
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 二叉树上应该怎么求,二叉搜索树上又应该怎么求?
# 501.二叉搜索树中的众数
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/)
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
* 结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
* 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
* 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
例如:
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],

返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
# 算法公开课
**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[不仅双指针,还有代码技巧可以惊艳到你! | LeetCode:501.二叉搜索树中的众数](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
# 思路
这道题目呢,递归法我从两个维度来讲。
首先如果不是二叉搜索树的话,应该怎么解题,是二叉搜索树,又应该如何解题,两种方式做一个比较,可以加深大家对二叉树的理解。
## 递归法
### 如果不是二叉搜索树
如果不是二叉搜索树,最直观的方法一定是把这个树都遍历了,用map统计频率,把频率排个序,最后取前面高频的元素的集合。
具体步骤如下:
1. 这个树都遍历了,用map统计频率
至于用前中后序哪种遍历也不重要,因为就是要全遍历一遍,怎么个遍历法都行,层序遍历都没毛病!
这里采用前序遍历,代码如下:
```CPP
// map key:元素,value:出现频率
void searchBST(TreeNode* cur, unordered_map& map) { // 前序遍历
if (cur == NULL) return ;
map[cur->val]++; // 统计元素频率
searchBST(cur->left, map);
searchBST(cur->right, map);
return ;
}
```
2. 把统计的出来的出现频率(即map中的value)排个序
有的同学可能可以想直接对map中的value排序,还真做不到,C++中如果使用std::map或者std::multimap可以对key排序,但不能对value排序。
所以要把map转化数组即vector,再进行排序,当然vector里面放的也是`pair`类型的数据,第一个int为元素,第二个int为出现频率。
代码如下:
```CPP
bool static cmp (const pair& a, const pair& b) {
return a.second > b.second; // 按照频率从大到小排序
}
vector> vec(map.begin(), map.end());
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp); // 给频率排个序
```
3. 取前面高频的元素
此时数组vector中已经是存放着按照频率排好序的pair,那么把前面高频的元素取出来就可以了。
代码如下:
```CPP
result.push_back(vec[0].first);
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) {
// 取最高的放到result数组中
if (vec[i].second == vec[0].second) result.push_back(vec[i].first);
else break;
}
return result;
```
整体C++代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
private:
void searchBST(TreeNode* cur, unordered_map& map) { // 前序遍历
if (cur == NULL) return ;
map[cur->val]++; // 统计元素频率
searchBST(cur->left, map);
searchBST(cur->right, map);
return ;
}
bool static cmp (const pair& a, const pair& b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
public:
vector findMode(TreeNode* root) {
unordered_map map; // key:元素,value:出现频率
vector result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
searchBST(root, map);
vector> vec(map.begin(), map.end());
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp); // 给频率排个序
result.push_back(vec[0].first);
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) {
// 取最高的放到result数组中
if (vec[i].second == vec[0].second) result.push_back(vec[i].first);
else break;
}
return result;
}
};
```
**所以如果本题没有说是二叉搜索树的话,那么就按照上面的思路写!**
### 是二叉搜索树
**既然是搜索树,它中序遍历就是有序的**。
如图:
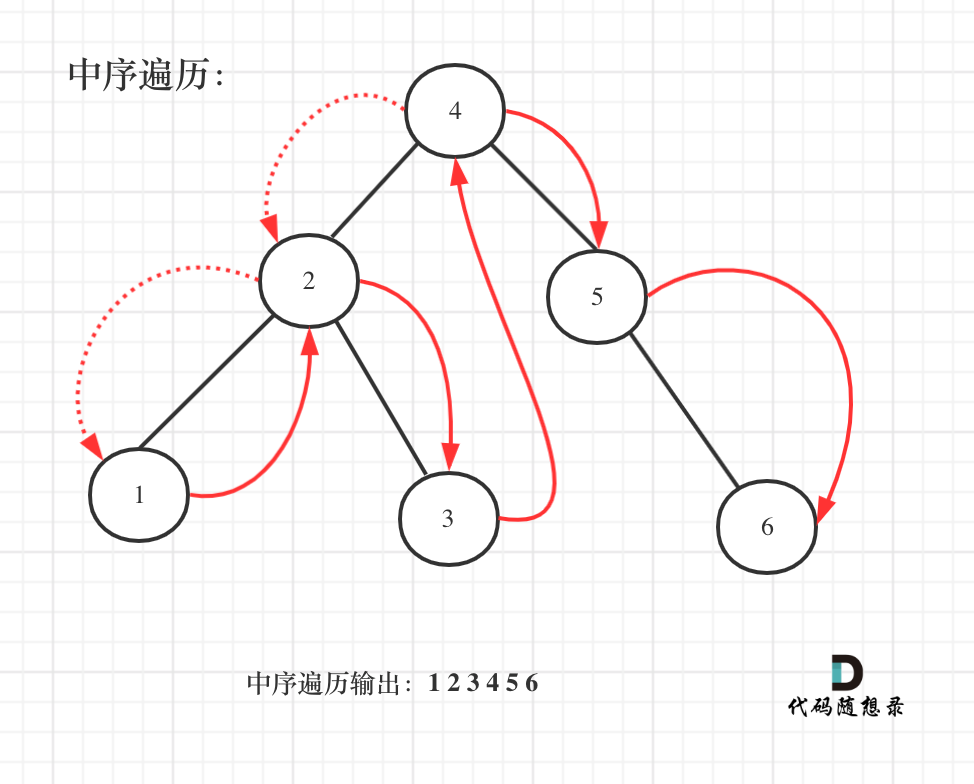
中序遍历代码如下:
```CPP
void searchBST(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return ;
searchBST(cur->left); // 左
(处理节点) // 中
searchBST(cur->right); // 右
return ;
}
```
遍历有序数组的元素出现频率,从头遍历,那么一定是相邻两个元素作比较,然后就把出现频率最高的元素输出就可以了。
关键是在有序数组上的话,好搞,在树上怎么搞呢?
这就考察对树的操作了。
在[二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](https://programmercarl.com/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.html)中我们就使用了pre指针和cur指针的技巧,这次又用上了。
弄一个指针指向前一个节点,这样每次cur(当前节点)才能和pre(前一个节点)作比较。
而且初始化的时候pre = NULL,这样当pre为NULL时候,我们就知道这是比较的第一个元素。
代码如下:
```CPP
if (pre == NULL) { // 第一个节点
count = 1; // 频率为1
} else if (pre->val == cur->val) { // 与前一个节点数值相同
count++;
} else { // 与前一个节点数值不同
count = 1;
}
pre = cur; // 更新上一个节点
```
此时又有问题了,因为要求最大频率的元素集合(注意是集合,不是一个元素,可以有多个众数),如果是数组上大家一般怎么办?
应该是先遍历一遍数组,找出最大频率(maxCount),然后再重新遍历一遍数组把出现频率为maxCount的元素放进集合。(因为众数有多个)
这种方式遍历了两遍数组。
