可以直接判定它一定不是回文字串。
+
+具体来说, 给定一个字符串`s`, 长度为```n```, 它成为回文字串的充分必要条件是```s[0] == s[n-1]```且```s[1:n-1]```是回文字串。
+
+大家如果熟悉动态规划这种算法的话, 我们可以高效地事先一次性计算出, 针对一个字符串```s```, 它的任何子串是否是回文字串, 然后在我们的回溯函数中直接查询即可, 省去了双指针移动判定这一步骤.
+
+具体参考代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+private:
+ vector> result;
+ vector path; // 放已经回文的子串
+ vector> isPalindrome; // 放事先计算好的是否回文子串的结果
+ void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
+ // 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
+ if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
+ result.push_back(path);
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
+ if (isPalindrome[startIndex][i]) { // 是回文子串
+ // 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
+ string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
+ path.push_back(str);
+ } else { // 不是回文,跳过
+ continue;
+ }
+ backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
+ path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在的子串
+ }
+ }
+ void computePalindrome(const string& s) {
+ // isPalindrome[i][j] 代表 s[i:j](双边包括)是否是回文字串
+ isPalindrome.resize(s.size(), vector(s.size(), false)); // 根据字符串s, 刷新布尔矩阵的大小
+ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ // 需要倒序计算, 保证在i行时, i+1行已经计算好了
+ for (int j = i; j < s.size(); j++) {
+ if (j == i) {isPalindrome[i][j] = true;}
+ else if (j - i == 1) {isPalindrome[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j]);}
+ else {isPalindrome[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j] && isPalindrome[i+1][j-1]);}
+ }
+ }
+ }
+public:
+ vector> partition(string s) {
+ result.clear();
+ path.clear();
+ computePalindrome(s);
+ backtracking(s, 0);
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
```
# 总结
@@ -442,7 +501,7 @@ var partition = function(s) {
}
for(let j = i; j < len; j++) {
if(!isPalindrome(s, i, j)) continue;
- path.push(s.substr(i, j - i + 1));
+ path.push(s.slice(i, j + 1));
backtracking(j + 1);
path.pop();
}
@@ -450,6 +509,43 @@ var partition = function(s) {
};
```
+## TypeScript
+
+```typescript
+function partition(s: string): string[][] {
+ const res: string[][] = []
+ const path: string[] = []
+ const isHuiwen = (
+ str: string,
+ startIndex: number,
+ endIndex: number
+ ): boolean => {
+ for (; startIndex < endIndex; startIndex++, endIndex--) {
+ if (str[startIndex] !== str[endIndex]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+ const rec = (str: string, index: number): void => {
+ if (index >= str.length) {
+ res.push([...path])
+ return
+ }
+ for (let i = index; i < str.length; i++) {
+ if (!isHuiwen(str, index, i)) {
+ continue
+ }
+ path.push(str.substring(index, i + 1))
+ rec(str, i + 1)
+ path.pop()
+ }
+ }
+ rec(s, 0)
+ return res
+};
+```
+
## C
```c
@@ -589,7 +685,8 @@ func partition(_ s: String) -> [[String]] {
## Rust
-```rust
+**回溯+函数判断回文串**
+```Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn partition(s: String) -> Vec> {
let mut ret = vec![];
@@ -639,5 +736,84 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+**回溯+动态规划预处理判断回文串**
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn backtracking(is_palindrome: &Vec>, result: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec, s: &Vec, start_index: usize) {
+ let len = s.len();
+ if start_index >= len {
+ result.push(path.to_vec());
+ return;
+ }
+ for i in start_index..len {
+ if is_palindrome[start_index][i] { path.push(s[start_index..=i].iter().collect::()); } else { continue; }
+ Self::backtracking(is_palindrome, result, path, s, i + 1);
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ }
+
+ pub fn partition(s: String) -> Vec> {
+ let mut result: Vec> = Vec::new();
+ let mut path: Vec = Vec::new();
+ let s = s.chars().collect::>();
+ let len: usize = s.len();
+ // 使用动态规划预先打表
+ // 当且仅当其为空串(i>j),或其长度为1(i=j),或者首尾字符相同且(s[i+1..j−1])时为回文串
+ let mut is_palindrome = vec![vec![true; len]; len];
+ for i in (0..len).rev() {
+ for j in (i + 1)..len {
+ is_palindrome[i][j] = s[i] == s[j] && is_palindrome[i + 1][j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ Self::backtracking(&is_palindrome, &mut result, &mut path, &s, 0);
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+## Scala
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+
+ import scala.collection.mutable
+
+ def partition(s: String): List[List[String]] = {
+ var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[String]]()
+ var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
+
+ // 判断字符串是否回文
+ def isPalindrome(start: Int, end: Int): Boolean = {
+ var (left, right) = (start, end)
+ while (left < right) {
+ if (s(left) != s(right)) return false
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ }
+ true
+ }
+
+ // 回溯算法
+ def backtracking(startIndex: Int): Unit = {
+ if (startIndex >= s.size) {
+ result.append(path.toList)
+ return
+ }
+ // 添加循环守卫,如果当前分割是回文子串则进入回溯
+ for (i <- startIndex until s.size if isPalindrome(startIndex, i)) {
+ path.append(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1))
+ backtracking(i + 1)
+ path = path.take(path.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+
+ backtracking(0)
+ result.toList
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
-----------------------






 -
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -721,10 +695,164 @@ func reverseWord(_ s: inout [Character]) {
}
```
+Scala:
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def reverseWords(s: String): String = {
+ var sb = removeSpace(s) // 移除多余的空格
+ reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length - 1) // 翻转字符串
+ reverseEachWord(sb)
+ sb.mkString
+ }
+
+ // 移除多余的空格
+ def removeSpace(s: String): Array[Char] = {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = s.length - 1
+ // 移除字符串前面的空格
+ while (start < s.length && s(start) == ' ') start += 1
+ // 移除字符串后面的空格
+ while (end >= 0 && s(end) == ' ') end -= 1
+ var sb = "" // String
+ // 当start小于等于end的时候,执行添加操作
+ while (start <= end) {
+ var c = s(start)
+ // 当前字符不等于空,sb的最后一个字符不等于空的时候添加到sb
+ if (c != ' ' || sb(sb.length - 1) != ' ') {
+ sb ++= c.toString
+ }
+ start += 1 // 指针向右移动
+ }
+ sb.toArray
+ }
+
+ // 翻转字符串
+ def reverseString(s: Array[Char], start: Int, end: Int): Unit = {
+ var (left, right) = (start, end)
+ while (left < right) {
+ var tmp = s(left)
+ s(left) = s(right)
+ s(right) = tmp
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 翻转每个单词
+ def reverseEachWord(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ // 向后迭代寻找每个单词的坐标
+ while (j < s.length && s(j) != ' ') j += 1
+ reverseString(s, i, j - 1) // 翻转每个单词
+ i = j + 1 // i往后更新
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+PHP:
+```php
+function reverseWords($s) {
+ $this->removeExtraSpaces($s);
+ $this->reverseString($s, 0, strlen($s)-1);
+ // 将每个单词反转
+ $start = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i <= strlen($s); $i++) {
+ // 到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
+ if ($i == strlen($s) || $s[$i] == ' ') {
+ // 翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
+ $this->reverseString($s, $start, $i-1);
+ // +1: 单词与单词直接有个空格
