
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 104.二叉树的最大深度
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
## 算法公开课
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉树的高度和深度有啥区别?究竟用什么遍历顺序?很多录友搞不懂 | 104.二叉树的最大深度](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Gd4y1V75u),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
看完本篇可以一起做了如下两道题目:
* [104.二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
* [559.n叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
### 递归法
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
* 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
**而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度**,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
这一点其实是很多同学没有想清楚的,很多题解同样没有讲清楚。
我先用后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度。
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
```CPP
int getdepth(TreeNode* node)
```
2. 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
代码如下:
```CPP
if (node == NULL) return 0;
```
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
代码如下:
```CPP
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
```
所以整体c++代码如下:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};
```
代码精简之后c++代码如下:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
```
**精简之后的代码根本看不出是哪种遍历方式,也看不出递归三部曲的步骤,所以如果对二叉树的操作还不熟练,尽量不要直接照着精简代码来学。**
本题当然也可以使用前序,代码如下:(**充分表现出求深度回溯的过程**)
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
if (node->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
```
**可以看出使用了前序(中左右)的遍历顺序,这才是真正求深度的逻辑!**
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) { // 右
getdepth(node->right, depth + 1);
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
```
### 迭代法
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
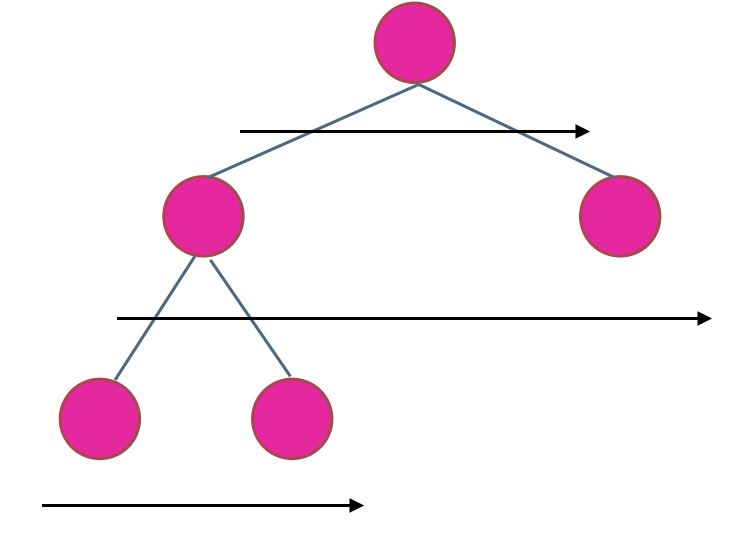
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
如果对层序遍历还不清楚的话,可以看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)
c++代码如下:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
```
那么我们可以顺便解决一下n叉树的最大深度问题
## 相关题目推荐
### 559.n叉树的最大深度
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
给定一个 n 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
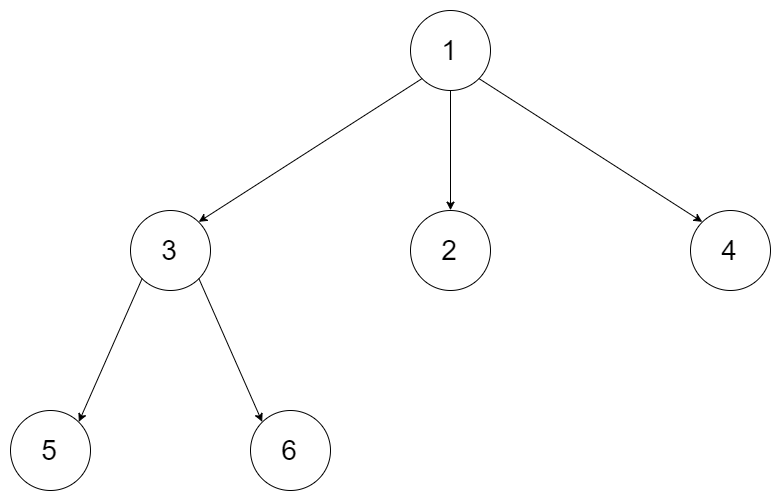
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
### 思路
依然可以提供递归法和迭代法,来解决这个问题,思路是和二叉树思路一样的,直接给出代码如下:
#### 递归法
c++代码:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
depth = max (depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};
```
#### 迭代法
依然是层序遍历,代码如下:
```CPP
class solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); j++) {
if (node->children[j]) que.push(node->children[j]);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
104.二叉树的最大深度
```java
class solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
```
```java
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法(求深度法)
*/
//定义最大深度
int maxnum = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
ans(root,0);
return maxnum;
}
//递归求解最大深度
void ans(TreeNode tr,int tmp){
if(tr==null) return;
tmp++;
maxnum = maxnum deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
```java
class Solution {
/*递归法,后序遍历求root节点的高度*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
if (root.children != null){
for (Node child : root.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(child));
}
}
return depth + 1; //中节点
}
}
```
```java
class solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while (!que.isEmpty())
{
depth ++;
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0)
{
Node node = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++)
if (node.children.get(i) != null)
que.offer(node.children.get(i));
len--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
```
### Python :
104.二叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```python
class solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
return self.getdepth(root)
def getdepth(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
leftheight = self.getdepth(node.left) #左
rightheight = self.getdepth(node.right) #右
height = 1 + max(leftheight, rightheight) #中
return height
```
递归法:精简代码
```python
class solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return 1 + max(self.maxdepth(root.left), self.maxdepth(root.right))
```
层序遍历迭代法:
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
depth = 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return depth
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```python
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
max_depth = 1
for child in root.children:
max_depth = max(max_depth, self.maxDepth(child) + 1)
return max_depth
```
迭代法:
```python
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
depth = 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
for child in node.children:
queue.append(child)
return depth
```
使用栈
```python
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
max_depth = 0
