mirror of
https://github.com/Estom/notes.git
synced 2026-02-03 02:23:31 +08:00
operator
This commit is contained in:
@@ -14,6 +14,14 @@ CRD+Controller=decalartive API,声明式 API 设计是 kubernetes 重要的设
|
||||
* 通用的Operator,由各大云厂商开发,为了满足统一的云需求。
|
||||
* 专用型Operator,解决一个特定应用的自动化管理。
|
||||
|
||||
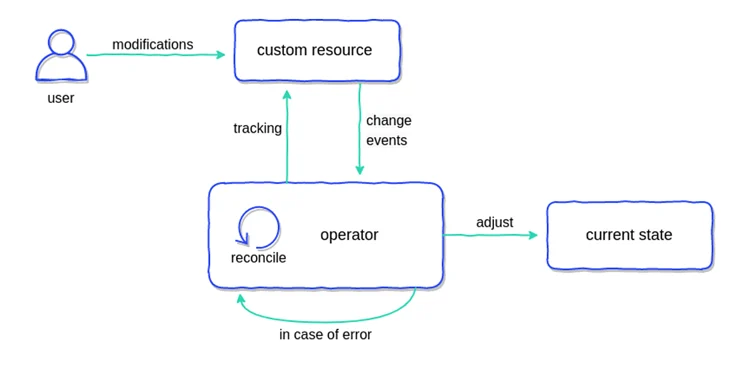
### Operator的运行原理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 开发方案
|
||||
|
||||
### 开发框架
|
||||
|
||||
Operator Framework 同样也是 CoreOS 开源的一个用于快速开发 Operator 的工具包,该框架包含两个主要的部分:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,5 +9,252 @@
|
||||
### 工作流程
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
## 2 执行流程
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2 使用流程
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装kubebuilder
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install kubebuilder
|
||||
kubebuilder version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建工程
|
||||
1. 初始化一个项目目录
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/ykl.com/customer-controller/
|
||||
|
||||
go mod init contollers.happyhacker.io
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. 定义crd所属的domain,生成一个工程.定义 crd 所属的 domain,这个指令会帮助你生成一个工程。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
kubebuilder init --domain controller.daocloud.io --license apache2 --owner "Holder"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建后的目录结构如下:
|
||||
* cmd目录下是启动脚本,编译后会在bin目录下生成manage可执行文件
|
||||
* config目录下是基础工程配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── Dockerfile
|
||||
├── Makefile
|
||||
├── PROJECT
|
||||
├── README.md
|
||||
├── cmd
|
||||
│ └── main.go
|
||||
├── config
|
||||
│ ├── default
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── manager_auth_proxy_patch.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── manager_config_patch.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── manager
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── manager.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── prometheus
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── monitor.yaml
|
||||
│ └── rbac
|
||||
│ ├── auth_proxy_client_clusterrole.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── auth_proxy_role.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── auth_proxy_role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── auth_proxy_service.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── leader_election_role.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── leader_election_role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ └── service_account.yaml
|
||||
├── go.mod
|
||||
├── go.sum
|
||||
└── hack
|
||||
└── boilerplate.go.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. 创建 crd 在 golang 工程中的结构体,以及其所需的 controller 逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
kubebuilder create api --group controller --version v1 --kind Application
|
||||
```
|
||||
关键文件主要包括以下三个部分。创建后的目录结构如下:
|
||||
* config/crd 用户自定义资源的定义。
|
||||
* config/sample controller,Reconcile函数实现了处理逻辑。
|
||||
* api/ crd和go模型的映射关系
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── Dockerfile
|
||||
├── Makefile
|
||||
├── PROJECT
|
||||
├── README.md
|
||||
├── api
|
||||
│ └── v1
|
||||
│ ├── application_types.go
|
||||
│ ├── groupversion_info.go
|
||||
│ └── zz_generated.deepcopy.go
|
||||
├── bin
|
||||
│ └── controller-gen
|
||||
├── cmd
|
||||
│ └── main.go
|
||||
├── config
|
||||
│ ├── crd
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomizeconfig.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── patches
|
||||
│ │ ├── cainjection_in_applications.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── webhook_in_applications.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── default
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── manager_auth_proxy_patch.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── manager_config_patch.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── manager
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── manager.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── prometheus
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── monitor.yaml
|
||||
│ ├── rbac
|
||||