+ $start = $i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return $s;
+}
+// 移除多余空格
+function removeExtraSpaces(&$s){
+ $slow = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
+ if ($s[$i] != ' ') {
+ if ($slow != 0){
+ $s[$slow++] = ' ';
+ }
+ while ($i < strlen($s) && $s[$i] != ' ') {
+ $s[$slow++] = $s[$i++];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // 移动覆盖处理,丢弃多余的脏数据。
+ $s = substr($s,0,$slow);
+ return ;
+}
+// 翻转字符串
+function reverseString(&$s, $start, $end) {
+ for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
+ $tmp = $s[$i];
+ $s[$i] = $s[$j];
+ $s[$j] = $tmp;
+ }
+ return ;
+}
+```
+Rust:
+
+```Rust
+// 根据C++版本二思路进行实现
+// 函数名根据Rust编译器建议由驼峰命名法改为蛇形命名法
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn reverse(s: &mut Vec, mut begin: usize, mut end: usize){
+ while begin < end {
+ let temp = s[begin];
+ s[begin] = s[end];
+ s[end] = temp;
+ begin += 1;
+ end -= 1;
+ }
+}
+pub fn remove_extra_spaces(s: &mut Vec) {
+ let mut slow: usize = 0;
+ let len = s.len();
+ // 注意这里不能用for循环,不然在里面那个while循环中对i的递增会失效
+ let mut i: usize = 0;
+ while i < len {
+ if !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ if slow != 0 {
+ s[slow] = ' ';
+ slow += 1;
+ }
+ while i < len && !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ s[slow] = s[i];
+ slow += 1;
+ i += 1;
+ }
+ }
+ i += 1;
+ }
+ s.resize(slow, ' ');
+ }
+ pub fn reverse_words(s: String) -> String {
+ let mut s = s.chars().collect::>();
+ Self::remove_extra_spaces(&mut s);
+ let len = s.len();
+ Self::reverse(&mut s, 0, len - 1);
+ let mut start = 0;
+ for i in 0..=len {
+ if i == len || s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ Self::reverse(&mut s, start, i - 1);
+ start = i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ s.iter().collect::()
+ }
+}
+```
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
index 61c558a1..8319fcba 100644
--- a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
+++ b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
-
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -721,10 +695,164 @@ func reverseWord(_ s: inout [Character]) {
}
```
+Scala:
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def reverseWords(s: String): String = {
+ var sb = removeSpace(s) // 移除多余的空格
+ reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length - 1) // 翻转字符串
+ reverseEachWord(sb)
+ sb.mkString
+ }
+
+ // 移除多余的空格
+ def removeSpace(s: String): Array[Char] = {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = s.length - 1
+ // 移除字符串前面的空格
+ while (start < s.length && s(start) == ' ') start += 1
+ // 移除字符串后面的空格
+ while (end >= 0 && s(end) == ' ') end -= 1
+ var sb = "" // String
+ // 当start小于等于end的时候,执行添加操作
+ while (start <= end) {
+ var c = s(start)
+ // 当前字符不等于空,sb的最后一个字符不等于空的时候添加到sb
+ if (c != ' ' || sb(sb.length - 1) != ' ') {
+ sb ++= c.toString
+ }
+ start += 1 // 指针向右移动
+ }
+ sb.toArray
+ }
+
+ // 翻转字符串
+ def reverseString(s: Array[Char], start: Int, end: Int): Unit = {
+ var (left, right) = (start, end)
+ while (left < right) {
+ var tmp = s(left)
+ s(left) = s(right)
+ s(right) = tmp
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 翻转每个单词
+ def reverseEachWord(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ // 向后迭代寻找每个单词的坐标
+ while (j < s.length && s(j) != ' ') j += 1
+ reverseString(s, i, j - 1) // 翻转每个单词
+ i = j + 1 // i往后更新
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+PHP:
+```php
+function reverseWords($s) {
+ $this->removeExtraSpaces($s);
+ $this->reverseString($s, 0, strlen($s)-1);
+ // 将每个单词反转
+ $start = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i <= strlen($s); $i++) {
+ // 到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
+ if ($i == strlen($s) || $s[$i] == ' ') {
+ // 翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
+ $this->reverseString($s, $start, $i-1);
+ // +1: 单词与单词直接有个空格
+ $start = $i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return $s;
+}
+// 移除多余空格
+function removeExtraSpaces(&$s){
+ $slow = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
+ if ($s[$i] != ' ') {
+ if ($slow != 0){
+ $s[$slow++] = ' ';
+ }
+ while ($i < strlen($s) && $s[$i] != ' ') {
+ $s[$slow++] = $s[$i++];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // 移动覆盖处理,丢弃多余的脏数据。
+ $s = substr($s,0,$slow);
+ return ;
+}
+// 翻转字符串
+function reverseString(&$s, $start, $end) {
+ for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
+ $tmp = $s[$i];
+ $s[$i] = $s[$j];
+ $s[$j] = $tmp;
+ }
+ return ;
+}
+```
+Rust:
+
+```Rust
+// 根据C++版本二思路进行实现
+// 函数名根据Rust编译器建议由驼峰命名法改为蛇形命名法
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn reverse(s: &mut Vec, mut begin: usize, mut end: usize){
+ while begin < end {
+ let temp = s[begin];
+ s[begin] = s[end];
+ s[end] = temp;
+ begin += 1;
+ end -= 1;
+ }
+}
+pub fn remove_extra_spaces(s: &mut Vec) {
+ let mut slow: usize = 0;
+ let len = s.len();
+ // 注意这里不能用for循环,不然在里面那个while循环中对i的递增会失效
+ let mut i: usize = 0;
+ while i < len {
+ if !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ if slow != 0 {
+ s[slow] = ' ';
+ slow += 1;
+ }
+ while i < len && !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ s[slow] = s[i];
+ slow += 1;
+ i += 1;
+ }
+ }
+ i += 1;
+ }
+ s.resize(slow, ' ');
+ }
+ pub fn reverse_words(s: String) -> String {
+ let mut s = s.chars().collect::>();
+ Self::remove_extra_spaces(&mut s);
+ let len = s.len();
+ Self::reverse(&mut s, 0, len - 1);
+ let mut start = 0;
+ for i in 0..=len {
+ if i == len || s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
+ Self::reverse(&mut s, start, i - 1);
+ start = i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ s.iter().collect::()
+ }
+}
+```
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
index 61c558a1..8319fcba 100644
--- a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
+++ b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV
+# 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/)
给定一个整数数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
@@ -409,5 +409,27 @@ var maxProfit = function(k, prices) {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(k: number, prices: number[]): number {
+ const length: number = prices.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0)
+ .map(_ => new Array(k * 2 + 1).fill(0));
+ for (let i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
+ dp[0][i * 2 - 1] = -prices[0];
+ }
+ for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ for (let j = 1; j < 2 * k + 1; j++) {
+ dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1] + Math.pow(-1, j) * prices[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[length - 1][2 * k];
+};
+```
+
+
+
-----------------------

参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 198.打家劫舍
+# 198.打家劫舍
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber/)
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
@@ -189,6 +189,29 @@ const rob = nums => {
};
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function rob(nums: number[]): number {
+ /**
+ dp[i]: 前i个房屋能偷到的最大金额
+ dp[0]: nums[0];
+ dp[1]: max(nums[0], nums[1]);
+ ...
