mirror of
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master.git
synced 2026-02-02 18:39:09 +08:00
864 lines
28 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
864 lines
28 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
|
||
* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
|
||
* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
|
||
|
||
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
|
||
|
||
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
|
||
|
||
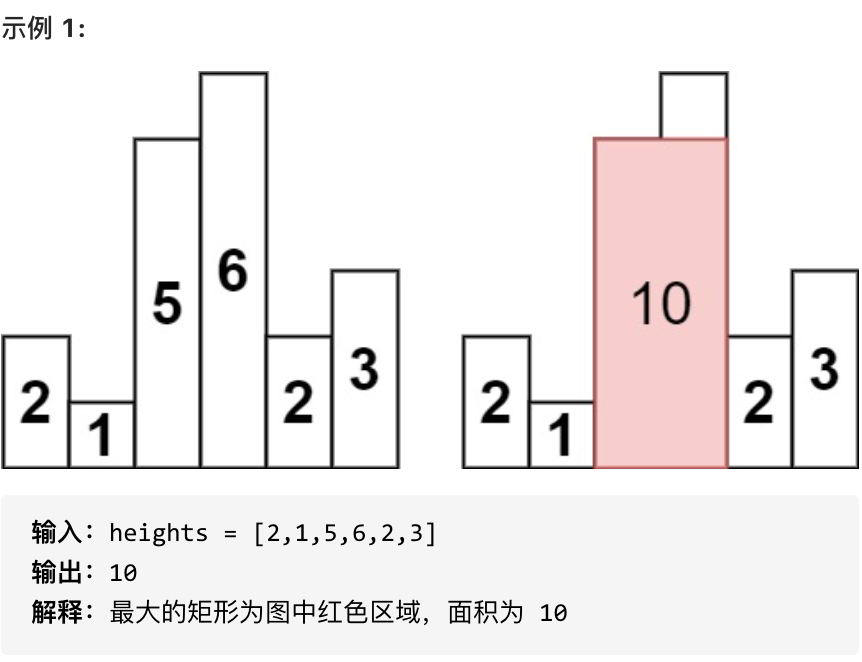
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
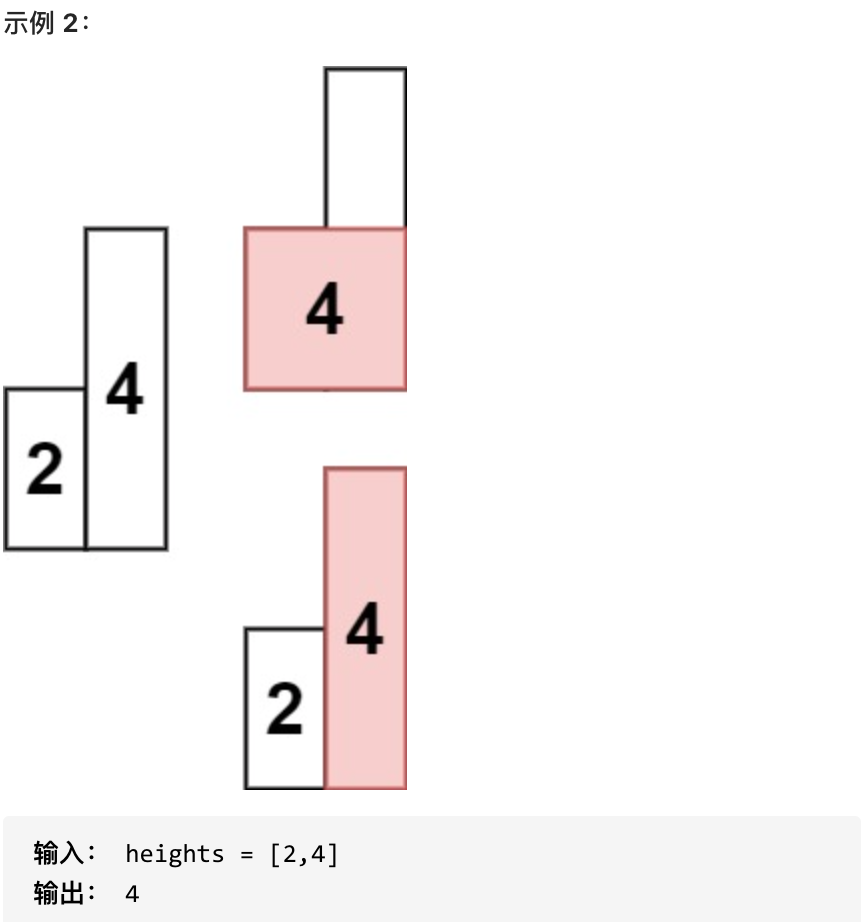
* 1 <= heights.length <=10^5
|
||
* 0 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
|
||
|
||
## 算法公开课
|
||
|
||
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[单调栈,又一次经典来袭! LeetCode:84.柱状图中最大的矩形](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ns4y1o7uB/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
本题和[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html),是遥相呼应的两道题目,建议都要仔细做一做,原理上有很多相同的地方,但细节上又有差异,更可以加深对单调栈的理解!
|
||
|
||
其实这两道题目先做那一道都可以,但我先写的42.接雨水的题解,所以如果没做过接雨水的话,建议先做一做接雨水,可以参考我的题解:[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)
|
||
|
||
我们先来看一下暴力解法的解法:
|
||
|
||
### 暴力解法
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
|
||
int sum = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
|
||
int left = i;
|
||
int right = i;
|
||
for (; left >= 0; left--) {
|
||
if (heights[left] < heights[i]) break;
|
||
}
|
||
for (; right < heights.size(); right++) {
|
||
if (heights[right] < heights[i]) break;
|
||
}
|
||
int w = right - left - 1;
|
||
int h = heights[i];
|
||
sum = max(sum, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如上代码并不能通过leetcode,超时了,因为时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$。
|
||
|
||
### 双指针解法
|
||
|
||