│ │ ├── application_editor_role.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── application_viewer_role.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── auth_proxy_client_clusterrole.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── auth_proxy_role.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── auth_proxy_role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── auth_proxy_service.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── leader_election_role.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── leader_election_role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ │ ├── role_binding.yaml
|
||||
│ │ └── service_account.yaml
|
||||
│ └── samples
|
||||
│ ├── controller_v1_application.yaml
|
||||
│ └── kustomization.yaml
|
||||
├── go.mod
|
||||
├── go.sum
|
||||
├── hack
|
||||
│ └── boilerplate.go.txt
|
||||
└── internal
|
||||
└── controller
|
||||
├── application_controller.go
|
||||
└── suite_test.go
|
||||
|
||||
15 directories, 38 files
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义CRD&Controller
|
||||
|
||||
1. 修改types.go文件,添加用户自定义字段,运行make可以生成新的crd
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Copyright 2023 Holder.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
package v1
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EDIT THIS FILE! THIS IS SCAFFOLDING FOR YOU TO OWN!
|
||||
// NOTE: json tags are required. Any new fields you add must have json tags for the fields to be serialized.
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplicationSpec defines the desired state of Application
|
||||
type ApplicationSpec struct {
|
||||
// INSERT ADDITIONAL SPEC FIELDS - desired state of cluster
|
||||
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
|
||||
|
||||
// Foo is an example field of Application. Edit application_types.go to remove/update
|
||||
Foo string `json:"foo,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplicationStatus defines the observed state of Application
|
||||
type ApplicationStatus struct {
|
||||
// INSERT ADDITIONAL STATUS FIELD - define observed state of cluster
|
||||
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//+kubebuilder:object:root=true
|
||||
//+kubebuilder:subresource:status
|
||||
|
||||
// Application is the Schema for the applications API
|
||||
type Application struct {
|
||||
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
|
||||
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
|
||||
|
||||
Spec ApplicationSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
|
||||
Status ApplicationStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//+kubebuilder:object:root=true
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplicationList contains a list of Application
|
||||
type ApplicationList struct {
|
||||
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
|
||||
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
|
||||
Items []Application `json:"items"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
SchemeBuilder.Register(&Application{}, &ApplicationList{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
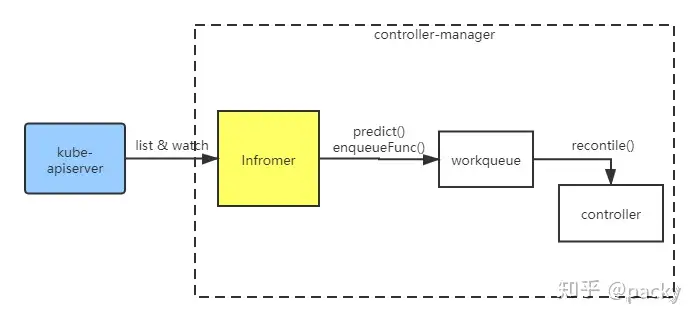
2. 修改contoller完善处理逻辑。controller对资源的监听依赖于Informer机制
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Informer 已经由kubebuilder和contorller-runtime 实现,监听到的资源的事件(创建、删除、更新、webhock)都会放在 Informer 中。然后这个事件会经过 predict()方法进行过滤,经过interface enqueue进行处理,最终放入 workqueue中。我们创建的 controller 则会依次从workqueue中拿取事件,并调用我们自己实现的 Recontile() 方法进行业务处理。控制器的处理函数,每当集群中有Sample资源的变动(CRUD),都会触发这个函数进行协调
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=sample.sample.io,resources=samples,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
|
||||
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=sample.sample.io,resources=samples/status,verbs=get;update;patch
|
||||
func (r *PlaybookReconciler) Reconcile(req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {
|
||||
_ = context.Background()
|
||||
_ = r.Log.WithValues("sample", req.NamespacedName)
|
||||
|
||||
// your logic here
|
||||
|
||||
return ctrl.Result{}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 部署crd和controller
|
||||
|
||||
部署operator主要包括两个步骤,一个是安装crd、一个是注册controller处理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
* 在项目主目录下执行make install,会自动调用 kustomize 创建部署 crd 的yml。执行 make run 则在本地启动 controller 主程序。
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ make run
|
||||
/root/go/bin/controller-gen object:headerFile="hack/boilerplate.go.txt" paths="./..."