+ dp[i]: max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+nums[i]);
+ */
+ const length: number = nums.length;
+ if (length === 1) return nums[0];
+ const dp: number[] = [];
+ dp[0] = nums[0];
+ dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
+ for (let i = 2; i < length; i++) {
+ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[length - 1];
+};
+```
+
diff --git a/problems/0200.岛屿数量.md b/problems/0200.岛屿数量.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b88e5fd2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/problems/0200.岛屿数量.md
@@ -0,0 +1,249 @@
+
+# 200. 岛屿数量
+
+[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-islands/)
+
+给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
+
+岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
+
+此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+* m == grid.length
+* n == grid[i].length
+* 1 <= m, n <= 300
+* grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
+
+## 思路
+
+注意题目中每座岛屿只能由**水平方向和/或竖直方向上**相邻的陆地连接形成。
+
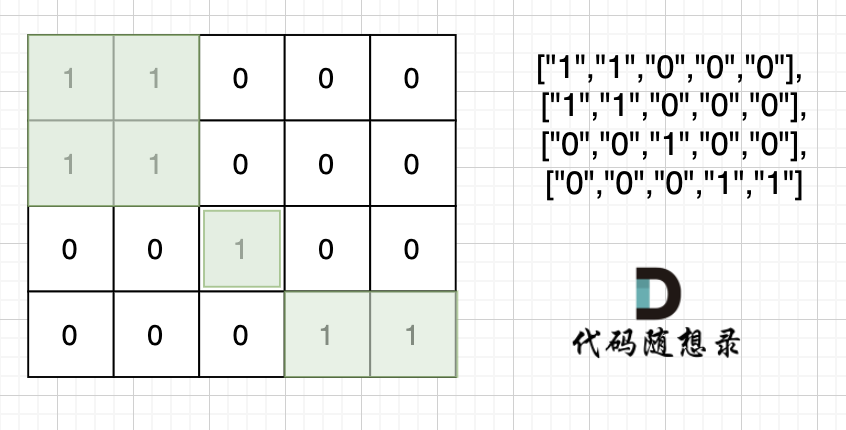
+也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
+
+
+
+这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
+
+本题思路,是用遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
+
+在遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
+
+那么如果把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
+
+### 深度优先搜索
+
+以下代码使用dfs实现,如果对dfs不太了解的话,建议先看这篇题解:[797.所有可能的路径](https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-paths-from-source-to-target/solution/by-carlsun-2-66pf/),
+
+C++代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 版本一
+class Solution {
+private:
+ int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
+ void dfs(vector>& grid, vector>& visited, int x, int y) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
+ int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
+ if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
+ if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
+
+ visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
+ dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+public:
+ int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
+ int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
+ vector> visited = vector>(n, vector(m, false));
+
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
+ if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
+ visited[i][j] = true;
+ result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
+ dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+很多录友可能有疑惑,为什么 以上代码中的dfs函数,没有终止条件呢? 感觉递归没有终止很危险。
+
+其实终止条件 就写在了,调用dfs的地方,如果遇到不合法的方向,直接不会去调用dfs。
+
+当然,也可以这么写:
+
+```CPP
+// 版本二
+class Solution {
+private:
+ int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
+ void dfs(vector>& grid, vector>& visited, int x, int y) {
+ if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == '0') return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
+ visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
+ int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
+ if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
+ dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
+ }
+ }
+public:
+ int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
+ int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
+ vector> visited = vector>(n, vector(m, false));
+
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
+ if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
+ result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
+ dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+这里大家应该能看出区别了,无疑就是版本一中 调用dfs 的条件,放在了 版本二 的 终止条件位置上。
+
+**版本一的写法**是 :下一个节点是否能合法已经判断完了,只要调用dfs就是可以合法的节点。
+
+**版本二的写法**是:不管节点是否合法,上来就dfs,然后在终止条件的地方进行判断,不合法再return。
+
+**理论上来讲,版本一的效率更高一些**,因为避免了 没有意义的递归调用,在调用dfs之前,就做合法性判断。 但从写法来说,可能版本二 更利于理解一些。(不过其实都差不太多)
+
+很多同学看了同一道题目,都是dfs,写法却不一样,有时候有终止条件,有时候连终止条件都没有,其实这就是根本原因,两种写法而已。
+
+
+### 广度优先搜索
+
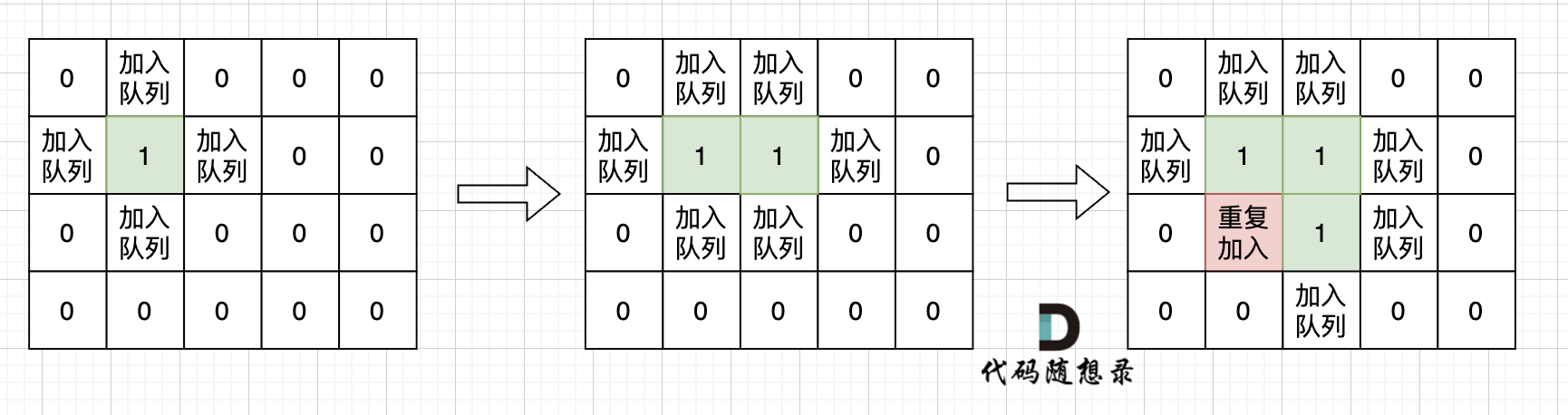
+不少同学用广搜做这道题目的时候,超时了。 这里有一个广搜中很重要的细节:
+
+根本原因是**只要 加入队列就代表 走过,就需要标记,而不是从队列拿出来的时候再去标记走过**。
+
+很多同学可能感觉这有区别吗?