那么我们遍历两遍二叉搜索树,把众数集合算出来也是可以的。
但这里其实只需要遍历一次就可以找到所有的众数。
那么如何只遍历一遍呢?
如果 频率count 等于 maxCount(最大频率),当然要把这个元素加入到结果集中(以下代码为result数组),代码如下:
```CPP
if (count == maxCount) { // 如果和最大值相同,放进result中
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
```
是不是感觉这里有问题,result怎么能轻易就把元素放进去了呢,万一,这个maxCount此时还不是真正最大频率呢。
所以下面要做如下操作:
频率count 大于 maxCount的时候,不仅要更新maxCount,而且要清空结果集(以下代码为result数组),因为结果集之前的元素都失效了。
```CPP
if (count > maxCount) { // 如果计数大于最大值
maxCount = count; // 更新最大频率
result.clear(); // 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
```
关键代码都讲完了,完整代码如下:(**只需要遍历一遍二叉搜索树,就求出了众数的集合**)
```CPP
class Solution {
private:
int maxCount = 0; // 最大频率
int count = 0; // 统计频率
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
vector result;
void searchBST(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return ;
searchBST(cur->left); // 左
// 中
if (pre == NULL) { // 第一个节点
count = 1;
} else if (pre->val == cur->val) { // 与前一个节点数值相同
count++;
} else { // 与前一个节点数值不同
count = 1;
}
pre = cur; // 更新上一个节点
if (count == maxCount) { // 如果和最大值相同,放进result中
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
if (count > maxCount) { // 如果计数大于最大值频率
maxCount = count; // 更新最大频率
result.clear(); // 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
searchBST(cur->right); // 右
return ;
}
public:
vector findMode(TreeNode* root) {
count = 0;
maxCount = 0;
TreeNode* pre = NULL; // 记录前一个节点
result.clear();
searchBST(root);
return result;
}
};
```
## 迭代法
只要把中序遍历转成迭代,中间节点的处理逻辑完全一样。
二叉树前中后序转迭代,传送门:
* [二叉树:前中后序迭代法](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的迭代遍历.html)
* [二叉树:前中后序统一风格的迭代方式](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的统一迭代法.html)
下面我给出其中的一种中序遍历的迭代法,其中间处理逻辑一点都没有变(我从递归法直接粘过来的代码,连注释都没改,哈哈)
代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
vector findMode(TreeNode* root) {
stack st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
int maxCount = 0; // 最大频率
int count = 0; // 统计频率
vector result;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top();
st.pop(); // 中
if (pre == NULL) { // 第一个节点
count = 1;
} else if (pre->val == cur->val) { // 与前一个节点数值相同
count++;
} else { // 与前一个节点数值不同
count = 1;
}
if (count == maxCount) { // 如果和最大值相同,放进result中
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
if (count > maxCount) { // 如果计数大于最大值频率
maxCount = count; // 更新最大频率
result.clear(); // 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
};
```
# 总结
本题在递归法中,我给出了如果是普通二叉树,应该怎么求众数。
知道了普通二叉树的做法时候,我再进一步给出二叉搜索树又应该怎么求众数,这样鲜明的对比,相信会对二叉树又有更深层次的理解了。
在递归遍历二叉搜索树的过程中,我还介绍了一个统计最高出现频率元素集合的技巧, 要不然就要遍历两次二叉搜索树才能把这个最高出现频率元素的集合求出来。
**为什么没有这个技巧一定要遍历两次呢? 因为要求的是集合,会有多个众数,如果规定只有一个众数,那么就遍历一次稳稳的了。**
最后我依然给出对应的迭代法,其实就是迭代法中序遍历的模板加上递归法中中间节点的处理逻辑,分分钟就可以写出来,中间逻辑的代码我都是从递归法中直接粘过来的。
**求二叉搜索树中的众数其实是一道简单题,但大家可以发现我写了这么一大篇幅的文章来讲解,主要是为了尽量从各个角度对本题进剖析,帮助大家更快更深入理解二叉树**。
> **需要强调的是 leetcode上的耗时统计是非常不准确的,看个大概就行,一样的代码耗时可以差百分之50以上**,所以leetcode的耗时统计别太当回事,知道理论上的效率优劣就行了。
# 其他语言版本
## Java
暴力法
```java
class Solution {
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
// 获得频率 Map
searchBST(root, map);
List> mapList = map.entrySet().stream()
.sorted((c1, c2) -> c2.getValue().compareTo(c1.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.add(mapList.get(0).getKey());
// 把频率最高的加入 list
for (int i = 1; i < mapList.size(); i++) {
if (mapList.get(i).getValue() == mapList.get(i - 1).getValue()) {
list.add(mapList.get(i).getKey());
} else {
break;
}
}
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
void searchBST(TreeNode curr, Map map) {
if (curr == null) return;
map.put(curr.val, map.getOrDefault(curr.val, 0) + 1);
searchBST(curr.left, map);
searchBST(curr.right, map);
}
}
```