|
||||
go fmt ./...
|
||||
go vet ./...
|
||||
/root/go/bin/controller-gen "crd:trivialVersions=true" rbac:roleName=manager-role webhook paths="./..." output:crd:artifacts:config=config/crd/bases
|
||||
go run ./main.go
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.839Z INFO controller-runtime.metrics metrics server is starting to listen {"addr": ":8081"}
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.840Z INFO setup starting manager
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.840Z INFO controller-runtime.manager starting metrics server {"path": "/metrics"}
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.840Z INFO controller-runtime.controller Starting EventSource {"controller": "sample", "source": "kind source: /, Kind="}
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.940Z INFO controller-runtime.controller Starting Controller {"controller": "sample"}
|
||||
2020-05-15T10:05:41.940Z INFO controller-runtime.controller Starting workers {"controller": "sample", "worker count": 1}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 以deployment 方式部署controller时,可以使用 Dockerfile 构建镜像,使用config/manager/manager.yml 部署。
|
||||
|
||||
333
kubenets/operator/04 处理逻辑.md
Normal file
333
kubenets/operator/04 处理逻辑.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,333 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在开发 operator,每种自定义资源只能包含有两种子资源——Status 和 Scale。这里探究一下Status的使用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 关键对象
|
||||
|
||||
### Status资源
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplicationSpec defines the desired state of Application
|
||||
type ApplicationSpec struct {
|
||||
// INSERT ADDITIONAL SPEC FIELDS - desired state of cluster
|
||||
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
|
||||
|
||||
// Foo is an example field of Application. Edit application_types.go to remove/update
|
||||
Foo string `json:"foo,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplicationStatus defines the observed state of Application
|
||||
type ApplicationStatus struct {
|
||||
// INSERT ADDITIONAL STATUS FIELD - define observed state of cluster
|
||||
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//+kubebuilder:object:root=true
|
||||
//+kubebuilder:subresource:status
|
||||
|
||||
// Application is the Schema for the applications API
|
||||
type Application struct {
|
||||
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
|
||||
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
|
||||
|
||||
Spec ApplicationSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
|
||||
Status ApplicationStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Spec 和 Status 都是 Sample 的成员变量,Status并不像Pod.Status一样,是Pod的subResource.因此,如果我们在controller的代码中调用到Status().Update(), 会触发panic,并报错:the server could not find the requested resource
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想像k8s中的设计那样,那么就要遵循k8s中status subresource的使用规范:
|
||||
|
||||
用户只能指定一个CRD实例的spec部分;
|
||||
CRD实例的status部分由控制器进行变更。
|
||||
此时我们需要在 Sample 中添加一行注解// +kubebuilder:subresource:status,标明 status 是 Sample 的子资源。
|
||||
|
||||
其实 Status 是一个非常重要的字段,在 Controller 中实现业务代码时,需要遵循 K8s 的声明式API的思想,因此需要依据 Status 的字段去进行 CR 处理的逻辑,即判断当前CR所处状态,对比其期望状态,然后做出一定的动作。