+
+如果从队列拿出节点,再去标记这个节点走过,就会发生下图所示的结果,会导致很多节点重复加入队列。
+
+
+
+超时写法 (从队列中取出节点再标记)
+
+```CPP
+int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
+void bfs(vector>& grid, vector>& visited, int x, int y) {
+ queue> que;
+ que.push({x, y});
+ while(!que.empty()) {
+ pair cur = que.front(); que.pop();
+ int curx = cur.first;
+ int cury = cur.second;
+ visited[curx][cury] = true; // 从队列中取出在标记走过
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
+ int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
+ if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
+ if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
+ que.push({nextx, nexty});
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+}
+```
+
+加入队列 就代表走过,立刻标记,正确写法:
+
+```CPP
+int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
+void bfs(vector>& grid, vector>& visited, int x, int y) {
+ queue> que;
+ que.push({x, y});
+ visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
+ while(!que.empty()) {
+ pair cur = que.front(); que.pop();
+ int curx = cur.first;
+ int cury = cur.second;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
+ int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
+ if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
+ if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
+ que.push({nextx, nexty});
+ visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+}
+```
+
+以上两个版本其实,其实只有细微区别,就是 `visited[x][y] = true;` 放在的地方,着去取决于我们对 代码中队列的定义,队列中的节点就表示已经走过的节点。 **所以只要加入队列,理解标记该节点走过**。
+
+本题完整广搜代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+private:
+int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
+void bfs(vector>& grid, vector>& visited, int x, int y) {
+ queue> que;
+ que.push({x, y});
+ visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
+ while(!que.empty()) {
+ pair cur = que.front(); que.pop();
+ int curx = cur.first;
+ int cury = cur.second;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
+ int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
+ if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
+ if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
+ que.push({nextx, nexty});
+ visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+public:
+ int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
+ int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
+ vector> visited = vector>(n, vector(m, false));
+
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
+ if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
+ result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
+ bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
+```
+
+## 总结
+
+其实本题是 dfs,bfs 模板题,但正是因为是模板题,所以大家或者一些题解把重要的细节都很忽略了,我这里把大家没注意的但以后会踩的坑 都给列出来了。
+
+
+
+
+
+## 其他语言版本
diff --git a/problems/0202.快乐数.md b/problems/0202.快乐数.md
index f0a46a40..d14ee770 100644
--- a/problems/0202.快乐数.md
+++ b/problems/0202.快乐数.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
# 第202题. 快乐数
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/)
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
@@ -315,5 +315,115 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+Rust:
+```Rust
+use std::collections::HashSet;
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn get_sum(mut n: i32) -> i32 {
+ let mut sum = 0;
+ while n > 0 {
+ sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
+ n /= 10;
+ }
+ sum
+ }
+
+ pub fn is_happy(n: i32) -> bool {
+ let mut n = n;
+ let mut set = HashSet::new();
+ loop {
+ let sum = Self::get_sum(n);
+ if sum == 1 {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if set.contains(&sum) {
+ return false;
+ } else { set.insert(sum); }
+ n = sum;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+C:
+```C
+typedef struct HashNodeTag {
+ int key; /* num */
+ struct HashNodeTag *next;
+}HashNode;
+
+/* Calcualte the hash key */
+static inline int hash(int key, int size) {
+ int index = key % size;
+ return (index > 0) ? (index) : (-index);
+}
+
+/* Calculate the sum of the squares of its digits*/
+static inline int calcSquareSum(int num) {
+ unsigned int sum = 0;
+ while(num > 0) {
+ sum += (num % 10) * (num % 10);
+ num = num/10;
+ }
+ return sum;
+}
+
+
+Scala:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ // 引入mutable
+ import scala.collection.mutable
+ def isHappy(n: Int): Boolean = {
+ // 存放每次计算后的结果
+ val set: mutable.HashSet[Int] = new mutable.HashSet[Int]()
+ var tmp = n // 因为形参是不可变量,所以需要找到一个临时变量
+ // 开始进入循环
+ while (true) {
+ val sum = getSum(tmp) // 获取这个数每个值的平方和
+ if (sum == 1) return true // 如果最终等于 1,则返回true
+ // 如果set里面已经有这个值了,说明进入无限循环,可以返回false,否则添加这个值到set
+ if (set.contains(sum)) return false
+ else set.add(sum)
+ tmp = sum
+ }
+ // 最终需要返回值,直接返回个false
+ false
+ }
+
+ def getSum(n: Int): Int = {
+ var sum = 0
+ var tmp = n
+ while (tmp != 0) {
+ sum += (tmp % 10) * (tmp % 10)
+ tmp = tmp / 10
+ }
+ sum
+ }
+```
+
+
+C#:
+```csharp
+public class Solution {
+ private int getSum(int n) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ //每位数的换算
+ while (n > 0) {
+ sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
+ n /= 10;
+ }
+ return sum;
+ }
+ public bool IsHappy(int n) {
+ HashSet set = new HashSet();
+ while(n != 1 && !set.Contains(n)) { //判断避免循环
+ set.Add(n);
+ n = getSum(n);
+ }
+ return n == 1;
+ }
+}
+```
-----------------------


参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 209.长度最小的子数组
+# 209.长度最小的子数组
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/)
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 s ,找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的 连续 子数组,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0。
@@ -17,10 +17,13 @@
输出:2
解释:子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的子数组。
+# 思路
+
+为了易于大家理解,我特意录制了B站视频[拿下滑动窗口! | LeetCode 209 长度最小的子数组](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tZ4y1q7XE),结合视频看本题解,事半功倍!
## 暴力解法
-这道题目暴力解法当然是 两个for循环,然后不断的寻找符合条件的子序列,时间复杂度很明显是O(n^2)。
+这道题目暴力解法当然是 两个for循环,然后不断的寻找符合条件的子序列,时间复杂度很明显是O(n^2)。
代码如下:
@@ -47,8 +50,10 @@ public:
}
};
```
-时间复杂度:O(n^2)
-空间复杂度:O(1)
+* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
+
+后面力扣更新了数据,暴力解法已经超时了。
## 滑动窗口
@@ -56,6 +61,20 @@ public:
所谓滑动窗口,**就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们要想的结果**。
+在暴力解法中,是一个for循环滑动窗口的起始位置,一个for循环为滑动窗口的终止位置,用两个for循环 完成了一个不断搜索区间的过程。
+
+那么滑动窗口如何用一个for循环来完成这个操作呢。
+
+首先要思考 如果用一个for循环,那么应该表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,还是终止位置。
+
+如果只用一个for循环来表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,那么如何遍历剩下的终止位置?