中序遍历-不使用额外空间,利用二叉搜索树特性
```Java
class Solution {
ArrayList resList;
int maxCount;
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
int[] res = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); i++) {
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void findMode1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
findMode1(root.left);
int rootValue = root.val;
// 计数
if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val) {
count = 1;
} else {
count++;
}
// 更新结果以及maxCount
if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(rootValue);
maxCount = count;
} else if (count == maxCount) {
resList.add(rootValue);
}
pre = root;
findMode1(root.right);
}
}
```
迭代法
```java
class Solution {
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode pre = null;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
List result = new ArrayList<>();
int maxCount = 0;
int count = 0;
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur =cur.left;
}else {
cur = stack.pop();
// 计数
if (pre == null || cur.val != pre.val) {
count = 1;
}else {
count++;
}
// 更新结果
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
result.clear();
result.add(cur.val);
}else if (count == maxCount) {
result.add(cur.val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
```
統一迭代法
```Java
class Solution {
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 0;
TreeNode pre = null;
LinkedList res = new LinkedList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null)
stack.add(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
if(curr != null){
stack.pop();
if(curr.right != null)
stack.add(curr.right);
stack.add(curr);
stack.add(null);
if(curr.left != null)
stack.add(curr.left);
}else{
stack.pop();
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
if(pre == null)
count = 1;
else if(pre != null && pre.val == temp.val)
count++;
else
count = 1;
pre = temp;
if(count == maxCount)
res.add(temp.val);
if(count > maxCount){
maxCount = count;
res.clear();
res.add(temp.val);
}
}
}
int[] result = new int[res.size()];
int i = 0;
for (int x : res){
result[i] = x;
i++;
}
return result;
}
}
```
## Python
> 递归法
> 常量空间,递归产生的栈不算
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.pre = TreeNode()
self.count = 0
self.max_count = 0
self.result = []
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if not root: return None
self.search_BST(root)
return self.result
def search_BST(self, cur: TreeNode) -> None:
if not cur: return None
self.search_BST(cur.left)
# 第一个节点
if not self.pre:
self.count = 1
# 与前一个节点数值相同
elif self.pre.val == cur.val:
self.count += 1
# 与前一个节点数值不相同
else:
self.count = 1
self.pre = cur
if self.count == self.max_count:
self.result.append(cur.val)
if self.count > self.max_count:
self.max_count = self.count
self.result = [cur.val] # 清空self.result,确保result之前的的元素都失效
self.search_BST(cur.right)
```
> 迭代法-中序遍历
> 利用二叉搜索树特性,在历遍过程中更新结果,一次历遍
> 但需要使用额外空间存储历遍的节点
```python
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
stack = []
cur = root
pre = None
maxCount, count = 0, 0
res = []
while cur or stack:
if cur: # 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
stack.append(cur)
cur = cur.left
else: # 逐一处理节点
cur = stack.pop()
if pre == None: # 第一个节点
count = 1
elif pre.val == cur.val: # 与前一个节点数值相同
count += 1
else:
count = 1
if count == maxCount:
res.append(cur.val)
if count > maxCount:
maxCount = count
res.clear()
res.append(cur.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
return res
```
## Go
计数法,不使用额外空间,利用二叉树性质,中序遍历
```go
func findMode(root *TreeNode) []int {
res := make([]int, 0)
count := 1
max := 1
var prev *TreeNode
var travel func(node *TreeNode)