|
||||
|
||||
### eventRecorder
|
||||
|
||||
Status 字段用于 CR 的逻辑处理,但在后期维护过程中,则一部分会依赖于 CR 所产生的 Event,这有些类似于在 CR 的业务逻辑中添加部分重要的日志,最终可以帮助我们定位问题。后期运行过程中,可以通过 kubectl describe cr -n xxx 看到这些 Event。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在controller的处理对象中添加Log和Recorder,并在业务逻辑中记录
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type SampleReconciler struct {
|
||||
client.Client
|
||||
Log logr.Logger
|
||||
Scheme *runtime.Scheme
|
||||
Recorder record.EventRecorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 在业务逻辑中记录
|
||||
func (r *SampleReconciler) Reconcile(req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {
|
||||
sample := &samplev1.Sample{}
|
||||
_ := r.Get(ctx, client.ObjectKey{Name: req.Name, Namespace: req.Namespace}, sample)
|
||||
// do something
|
||||
r.Recorder.Eventf(sample, corev1.EventTypeWarning, "Error", "some error")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
K8s 为我们提供了2种等级的 event,分别是 Normal 和 Warning。
|
||||
|
||||
### finalizer
|
||||
|
||||
finalizer即终结器,存在于每一个k8s内的资源实例中,即**.metadata.finalizers,它是一个字符串数组,每一个成员表示一个finalizer。
|
||||
|
||||
控制器在删除某个资源时,K8s 会更新 CR 的 DeletionTimestamp 字段,这样会触发一个 Update 动作,我们的 controller 可以监听这个字段的变更,实现 CR 的预删除处理,比如删除由 CR 创建的某些资源。
|
||||
|
||||
当我们需要设计这类finalizer时,就可以自定义一个controller来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (c *SampleReconciler) finalize(ctx context.Context, sample *samplev1.Sample) error {
|
||||
logs := c.getLog(sample)
|
||||
// 这里我们自定义一个 finalizer 字段
|
||||
myFinalizerName := "sample.finalizers.io"
|
||||
|
||||
if sample.ObjectMeta.DeletionTimestamp.IsZero() {
|
||||
//这里由于 DeletionTimestamp 是0,即没有删除操作,则不进行处理,只检查 CR 中是否含有自定义 finalizer 字符,若没有则增加。
|
||||
if !containsString(sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers, myFinalizerName) {
|
||||
sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers = append(sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers, myFinalizerName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//进行预删除操作
|
||||
if containsString(sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers, myFinalizerName) {
|
||||
// do something
|
||||
// 从 CR 中删除自定义 finalizer 字段。
|
||||
sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers = removeString(sample.ObjectMeta.Finalizers, myFinalizerName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Reconsiler的处理
|
||||
|
||||
了解 controller-runtime 包的处理逻辑。Informer 机制在包中已经实现,我们就不再过多关注,假设现在已经监听到 CR 的变化事件(包括 创建、更新、删除、扩展),这个事件则会进入 WorkQueue 中。在进入 WorkQueue 之前, controller-runtime 会进行一些过滤处理和业务处理。主要涉及接口是 EventHandler 和 Predicate。
|
||||
|
||||
EventHandler 可以在事件入队列之前加入其他逻辑,其定义如下
|
||||
|
||||
### EventHandler
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
//controller-runtime@v0.5.0\pkg\handler\eventhandler.go
|
||||
//此处定义了针对不同事件的处理接口,我们可以通过实现此接口完成扩展业务逻辑
|
||||
type EventHandler interface {
|
||||
// Create is called in response to an create event - e.g. Pod Creation.
|
||||
Create(event.CreateEvent, workqueue.RateLimitingInterface)
|
||||
|
||||
// Update is called in response to an update event - e.g. Pod Updated.
|
||||
Update(event.UpdateEvent, workqueue.RateLimitingInterface)
|
||||
|
||||
// Delete is called in response to a delete event - e.g. Pod Deleted.