+
+此时难免再次陷入 暴力解法的怪圈。
+
+所以 只用一个for循环,那么这个循环的索引,一定是表示 滑动窗口的终止位置。
+
+那么问题来了, 滑动窗口的起始位置如何移动呢?
+
这里还是以题目中的示例来举例,s=7, 数组是 2,3,1,2,4,3,来看一下查找的过程:

@@ -74,7 +93,7 @@ public:
窗口的起始位置如何移动:如果当前窗口的值大于s了,窗口就要向前移动了(也就是该缩小了)。
-窗口的结束位置如何移动:窗口的结束位置就是遍历数组的指针,窗口的起始位置设置为数组的起始位置就可以了。
+窗口的结束位置如何移动:窗口的结束位置就是遍历数组的指针,也就是for循环里的索引。
解题的关键在于 窗口的起始位置如何移动,如图所示:
@@ -107,17 +126,17 @@ public:
};
```
-时间复杂度:O(n)
-空间复杂度:O(1)
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
**一些录友会疑惑为什么时间复杂度是O(n)**。
-不要以为for里放一个while就以为是O(n^2)啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是 2 × n 也就是O(n)。
+不要以为for里放一个while就以为是O(n^2)啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是 2 × n 也就是O(n)。
## 相关题目推荐
-* [904.水果成篮](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fruit-into-baskets/)
-* [76.最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
+* [904.水果成篮](https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/)
+* [76.最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
@@ -162,8 +181,27 @@ class Solution:
index += 1
return 0 if res==float("inf") else res
```
-
-
+```python3
+#滑动窗口
+class Solution:
+ def minSubArrayLen(self, target: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ if nums is None or len(nums)==0:
+ return 0
+ lenf=len(nums)+1
+ total=0
+ i=j=0
+ while (j=target):
+ lenf=min(lenf,j-i)
+ total=total-nums[i]
+ i+=1
+ if lenf==len(nums)+1:
+ return 0
+ else:
+ return lenf
+```
Go:
```go
func minSubArrayLen(target int, nums []int) int {
@@ -198,7 +236,7 @@ JavaScript:
var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) {
// 长度计算一次
const len = nums.length;
- let l = r = sum = 0,
+ let l = r = sum = 0,
res = len + 1; // 子数组最大不会超过自身
while(r < len) {
sum += nums[r++];
@@ -260,12 +298,12 @@ Rust:
```rust
impl Solution {
- pub fn min_sub_array_len(target: i32, nums: Vec) -> i32 {
+ pub fn min_sub_array_len(target: i32, nums: Vec) -> i32 {
let (mut result, mut subLength): (i32, i32) = (i32::MAX, 0);
let (mut sum, mut i) = (0, 0);
-
+
for (pos, val) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
- sum += val;
+ sum += val;
while sum >= target {
subLength = (pos - i + 1) as i32;
if result > subLength {
@@ -364,7 +402,7 @@ int minSubArrayLen(int target, int* nums, int numsSize){
int minLength = INT_MAX;
int sum = 0;
- int left = 0, right = 0;
+ int left = 0, right = 0;
//右边界向右扩展
for(; right < numsSize; ++right) {
sum += nums[right];
@@ -380,5 +418,127 @@ int minSubArrayLen(int target, int* nums, int numsSize){
}
```
+Kotlin:
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = 0
+ var ret = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var count = 0
+ while (end < nums.size) {
+ count += nums[end]
+ while (count >= target) {
+ ret = if (ret > (end - start + 1)) end - start + 1 else ret
+ count -= nums[start++]
+ }
+ end++
+ }
+ return if (ret == Int.MAX_VALUE) 0 else ret
+ }
+}
+```
+滑动窗口
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
+ // 左边界 和 右边界
+ var left: Int = 0
+ var right: Int = 0
+ // sum 用来记录和
+ var sum: Int = 0
+ // result记录一个固定值,便于判断是否存在的这样的数组
+ var result: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ // subLenth记录长度
+ var subLength = Int.MAX_VALUE
+
+
+ while (right < nums.size) {
+ // 从数组首元素开始逐次求和
+ sum += nums[right++]
+ // 判断
+ while (sum >= target) {
+ var temp = right - left
+ // 每次和上一次比较求出最小数组长度
+ subLength = if (subLength > temp) temp else subLength
+ // sum减少,左边界右移
+ sum -= nums[left++]
+ }
+ }
+ // 如果subLength为初始值,则说明长度为0,否则返回subLength
+ return if(subLength == result) 0 else subLength
+ }
+}
+```
+Scala:
+
+滑动窗口:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
+ var result = Int.MaxValue // 返回结果,默认最大值
+ var left = 0 // 慢指针,当sum>=target,向右移动
+ var sum = 0 // 窗口值的总和
+ for (right <- 0 until nums.length) {
+ sum += nums(right)
+ while (sum >= target) {
+ result = math.min(result, right - left + 1) // 产生新结果
+ sum -= nums(left) // 左指针移动,窗口总和减去左指针的值
+ left += 1 // 左指针向右移动
+ }
+ }
+ // 相当于三元运算符,return关键字可以省略
+ if (result == Int.MaxValue) 0 else result
+ }
+}
+```
+
+暴力解法:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
+ import scala.util.control.Breaks
+ var res = Int.MaxValue
+ var subLength = 0
+ for (i <- 0 until nums.length) {
+ var sum = 0
+ Breaks.breakable(
+ for (j <- i until nums.length) {
+ sum += nums(j)
+ if (sum >= target) {
+ subLength = j - i + 1
+ res = math.min(subLength, res)
+ Breaks.break()
+ }
+ }
+ )
+ }
+ // 相当于三元运算符
+ if (res == Int.MaxValue) 0 else res
+ }
+}
+```
+C#:
+```csharp
+public class Solution {
+ public int MinSubArrayLen(int s, int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.Length;
+ int ans = int.MaxValue;
+ int start = 0, end = 0;
+ int sum = 0;
+ while (end < n) {
+ sum += nums[end];
+ while (sum >= s)
+ {
+ ans = Math.Min(ans, end - start + 1);
+ sum -= nums[start];
+ start++;
+ }
+ end++;
+ }
+ return ans == int.MaxValue ? 0 : ans;
+ }
+}
+```
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0213.打家劫舍II.md b/problems/0213.打家劫舍II.md
index 8e569e46..7ae7aae0 100644
--- a/problems/0213.打家劫舍II.md
+++ b/problems/0213.打家劫舍II.md
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-## 213.打家劫舍II
+# 213.打家劫舍II
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-ii/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-ii/)
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋,每间房内都藏有一定的现金。这个地方所有的房屋都 围成一圈 ,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的。同时,相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警 。
@@ -165,7 +165,30 @@ const robRange = (nums, start, end) => {
return dp[end]
}
```
+TypeScript:
+
+```typescript
+function rob(nums: number[]): number {
+ const length: number = nums.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ if (length === 1) return nums[0];
+ return Math.max(robRange(nums, 0, length - 2),
+ robRange(nums, 1, length - 1));
+};
+function robRange(nums: number[], start: number, end: number): number {
+ if (start === end) return nums[start];
+ const dp: number[] = [];
+ dp[start] = nums[start];
+ dp[start + 1] = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]);
+ for (let i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) {
+ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[end];
+}
+```
+
Go:
+
```go
// 打家劫舍Ⅱ 动态规划
// 时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(n)
diff --git a/problems/0216.组合总和III.md b/problems/0216.组合总和III.md
index 0bb42192..1ef278ff 100644
--- a/problems/0216.组合总和III.md
+++ b/problems/0216.组合总和III.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
# 216.组合总和III
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iii/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/)
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ public:
# 总结
-开篇就介绍了本题与[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)的区别,相对来说加了元素总和的限制,如果做完[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)再做本题在合适不过。
+开篇就介绍了本题与[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)的区别,相对来说加了元素总和的限制,如果做完[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)再做本题在合适不过。
分析完区别,依然把问题抽象为树形结构,按照回溯三部曲进行讲解,最后给出剪枝的优化。
@@ -360,42 +360,86 @@ func backTree(n,k,startIndex int,track *[]int,result *[][]int){
## javaScript
```js
-// 等差数列
-var maxV = k => k * (9 + 10 - k) / 2;
-var minV = k => k * (1 + k) / 2;
+/**
+ * @param {number} k