stack = [(root, 1)]
while stack:
node, depth = stack.pop()
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
for child in node.children:
stack.append((child, depth + 1))
return max_depth
```
### Go:
104.二叉树的最大深度
```go
/**
* definition for a binary tree node.
* type treenode struct {
* val int
* left *treenode
* right *treenode
* }
*/
func max (a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a;
}
return b;
}
// 递归
func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0;
}
return max(maxdepth(root.left), maxdepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
// 遍历
func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
levl := 0;
queue := make([]*treenode, 0);
if root != nil {
queue = append(queue, root);
}
for l := len(queue); l > 0; {
for ;l > 0;l-- {
node := queue[0];
if node.left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.left);
}
if node.right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.right);
}
queue = queue[1:];
}
levl++;
l = len(queue);
}
return levl;
}
```
559. n叉树的最大深度
```go
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
q := list.New()
q.PushBack(root)
depth := 0
for q.Len() > 0 {
n := q.Len()
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
node := q.Remove(q.Front()).(*Node)
for j := range node.Children {
q.PushBack(node.Children[j])
}
}
depth++
}
return depth
}
```
### Javascript :
104.二叉树的最大深度
```javascript
var maxdepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
return 1 + Math.max(maxdepth(root.left), maxdepth(root.right))
};
```
二叉树最大深度递归遍历
```javascript
var maxdepth = function(root) {
//使用递归的方法 递归三部曲
//1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
const getdepth = function(node) {
//2. 确定终止条件
if(node === null) {
return 0;
}
//3. 确定单层逻辑
let leftdepth = getdepth(node.left);
let rightdepth = getdepth(node.right);
let depth = 1 + Math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth);
return depth;
}
return getdepth(root);
};
```
二叉树最大深度层级遍历
```javascript
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let count = 0
const queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length
/* 层数+1 */
count++
while(size--) {
let node = queue.shift();
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return count
};
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
N叉树的最大深度 递归写法
```js
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let depth = 0
for(let node of root.children) {
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
return depth + 1
}
```
N叉树的最大深度 层序遍历
```js
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let count = 0
let queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length
count++
while(size--) {
let node = queue.shift()
for (let item of node.children) {
item && queue.push(item);
}
}
}
return count
};
```
### TypeScript:
104.二叉树的最大深度
```typescript
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
};
// 前序遍历(自上而下)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
function recur(node: TreeNode | null, count: number) {
if (node === null) {
resMax = resMax > count ? resMax : count;
return;
}
recur(node.left, count + 1);
recur(node.right, count + 1);
}
let resMax: number = 0;
let count: number = 0;
recur(root, count);
return resMax;
};
// 层序遍历(迭代法)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let helperQueue: TreeNode[] = [];
let resDepth: number = 0;
let tempNode: TreeNode;
if (root !== null) helperQueue.push(root);
while (helperQueue.length > 0) {
resDepth++;
for (let i = 0, length = helperQueue.length; i < length; i++) {
tempNode = helperQueue.shift()!;
if (tempNode.left) helperQueue.push(tempNode.left);
if (tempNode.right) helperQueue.push(tempNode.right);
}
}
return resDepth;
};
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
```typescript
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
};
// 前序遍历(自上而下)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
function recur(node: TreeNode | null, count: number) {
if (node === null) {
resMax = resMax > count ? resMax : count;
return;
}
recur(node.left, count + 1);
recur(node.right, count + 1);
}
let resMax: number = 0;
let count: number = 0;
recur(root, count);
return resMax;
};
```
### C:
104.二叉树的最大深度
二叉树最大深度递归
```c
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
//若传入结点为NULL,返回0
if(!root)
return 0;
//求出左子树深度
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
//求出右子树深度
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
//求出左子树深度和右子树深度的较大值
int max = left > right ? left : right;
//返回较大值+1(1为当前层数)
return max + 1;
}
```
二叉树最大深度迭代
```c
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
//若传入根节点为NULL,返回0
if(!root)
return 0;
int depth = 0;
//开辟队列空间
struct TreeNode** queue = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 6000);
int queueFront = 0;
int queueEnd = 0;
//将根结点入队
queue[queueEnd++] = root;
int queueSize;
//求出当前队列中元素个数
while(queueSize = queueEnd - queueFront) {