本题双指针的写法整体思路和[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)是一致的,但要比[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)难一些。
|
||
|
||
难就难在本题要记录记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标,而不是左边第一个小于该柱子的高度。
|
||
|
||
所以需要循环查找,也就是下面在寻找的过程中使用了while,详细请看下面注释,整理思路在题解:[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)中已经介绍了。
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
|
||
vector<int> minLeftIndex(heights.size());
|
||
vector<int> minRightIndex(heights.size());
|
||
int size = heights.size();
|
||
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minLeftIndex[0] = -1; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
|
||
int t = i - 1;
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
|
||
while (t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = minLeftIndex[t];
|
||
minLeftIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minRightIndex[size - 1] = size; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for (int i = size - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
int t = i + 1;
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
|
||
while (t < size && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = minRightIndex[t];
|
||
minRightIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 求和
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||
int sum = heights[i] * (minRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1);
|
||
result = max(sum, result);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 单调栈
|
||
|
||
本地单调栈的解法和接雨水的题目是遥相呼应的。
|
||
|
||
为什么这么说呢,[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)是找每个柱子左右两边第一个大于该柱子高度的柱子,而本题是找每个柱子左右两边第一个小于该柱子的柱子。
|
||
|
||
**这里就涉及到了单调栈很重要的性质,就是单调栈里的顺序,是从小到大还是从大到小**。
|
||
|
||
在题解[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)中我讲解了接雨水的单调栈从栈头(元素从栈头弹出)到栈底的顺序应该是从小到大的顺序。
|
||
|
||
那么因为本题是要找每个柱子左右两边第一个小于该柱子的柱子,所以从栈头(元素从栈头弹出)到栈底的顺序应该是从大到小的顺序!