+ * @param {number} n
+ * @return {number[][]}
+ */
var combinationSum3 = function(k, n) {
- if (k > 9 || k < 1) return [];
- // if (n > maxV(k) || n < minV(k)) return [];
- // if (n === maxV(k)) return [Array.from({length: k}).map((v, i) => 9 - i)];
- // if (n === minV(k)) return [Array.from({length: k}).map((v, i) => i + 1)];
-
- const res = [], path = [];
- backtracking(k, n, 1, 0);
- return res;
- function backtracking(k, n, i, sum){
- const len = path.length;
- if (len > k || sum > n) return;
- if (maxV(k - len) < n - sum) return;
- if (minV(k - len) > n - sum) return;
-
- if(len === k && sum == n) {
- res.push(Array.from(path));
+ const backtrack = (start) => {
+ const l = path.length;
+ if (l === k) {
+ const sum = path.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
+ if (sum === n) {
+ res.push([...path]);
+ }
return;
}
-
- const min = Math.min(n - sum, 9 + len - k + 1);
-
- for(let a = i; a <= min; a++) {
- path.push(a);
- sum += a;
- backtracking(k, n, a + 1, sum);
+ for (let i = start; i <= 9 - (k - l) + 1; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ backtrack(i + 1);
path.pop();
- sum -= a;
}
}
+ let res = [], path = [];
+ backtrack(1);
+ return res;
};
```
+## TypeScript
+
+```typescript
+function combinationSum3(k: number, n: number): number[][] {
+ const resArr: number[][] = [];
+ function backTracking(k: number, n: number, sum: number, startIndex: number, tempArr: number[]): void {
+ if (sum > n) return;
+ if (tempArr.length === k) {
+ if (sum === n) {
+ resArr.push(tempArr.slice());
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (k - tempArr.length) + 1; i++) {
+ tempArr.push(i);
+ backTracking(k, n, sum + i, i + 1, tempArr);
+ tempArr.pop();
+ }
+ }
+ backTracking(k, n, 0, 1, []);
+ return resArr;
+};
+```
+
+## Rust
+
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec>, path:&mut Vec, targetSum:i32, k: i32, mut sum: i32, startIndex: i32) {
+ let len = path.len() as i32;
+ if len == k {
+ if sum == targetSum {
+ result.push(path.to_vec());
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for i in startIndex..=9 {
+ sum += i;
+ path.push(i);
+ Self::backtracking(result, path, targetSum, k, sum, i+1);
+ sum -= i;
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ }
+ pub fn combination_sum3(k: i32, n: i32) -> Vec> {
+ let mut result: Vec> = Vec::new();
+ let mut path: Vec = Vec::new();
+ Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, n, k, 0, 1);
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
+
## C
```c
@@ -487,5 +531,35 @@ func combinationSum3(_ count: Int, _ targetSum: Int) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
+## Scala
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ import scala.collection.mutable
+ def combinationSum3(k: Int, n: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
+ var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
+ var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
+
+ def backtracking(k: Int, n: Int, sum: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
+ if (sum > n) return // 剪枝,如果sum>目标和,就返回
+ if (sum == n && path.size == k) {
+ result.append(path.toList)
+ return
+ }
+ // 剪枝
+ for (i <- startIndex to (9 - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
+ path.append(i)
+ backtracking(k, n, sum + i, i + 1)
+ path = path.take(path.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+
+ backtracking(k, n, 0, 1) // 调用递归方法
+ result.toList // 最终返回结果集的List形式
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md b/problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md
index ba7acc5a..e2825cfb 100644
--- a/problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md
+++ b/problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
# 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
@@ -646,5 +646,68 @@ func countNodes(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
}
```
+## Scala
+
+递归:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
+ if(root == null) return 0
+ 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+层序遍历:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ import scala.collection.mutable
+ def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
+ if (root == null) return 0
+ val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
+ var node = 0
+ queue.enqueue(root)
+ while (!queue.isEmpty) {
+ val len = queue.size
+ for (i <- 0 until len) {
+ node += 1
+ val curNode = queue.dequeue()
+ if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
+ if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
+ }
+ }
+ node
+ }
+}
+```
+
+利用完全二叉树性质:
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
+ if (root == null) return 0
+ var leftNode = root.left
+ var rightNode = root.right
+ // 向左向右往下探
+ var leftDepth = 0
+ while (leftNode != null) {
+ leftDepth += 1
+ leftNode = leftNode.left
+ }
+ var rightDepth = 0
+ while (rightNode != null) {
+ rightDepth += 1
+ rightNode = rightNode.right
+ }
+ // 如果相等就是一个满二叉树
+ if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
+ return (2 << leftDepth) - 1
+ }
+ // 如果不相等就不是一个完全二叉树,继续向下递归
+ countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1
+ }
+}
+```
+
-----------------------
diff --git a/problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md b/problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md
index 3457c4b3..fb2851f1 100644
--- a/problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md
+++ b/problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
# 225. 用队列实现栈
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
+[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
@@ -28,6 +28,10 @@
# 思路
+
+《代码随想录》算法公开课:[队列的基本操作! | LeetCode:225. 用队列实现栈](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Fd4y1K7sm),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
+
+
(这里要强调是单向队列)
有的同学可能疑惑这种题目有什么实际工程意义,**其实很多算法题目主要是对知识点的考察和教学意义远大于其工程实践的意义,所以面试题也是这样!**
@@ -815,6 +819,203 @@ class MyStack {
}
}
```
+Scala:
+使用两个队列模拟栈:
+```scala
+import scala.collection.mutable
+class MyStack() {
+
+ val queue1 = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
+ val queue2 = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
+
+ def push(x: Int) {
+ queue1.enqueue(x)
+ }
+
+ def pop(): Int = {
+ var size = queue1.size
+ // 将queue1中的每个元素都移动到queue2
+ for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
+ queue2.enqueue(queue1.dequeue())
+ }
+ var res = queue1.dequeue()
+ // 再将queue2中的每个元素都移动到queue1
+ while (!queue2.isEmpty) {
+ queue1.enqueue(queue2.dequeue())
+ }
+ res
+ }
+
+ def top(): Int = {
+ var size = queue1.size
+ for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
+ queue2.enqueue(queue1.dequeue())
+ }
+ var res = queue1.dequeue()
+ while (!queue2.isEmpty) {
+ queue1.enqueue(queue2.dequeue())
+ }
+ // 最终还需要把res送进queue1
+ queue1.enqueue(res)
+ res
+ }
+
+ def empty(): Boolean = {
+ queue1.isEmpty
+ }
+}
+```
+使用一个队列模拟:
+```scala
+import scala.collection.mutable
+
+class MyStack() {
+
+ val queue = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
+
+ def push(x: Int) {
+ queue.enqueue(x)
+ }
+
+ def pop(): Int = {
+ var size = queue.size
+ for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
+ queue.enqueue(queue.head) // 把头添到队列最后
+ queue.dequeue() // 再出队
+ }