int i;
//若当前队列中结点有左右子树,则将它们的左右子树入队
for(i = 0; i < queueSize; i++) {
struct TreeNode* tempNode = queue[queueFront + i];
if(tempNode->left)
queue[queueEnd++] = tempNode->left;
if(tempNode->right)
queue[queueEnd++] = tempNode->right;
}
//更新队头下标
queueFront += queueSize;
//深度+1
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
```
### Swift:
104.二叉树的最大深度
```swift
// 递归 - 后序
func maxDepth1(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
return _maxDepth1(root)
}
func _maxDepth1(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
let leftDepth = _maxDepth1(root!.left)
let rightDepth = _maxDepth1(root!.right)
return 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth)
}
// 层序
func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var queue = [TreeNode]()
queue.append(root)
var res: Int = 0
while !queue.isEmpty {
res += 1
for _ in 0 ..< queue.count {
let node = queue.removeFirst()
if let left = node.left {
queue.append(left)
}
if let right = node.right {
queue.append(right)
}
}
}
return res
}
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
```swift
// 递归
func maxDepth(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var depth = 0
for node in root.children {
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
return depth + 1
}
// 迭代-层序遍历
func maxDepth1(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var depth = 0
var queue = [Node]()
queue.append(root)
while !queue.isEmpty {
let size = queue.count
depth += 1
for _ in 0 ..< size {
let node = queue.removeFirst()
for child in node.children {
queue.append(child)
}
}
}
return depth
}
```
### Scala:
104.二叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```scala
object Solution {
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
def process(curNode: TreeNode): Int = {
if (curNode == null) return 0
// 递归左节点和右节点,返回最大的,最后+1
math.max(process(curNode.left), process(curNode.right)) + 1
}
// 调用递归方法,return关键字可以省略
process(root)
}
}
```
迭代法:
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var depth = 0
if (root == null) return depth
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
queue.enqueue(root)
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
val len = queue.size
for (i <- 0 until len) {
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
}
depth += 1 // 只要有层次就+=1
}
depth
}
}
```
559.n叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```scala
object Solution {
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
if (root == null) return 0
var depth = 0
for (node <- root.children) {
depth = math.max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
depth + 1
}
}
```
迭代法: (层序遍历)
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
if (root == null) return 0
var depth = 0
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
queue.enqueue(root)
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
val len = queue.size
depth += 1
for (i <- 0 until len) {
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
for (node <- curNode.children) queue.enqueue(node)
}
}
depth
}
}
```
### Rust:
0104.二叉树的最大深度
递归:
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
std::cmp::max(
Self::max_depth(root.clone().unwrap().borrow().left.clone()),
Self::max_depth(root.unwrap().borrow().right.clone()),
) + 1
}
}
```
迭代:
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none(){
return 0;
}
let mut max_depth: i32 = 0;
let mut stack = vec![root.unwrap()];
while !stack.is_empty() {
let num = stack.len();
for _i in 0..num{
let top = stack.remove(0);
if top.borrow_mut().left.is_some(){
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().left.take().unwrap());
}
if top.borrow_mut().right.is_some(){
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().right.take().unwrap());
}
}
max_depth+=1;
}
max_depth
}
```
### C#
```C#
// 递归法
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = MaxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = MaxDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.Max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
```
```C#
// 前序遍历
int result = 0;
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return result;
GetDepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
public void GetDepth(TreeNode root, int depth)
{
result = depth > result ? depth : result;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return;
if (root.left != null)
GetDepth(root.left, depth + 1);
if (root.right != null)
GetDepth(root.right, depth + 1);
return;
}
```
```C#
// 迭代法
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
{
int depth = 0;
Queue que = new();
if (root == null) return depth;
que.Enqueue(root);
while (que.Count != 0)
{
int size = que.Count;
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
var node = que.Dequeue();
if (node.left != null) que.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null) que.Enqueue(node.right);
}
}
return depth;
}
```