|
||||
Delete(event.DeleteEvent, workqueue.RateLimitingInterface)
|
||||
|
||||
// Generic is called in response to an event of an unknown type or a synthetic event triggered as a cron or
|
||||
// external trigger request - e.g. reconcile Autoscaling, or a Webhook.
|
||||
Generic(event.GenericEvent, workqueue.RateLimitingInterface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Predicate
|
||||
|
||||
Predicate 则是对监听到的事件进行过滤,让我们只关注我们想要的时间,其结构体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type Predicate interface {
|
||||
// Create returns true if the Create event should be processed
|
||||
Create(event.CreateEvent) bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Delete returns true if the Delete event should be processed
|
||||
Delete(event.DeleteEvent) bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Update returns true if the Update event should be processed
|
||||
Update(event.UpdateEvent) bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Generic returns true if the Generic event should be processed
|
||||
Generic(event.GenericEvent) bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### controller-runtime的处理逻辑如下
|
||||
```go
|
||||
//controller-runtime@v0.5.0\pkg\source\internal\eventsource.go
|
||||
type EventHandler struct {
|
||||
EventHandler handler.EventHandler
|
||||
Queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
|
||||
Predicates []predicate.Predicate
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e EventHandler) OnAdd(obj interface{}) {
|
||||
c := event.CreateEvent{}
|
||||
...
|
||||
// 这里可以自定义 Predicates,将事件进行过滤
|
||||
for _, p := range e.Predicates {
|
||||
if !p.Create(c) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 调用了上面的 EventHandler 对应的逻辑
|
||||
e.EventHandler.Create(c, e.Queue)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 除了 OnAdd 外,还有 OnUpdate OnDelete
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终入队列的数据结构如下,即只有 namespace 和name,并没有资源的类型。
|
||||
```
|
||||
type NamespacedName struct {
|
||||
Namespace string
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 controller-runtime 包中的 controller.Start()方法中,则会循环从队列中拿取一个事件
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// controller.go
|
||||
func (c *Controller) Start(stop <-chan struct{}) error {
|
||||
...
|
||||
// 启动多个 worker 线程,处理事件
|
||||
log.Info("Starting workers", "controller", c.Name, "worker count", c.MaxConcurrentReconciles)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < c.MaxConcurrentReconciles; i++ {
|
||||
go wait.Until(c.worker, c.JitterPeriod, stop)
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
func (c *Controller) worker() {
|
||||
for c.processNextWorkItem() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
func (c *Controller) processNextWorkItem() bool {
|
||||
// 拿取一个事件
|
||||
obj, shutdown := c.Queue.Get()
|
||||
if shutdown {
|
||||
// Stop working
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We call Done here so the workqueue knows we have finished
|
||||
// processing this item. We also must remember to call Forget if we
|
||||
// do not want this work item being re-queued. For example, we do
|
||||
// not call Forget if a transient error occurs, instead the item is
|
||||
// put back on the workqueue and attempted again after a back-off
|
||||
// period.
|
||||
defer c.Queue.Done(obj)
|
||||
//处理事件
|
||||
return c.reconcileHandler(obj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 监控多个资源变化(如何监听)
|
||||
|
||||
可能会遇到 CR -> Deployment -> Pod 的逻辑,即由CR 创建deployment,最终落入pod。这时,我们不仅需要监听 CR 的变化, deployment 以及 pod 的变化我们也需要关注,这就意味着我们在 reconciler 中也需要根据deployment变化进行相应的处理。我们在SampleReconciler的SetupWithManager方法中,可以看到:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (r *SampleReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
|
||||
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
|
||||
For(&samplev1.Sample{}).