+ queue.dequeue()
+ }
+
+ def top(): Int = {
+ var size = queue.size
+ var res = 0
+ for (i <- 0 until size) {
+ queue.enqueue(queue.head) // 把头添到队列最后
+ res = queue.dequeue() // 再出队
+ }
+ res
+ }
+
+ def empty(): Boolean = {
+ queue.isEmpty
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+
+C#:
+```csharp
+public class MyStack {
+ Queue queue1;
+ Queue queue2;
+ public MyStack() {
+ queue1 = new Queue  1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
-2. [二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
-3. [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
-4. [二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么?](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:层序遍历登场!](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:你真的会翻转二叉树么?](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
+3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
+4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
-8. [二叉树:我对称么?](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
-9. [二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
-10. [二叉树:看看这些树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
-11. [二叉树:我有多少个节点?](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
-12. [二叉树:我平衡么?](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
-13. [二叉树:找我的所有路径?](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
+8. [二叉树:对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
+9. [二叉树:二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
+10. [二叉树:二叉树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
+11. [二叉树:完全二叉树的节点个数](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
+12. [二叉树:平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
+13. [二叉树:二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!二叉树系列二](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:以为使用了递归,其实还隐藏着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
-16. [二叉树:做了这么多题目了,我的左叶子之和是多少?](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
-17. [二叉树:我的左下角的值是多少?](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
+15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
+16. [二叉树:左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
+17. [二叉树:找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
-19. [二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
-20. [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
+19. [二叉树:构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
+20. [二叉树:最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
21. [本周小结!(二叉树系列三)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
-24. [二叉树:我是不是一棵二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
+24. [二叉树:验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
25. [二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](./problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md)
-26. [二叉树:我的众数是多少?](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
+26. [二叉树:二叉搜索树中的众数](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
27. [二叉树:公共祖先问题](./problems/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.md)
28. [本周小结!(二叉树系列四)](./problems/周总结/20201017二叉树周末总结.md)
-29. [二叉树:搜索树的公共祖先问题](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
+29. [二叉树:搜索树的最近公共祖先](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
30. [二叉树:搜索树中的插入操作](./problems/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.md)
31. [二叉树:搜索树中的删除操作](./problems/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.md)
32. [二叉树:修剪一棵搜索树](./problems/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.md)
33. [二叉树:构造一棵搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:搜索树转成累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
-
+
## 回溯算法
题目分类大纲如下:
@@ -538,29 +501,14 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-
-
-# B站算法视频讲解
-
-以下为[B站「代码随想录」](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)算法讲解视频:
-
-* [KMP算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd)
-* [KMP算法(代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
-* [回溯算法理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM)
-* [回溯算法之组合问题(力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)
-* [组合问题的剪枝操作(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er)
-* [组合总和(对应力扣题目:39.组合总和)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
-* [分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6)
-* [二叉树理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Hy4y1t7ij)
-* [二叉树的递归遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wh411S7xt)
-* [二叉树的非递归遍历(一)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
# 贡献者
[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+# Star 趋势
+
+[](https://star-history.com/#youngyangyang04/leetcode-master&Date)
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -569,7 +517,8 @@
如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-
1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
-2. [二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
-3. [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
-4. [二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么?](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:层序遍历登场!](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:你真的会翻转二叉树么?](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
+3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
+4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
-8. [二叉树:我对称么?](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
-9. [二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
-10. [二叉树:看看这些树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
-11. [二叉树:我有多少个节点?](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
-12. [二叉树:我平衡么?](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
-13. [二叉树:找我的所有路径?](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
+8. [二叉树:对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
+9. [二叉树:二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
+10. [二叉树:二叉树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
+11. [二叉树:完全二叉树的节点个数](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
+12. [二叉树:平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
+13. [二叉树:二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!二叉树系列二](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:以为使用了递归,其实还隐藏着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
-16. [二叉树:做了这么多题目了,我的左叶子之和是多少?](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
-17. [二叉树:我的左下角的值是多少?](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
+15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
+16. [二叉树:左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
+17. [二叉树:找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
-19. [二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
-20. [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
+19. [二叉树:构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
+20. [二叉树:最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
21. [本周小结!(二叉树系列三)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
-24. [二叉树:我是不是一棵二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
+24. [二叉树:验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
25. [二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](./problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md)