|
||
|
||
我来举一个例子,如图:
|
||
|
||
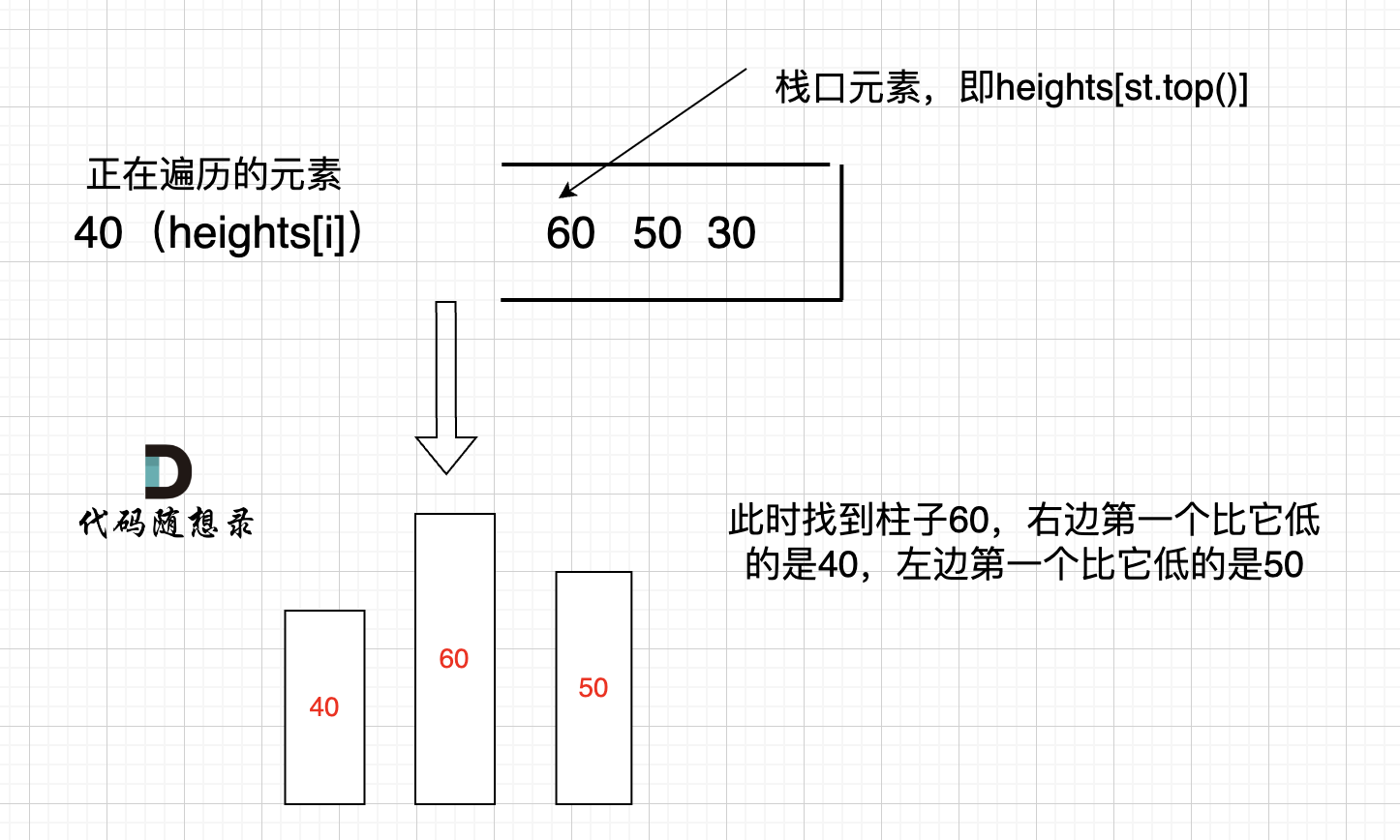
|
||
|
||
只有栈里从大到小的顺序,才能保证栈顶元素找到左右两边第一个小于栈顶元素的柱子。
|
||
|
||
所以本题单调栈的顺序正好与接雨水反过来。
|
||
|
||
此时大家应该可以发现其实就是**栈顶和栈顶的下一个元素以及要入栈的三个元素组成了我们要求最大面积的高度和宽度**
|
||
|
||
理解这一点,对单调栈就掌握的比较到位了。
|
||
|
||
除了栈内元素顺序和接雨水不同,剩下的逻辑就都差不多了,在题解[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)我已经对单调栈的各个方面做了详细讲解,这里就不赘述了。
|
||
|
||
主要就是分析清楚如下三种情况:
|
||
|
||
* 情况一:当前遍历的元素heights[i]大于栈顶元素heights[st.top()]的情况
|
||
* 情况二:当前遍历的元素heights[i]等于栈顶元素heights[st.top()]的情况
|
||
* 情况三:当前遍历的元素heights[i]小于栈顶元素heights[st.top()]的情况
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
// 版本一
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
stack<int> st;
|
||
heights.insert(heights.begin(), 0); // 数组头部加入元素0
|
||
heights.push_back(0); // 数组尾部加入元素0
|
||
st.push(0);
|
||
|
||
// 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < heights.size(); i++) {