|
||||
Complete(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里的 For 则可以指定需要监听的资源。进一步,我们看NewControllerManagedBy()的源码可以发现pkg\builder\controller.go 中实现了 构建者模式,controller-runtime 提供了一个 builder 方便我们进行配置。其中监听资源的有 For() Owns() 和Watch() ,For() Owns()都是基于Watch()实现,只不过是入队列前的 eventHandler 不同。
|
||||
|
||||
简单来说,我们可以调用Watch()实现监听deployment
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (r *SampleReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
|
||||
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
|
||||
For(&samplev1.Sample{}).
|
||||
// 这里可以供我们指定 eventhandler
|
||||
Watches(&source.Kind{Type: &apps.Deployment{}}, &handler.EnqueueRequestForObject{}).
|
||||
Complete(r)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但这样做会监听所有 deployment 事件变化,如果我们想只关注由 CR 创建的 Deployment 因此我们可以采用 Owns() 方法。
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (r *SampleReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
|
||||
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
|
||||
For(&samplev1.Sample{}).
|
||||
// 这里可以供我们指定 eventhandler
|
||||
Owns(&apps.Deployment{}).
|
||||
Complete(r)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当我们使用 CR 创建 deployment 时,可以为他塞入一个从属关系,类似于 Pod 资源的Metadata 里会有一个OnwerReference字段.这样在监听时,只会监听到带有 OwnerShip 的 deployment。
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
_ = controllerutil.SetControllerReference(sample, &deployment, r.Scheme)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 监听多资源下evnetHandler 和 Reconciler 的逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们的 controller Reconciler 业务逻辑,实际上只应该处理 CR 的变化,但有时是 CR 所拥有的 Deployment 发生了变化,但对应的 CR 并不会有更新事件,因此我们需要在自定义eventHandler中,对资源进行判断。若是 CR 的变化,则直接向队列写入 namespace 和 name,若是 deployment 的变化,则向队列写入 deployment 对应 CR 的namespace 和name,触发 Reconciler 的逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (e *EnqueueRequestForDP) Create(evt event.CreateEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
|
||||
if evt.Meta == nil {
|
||||
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "CreateEvent received with no metadata", "event", evt)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, ok := evt.Object.(*samplev1.Sample)
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
|
||||
Name: evt.Meta.Name,
|
||||
Namespace: evt.Meta.GetNamespace(),
|
||||
}})
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
deploy ,_:= evt.Object.(*v1.Deployment)
|
||||
for _, owner := range deploy.OwnerReferences {
|
||||
if owner.Kind == "Sample" {
|
||||
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
|
||||
Name: owner.Name,
|
||||
Namespace: evt.Meta.GetNamespace(),
|
||||
}})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 监听指定字段变化
|
||||
|
||||
依据上文,自定义 predicate 即可实现。 比如我们只对 CR 改变 label 的事件感兴趣,我们此时可以自定义 Predicate 以及其 OnUpdate() 方法
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func (rl *ResourceLabelChangedPredicate) Update (e event.UpdateEvent) bool{
|
||||
_, ok1 = e.ObjectOld.(*samplev1.Sample)
|
||||
_, ok2 = e.ObjectNew.(*samplev1.Sample)
|
||||
if ok1 && ok2 {
|
||||
if !compareMaps(e.MetaOld.GetLabels(), e.MetaNew.GetLabels()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当我们监听多个资源后, deployment 的更新事件也会进入到这个方法,所以在方法中,需要通过 _, ok = e.Object(*xxx) 判断资源的类型。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 多版本切换
|
||||
|
||||
在crd的开发和演进过程中,必然会存在一个crd的不同版本。 kubebuilder支持以一个conversion webhook的方式,支持对一个crd资源以不同版本进行读取。简单地描述就是:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
kubectl apply -f config/samples/batch_v2_cronjob.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个v2的cronjob后,可以通过v1和v2两种版本进行读取:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
kubectl get cronjobs.v2.batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io -o yaml
|
||||
kubectl get cronjobs.v1.batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io -o yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
显然,get命令得到的v1和v2版本的cronjob会存在一些字段上的不同,conversion webhook会负责进行不同版本的cronjob之间的数据转换。
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user