-26. [二叉树:我的众数是多少?](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
+26. [二叉树:二叉搜索树中的众数](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
27. [二叉树:公共祖先问题](./problems/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.md)
28. [本周小结!(二叉树系列四)](./problems/周总结/20201017二叉树周末总结.md)
-29. [二叉树:搜索树的公共祖先问题](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
+29. [二叉树:搜索树的最近公共祖先](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
30. [二叉树:搜索树中的插入操作](./problems/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.md)
31. [二叉树:搜索树中的删除操作](./problems/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.md)
32. [二叉树:修剪一棵搜索树](./problems/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.md)
33. [二叉树:构造一棵搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:搜索树转成累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
-
+
## 回溯算法
题目分类大纲如下:
@@ -538,29 +501,14 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-
-
-# B站算法视频讲解
-
-以下为[B站「代码随想录」](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)算法讲解视频:
-
-* [KMP算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd)
-* [KMP算法(代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
-* [回溯算法理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM)
-* [回溯算法之组合问题(力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)
-* [组合问题的剪枝操作(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er)
-* [组合总和(对应力扣题目:39.组合总和)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
-* [分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6)
-* [二叉树理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Hy4y1t7ij)
-* [二叉树的递归遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wh411S7xt)
-* [二叉树的非递归遍历(一)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
# 贡献者
[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+# Star 趋势
+
+[](https://star-history.com/#youngyangyang04/leetcode-master&Date)
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -569,7 +517,8 @@
如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-




 -
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -721,10 +695,164 @@ func reverseWord(_ s: inout [Character]) {
}
```
+Scala:
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def reverseWords(s: String): String = {
+ var sb = removeSpace(s) // 移除多余的空格
+ reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length - 1) // 翻转字符串
+ reverseEachWord(sb)
+ sb.mkString
+ }
+
+ // 移除多余的空格
+ def removeSpace(s: String): Array[Char] = {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = s.length - 1
+ // 移除字符串前面的空格
+ while (start < s.length && s(start) == ' ') start += 1
+ // 移除字符串后面的空格
+ while (end >= 0 && s(end) == ' ') end -= 1
+ var sb = "" // String
+ // 当start小于等于end的时候,执行添加操作
+ while (start <= end) {
+ var c = s(start)
+ // 当前字符不等于空,sb的最后一个字符不等于空的时候添加到sb
+ if (c != ' ' || sb(sb.length - 1) != ' ') {
+ sb ++= c.toString
+ }
+ start += 1 // 指针向右移动
+ }
+ sb.toArray
+ }
+
+ // 翻转字符串
+ def reverseString(s: Array[Char], start: Int, end: Int): Unit = {
+ var (left, right) = (start, end)
+ while (left < right) {
+ var tmp = s(left)
+ s(left) = s(right)
+ s(right) = tmp
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 翻转每个单词
+ def reverseEachWord(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ // 向后迭代寻找每个单词的坐标
+ while (j < s.length && s(j) != ' ') j += 1
+ reverseString(s, i, j - 1) // 翻转每个单词
+ i = j + 1 // i往后更新
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+PHP:
+```php
+function reverseWords($s) {
+ $this->removeExtraSpaces($s);
+ $this->reverseString($s, 0, strlen($s)-1);
+ // 将每个单词反转
+ $start = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i <= strlen($s); $i++) {
+ // 到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
+ if ($i == strlen($s) || $s[$i] == ' ') {
+ // 翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
+ $this->reverseString($s, $start, $i-1);
+ // +1: 单词与单词直接有个空格
+ $start = $i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return $s;
+}
+// 移除多余空格
+function removeExtraSpaces(&$s){
+ $slow = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
+ if ($s[$i] != ' ') {
+ if ($slow != 0){
+ $s[$slow++] = ' ';
+ }
+ while ($i < strlen($s) && $s[$i] != ' ') {
+ $s[$slow++] = $s[$i++];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // 移动覆盖处理,丢弃多余的脏数据。
+ $s = substr($s,0,$slow);
+ return ;
+}
+// 翻转字符串
+function reverseString(&$s, $start, $end) {
+ for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
+ $tmp = $s[$i];
+ $s[$i] = $s[$j];
+ $s[$j] = $tmp;
+ }
+ return ;
+}
+```
+Rust:
+
+```Rust
+// 根据C++版本二思路进行实现
+// 函数名根据Rust编译器建议由驼峰命名法改为蛇形命名法
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn reverse(s: &mut Vec
-
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -721,10 +695,164 @@ func reverseWord(_ s: inout [Character]) {
}
```
+Scala:
+
+```scala
+object Solution {
+ def reverseWords(s: String): String = {
+ var sb = removeSpace(s) // 移除多余的空格
+ reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length - 1) // 翻转字符串
+ reverseEachWord(sb)
+ sb.mkString
+ }
+
+ // 移除多余的空格
+ def removeSpace(s: String): Array[Char] = {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = s.length - 1
+ // 移除字符串前面的空格
+ while (start < s.length && s(start) == ' ') start += 1
+ // 移除字符串后面的空格
+ while (end >= 0 && s(end) == ' ') end -= 1
+ var sb = "" // String
+ // 当start小于等于end的时候,执行添加操作
+ while (start <= end) {
+ var c = s(start)
+ // 当前字符不等于空,sb的最后一个字符不等于空的时候添加到sb
+ if (c != ' ' || sb(sb.length - 1) != ' ') {
+ sb ++= c.toString
+ }
+ start += 1 // 指针向右移动
+ }
+ sb.toArray
+ }
+
+ // 翻转字符串
+ def reverseString(s: Array[Char], start: Int, end: Int): Unit = {
+ var (left, right) = (start, end)
+ while (left < right) {
+ var tmp = s(left)
+ s(left) = s(right)
+ s(right) = tmp
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 翻转每个单词
+ def reverseEachWord(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ // 向后迭代寻找每个单词的坐标
+ while (j < s.length && s(j) != ' ') j += 1
+ reverseString(s, i, j - 1) // 翻转每个单词
+ i = j + 1 // i往后更新
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+PHP:
+```php
+function reverseWords($s) {
+ $this->removeExtraSpaces($s);
+ $this->reverseString($s, 0, strlen($s)-1);
+ // 将每个单词反转
+ $start = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i <= strlen($s); $i++) {
+ // 到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
+ if ($i == strlen($s) || $s[$i] == ' ') {
+ // 翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
+ $this->reverseString($s, $start, $i-1);
+ // +1: 单词与单词直接有个空格
+ $start = $i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return $s;
+}
+// 移除多余空格
+function removeExtraSpaces(&$s){
+ $slow = 0;
+ for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
+ if ($s[$i] != ' ') {
+ if ($slow != 0){
+ $s[$slow++] = ' ';
+ }
+ while ($i < strlen($s) && $s[$i] != ' ') {
+ $s[$slow++] = $s[$i++];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // 移动覆盖处理,丢弃多余的脏数据。
+ $s = substr($s,0,$slow);
+ return ;
+}
+// 翻转字符串
+function reverseString(&$s, $start, $end) {
+ for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
+ $tmp = $s[$i];
+ $s[$i] = $s[$j];
+ $s[$j] = $tmp;
+ }
+ return ;
+}
+```
+Rust:
+
+```Rust
+// 根据C++版本二思路进行实现
+// 函数名根据Rust编译器建议由驼峰命名法改为蛇形命名法
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn reverse(s: &mut Vec