|
||
if (heights[i] > heights[st.top()]) { // 情况一
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
} else if (heights[i] == heights[st.top()]) { // 情况二
|
||
st.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
} else { // 情况三
|
||
while (!st.empty() && heights[i] < heights[st.top()]) { // 注意是while
|
||
int mid = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
if (!st.empty()) {
|
||
int left = st.top();
|
||
int right = i;
|
||
int w = right - left - 1;
|
||
int h = heights[mid];
|
||
result = max(result, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
细心的录友会发现,我在 height数组上后,都加了一个元素0, 为什么这么做呢?
|
||
|
||
首先来说末尾为什么要加元素0?
|
||
|
||
如果数组本身就是升序的,例如[2,4,6,8],那么入栈之后 都是单调递减,一直都没有走 情况三 计算结果的哪一步,所以最后输出的就是0了。 如图:
|
||
|
||
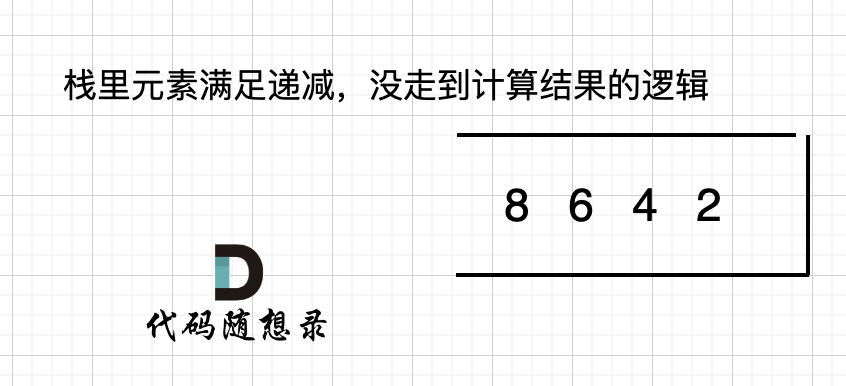
|
||
|
||
那么结尾加一个0,就会让栈里的所有元素,走到情况三的逻辑。
|
||
|
||
|
||
开头为什么要加元素0?