travel = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
travel(node.Left)
if prev != nil && prev.Val == node.Val {
count++
} else {
count = 1
}
if count >= max {
if count > max && len(res) > 0 {
res = []int{node.Val}
} else {
res = append(res, node.Val)
}
max = count
}
prev = node
travel(node.Right)
}
travel(root)
return res
}
```
## JavaScript
使用额外空间map的方法
```javascript
var findMode = function(root) {
// 使用递归中序遍历
let map = new Map();
// 1. 确定递归函数以及函数参数
const traverTree = function(root) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null) {
return ;
}
traverTree(root.left);
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
map.set(root.val,map.has(root.val)?map.get(root.val)+1:1);
traverTree(root.right);
}
traverTree(root);
//上面把数据都存储到map
//下面开始寻找map里面的
// 定义一个最大出现次数的初始值为root.val的出现次数
let maxCount = map.get(root.val);
// 定义一个存放结果的数组res
let res = [];
for(let [key,value] of map) {
// 如果当前值等于最大出现次数就直接在res增加该值
if(value === maxCount) {
res.push(key);
}
// 如果value的值大于原本的maxCount就清空res的所有值,因为找到了更大的
if(value>maxCount) {
res = [];
maxCount = value;
res.push(key);
}
}
return res;
};
```
不使用额外空间,利用二叉树性质,中序遍历(有序):
```javascript
var findMode = function(root) {
// 不使用额外空间,使用中序遍历,设置出现最大次数初始值为1
let count = 0,maxCount = 1;
let pre = root,res = [];
// 1.确定递归函数及函数参数
const travelTree = function(cur) {
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(cur === null) {
return ;
}
travelTree(cur.left);
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
if(pre.val === cur.val) {
count++;
}else {
count = 1;
}
pre = cur;
if(count === maxCount) {
res.push(cur.val);
}
if(count > maxCount) {
res = [];
maxCount = count;
res.push(cur.val);
}
travelTree(cur.right);
}
travelTree(root);
return res;
};
```
## TypeScript
> 辅助Map法
```typescript
function findMode(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
if (root === null) return [];
const countMap: Map = new Map();
function traverse(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
countMap.set(root.val, (countMap.get(root.val) || 0) + 1);
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
}
traverse(root);
const countArr: number[][] = Array.from(countMap);
countArr.sort((a, b) => {
return b[1] - a[1];
})
const resArr: number[] = [];
const maxCount: number = countArr[0][1];
for (let i of countArr) {
if (i[1] === maxCount) resArr.push(i[0]);
}
return resArr;
};
```
> 递归中直接解决
```typescript
function findMode(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
let preNode: TreeNode | null = null;
let maxCount: number = 0;
let count: number = 0;
let resArr: number[] = [];
function traverse(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
traverse(root.left);
if (preNode === null) { // 第一个节点
count = 1;
} else if (preNode.val === root.val) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
if (count === maxCount) {
resArr.push(root.val);
} else if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
resArr.length = 0;
resArr.push(root.val);
}
preNode = root;
traverse(root.right);
}
traverse(root);
return resArr;
};
```
> 迭代法
```typescript
function findMode(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
const helperStack: TreeNode[] = [];
const resArr: number[] = [];
let maxCount: number = 0;
let count: number = 0;
let preNode: TreeNode | null = null;
let curNode: TreeNode | null = root;
while (curNode !== null || helperStack.length > 0) {
if (curNode !== null) {
helperStack.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.left;
} else {
curNode = helperStack.pop()!;
if (preNode === null) { // 第一个节点
count = 1;
} else if (preNode.val === curNode.val) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
if (count === maxCount) {
resArr.push(curNode.val);
} else if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
resArr.length = 0;
resArr.push(curNode.val);
}
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode.right;
}
}
return resArr;
};
```
## Scala
暴力:
```scala
object Solution {
// 导包
import scala.collection.mutable // 集合包
import scala.util.control.Breaks.{break, breakable} // 流程控制包
def findMode(root: TreeNode): Array[Int] = {
var map = mutable.HashMap[Int, Int]() // 存储节点的值,和该值出现的次数
def searchBST(curNode: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (curNode == null) return
var value = map.getOrElse(curNode.value, 0)
map.put(curNode.value, value + 1)
searchBST(curNode.left)
searchBST(curNode.right)
}
searchBST(root) // 前序遍历把每个节点的值加入到里面
// 将map转换为list,随后根据元组的第二个值进行排序
val list = map.toList.sortWith((map1, map2) => {
if (map1._2 > map2._2) true else false
})
var res = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int]()
res.append(list(0)._1) // 将第一个加入结果集
breakable {
for (i <- 1 until list.size) {
// 如果值相同就加入结果集合,反之break
if (list(i)._2 == list(0)._2) res.append(list(i)._1)
else break
}
}
res.toArray // 最终返回res的Array格式,return关键字可以省略
}
}
```
递归(利用二叉搜索树的性质):
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def findMode(root: TreeNode): Array[Int] = {
var maxCount = 0 // 最大频率
var count = 0 // 统计频率
var pre: TreeNode = null
var result = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int]()
def searchBST(cur: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (cur == null) return
searchBST(cur.left)
if (pre == null) count = 1 // 等于空置为1
else if (pre.value == cur.value) count += 1 // 与上一个节点的值相同加1
else count = 1 // 与上一个节点的值不同
pre = cur
// 如果和最大值相同,则放入结果集
if (count == maxCount) result.append(cur.value)
// 如果当前计数大于最大值频率,更新最大值,清空结果集
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count
result.clear()
result.append(cur.value)
}
searchBST(cur.right)
}
searchBST(root)
result.toArray // return关键字可以省略
}
}
```
## rust
递归:
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_mode(root: Option>>) -> Vec {
let mut count = 0;
let mut max_count = 0;
let mut res = vec![];
let mut pre = i32::MIN;
Self::search_bst(&root, &mut pre, &mut res, &mut count, &mut max_count);
res
}
pub fn search_bst(
cur: &Option>>,
mut pre: &mut i32,
res: &mut Vec,
count: &mut i32,
max_count: &mut i32,
) {
if cur.is_none() {
return;
}
let cur_node = cur.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::search_bst(&cur_node.left, pre, res, count, max_count);
if *pre == i32::MIN {
*count = 1;
} else if *pre == cur_node.val {
*count += 1;
} else {
*count = 1;
};
match count.cmp(&max_count) {
std::cmp::Ordering::Equal => res.push(cur_node.val),
std::cmp::Ordering::Greater => {
*max_count = *count;
res.clear();
res.push(cur_node.val);
}
_ => {}
};
*pre = cur_node.val;
Self::search_bst(&cur_node.right, pre, res, count, max_count);
}
}
```
迭代:
```rust
pub fn find_mode(root: Option>>) -> Vec {
let (mut cur, mut pre) = (root, i32::MIN);
let mut res = vec![];
let mut stack = vec![];
let (mut count, mut max_count) = (0, 0);
while !stack.is_empty() || cur.is_some() {
while let Some(node) = cur {
cur = node.borrow().left.clone();
stack.push(node);
}
if let Some(node) = stack.pop() {
if pre == i32::MIN {
count = 1;
} else if pre == node.borrow().val {
count += 1;
} else {
count = 1;
}
match count.cmp(&max_count) {
std::cmp::Ordering::Equal => res.push(node.borrow().val),
std::cmp::Ordering::Greater => {
max_count = count;
res.clear();
res.push(node.borrow().val);
}
_ => {}
}
pre = node.borrow().val;
cur = node.borrow().right.clone();
}
}
res
}
```