|
||
|
||
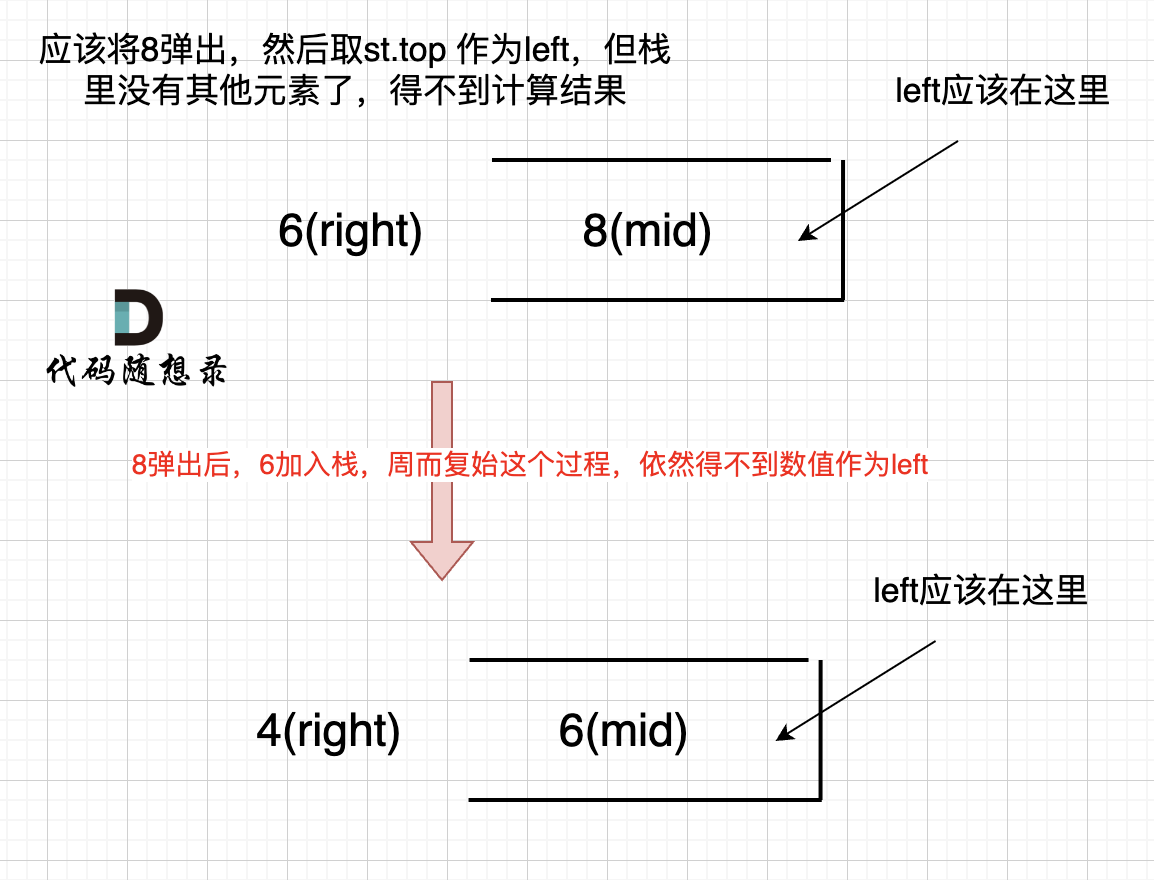
如果数组本身是降序的,例如 [8,6,4,2],在 8 入栈后,6 开始与8 进行比较,此时我们得到 mid(8),right(6),但是得不到 left。
|
||
|
||
(mid、left,right 都是对应版本一里的逻辑)
|
||
|
||
因为 将 8 弹出之后,栈里没有元素了,那么为了避免空栈取值,直接跳过了计算结果的逻辑。
|
||
|
||
之后又将6 加入栈(此时8已经弹出了),然后 就是 4 与 栈口元素 6 进行比较,周而复始,那么计算的最后结果result就是0。 如图所示:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
所以我们需要在 height数组前后各加一个元素0。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
版本一代码精简之后:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
// 版本二
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
|
||
stack<int> st;
|
||
heights.insert(heights.begin(), 0); // 数组头部加入元素0
|
||
heights.push_back(0); // 数组尾部加入元素0
|
||
st.push(0);
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < heights.size(); i++) {
|
||
while (heights[i] < heights[st.top()]) {
|
||
int mid = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
int w = i - st.top() - 1;
|
||
int h = heights[mid];
|
||
result = max(result, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
这里我依然建议大家按部就班把版本一写出来,把情况一二三分析清楚,然后在精简代码到版本二。 直接看版本二容易忽略细节!
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java:
|
||
|
||
暴力解法:
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
|
||
int length = heights.length;
|
||
int[] minLeftIndex = new int [length];
|
||
int[] minRightIndex = new int [length];
|
||
// 记录左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minLeftIndex[0] = -1 ;
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||
int t = i - 1;
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
|
||
while (t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = minLeftIndex[t];
|
||
minLeftIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 记录每个柱子右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minRightIndex[length - 1] = length;
|
||
for (int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
int t = i + 1;
|
||
while(t < length && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = minRightIndex[t];
|
||
minRightIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 求和
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||
int sum = heights[i] * (minRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1);
|
||
result = Math.max(sum, result);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
单调栈:
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
|
||
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
|
||
|
||
// 数组扩容,在头和尾各加入一个元素
|
||
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
|
||
newHeights[0] = 0;
|
||
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
|
||
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
|
||
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
heights = newHeights;
|
||
|
||
st.push(0);
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
// 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < heights.length; i++) {
|
||
// 注意heights[i] 是和heights[st.top()] 比较 ,st.top()是下标
|
||
if (heights[i] > heights[st.peek()]) {
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
} else if (heights[i] == heights[st.peek()]) {
|
||
st.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
} else {
|
||
while (heights[i] < heights[st.peek()]) { // 注意是while
|
||
int mid = st.peek();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
int left = st.peek();
|
||
int right = i;
|
||
int w = right - left - 1;
|
||
int h = heights[mid];
|
||
result = Math.max(result, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
st.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
单调栈精简
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
|
||
int[] newHeight = new int[heights.length + 2];
|
||
System.arraycopy(heights, 0, newHeight, 1, heights.length);
|
||
newHeight[heights.length+1] = 0;
|
||
newHeight[0] = 0;
|
||
|
||
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
|
||
stack.push(0);
|
||
|
||
int res = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 1; i < newHeight.length; i++) {
|
||
while (newHeight[i] < newHeight[stack.peek()]) {
|
||
int mid = stack.pop();
|
||
int w = i - stack.peek() - 1;
|
||
int h = newHeight[mid];
|
||
res = Math.max(res, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python3:
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
|
||
# 暴力解法(leetcode超时)
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
# 从左向右遍历:以每一根柱子为主心骨(当前轮最高的参照物),迭代直到找到左侧和右侧各第一个矮一级的柱子
|
||
res = 0
|
||
|
||
for i in range(len(heights)):
|
||
left = i
|
||
right = i
|
||
# 向左侧遍历:寻找第一个矮一级的柱子
|
||
for _ in range(left, -1, -1):
|
||
if heights[left] < heights[i]:
|
||
break
|
||
left -= 1
|
||
# 向右侧遍历:寻找第一个矮一级的柱子
|
||
for _ in range(right, len(heights)):
|
||
if heights[right] < heights[i]:
|
||
break
|
||
right += 1
|
||
|
||
width = right - left - 1
|
||
height = heights[i]
|
||
res = max(res, width * height)
|
||
|
||
return res
|
||
|
||
# 双指针
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
size = len(heights)
|
||
# 两个DP数列储存的均是下标index
|
||
min_left_index = [0] * size
|
||
min_right_index = [0] * size
|
||
result = 0
|
||
|
||
# 记录每个柱子的左侧第一个矮一级的柱子的下标
|
||
min_left_index[0] = -1 # 初始化防止while死循环
|
||
for i in range(1, size):
|
||
# 以当前柱子为主心骨,向左迭代寻找次级柱子
|
||
temp = i - 1
|
||
while temp >= 0 and heights[temp] >= heights[i]:
|
||
# 当左侧的柱子持续较高时,尝试这个高柱子自己的次级柱子(DP
|
||
temp = min_left_index[temp]
|
||
# 当找到左侧矮一级的目标柱子时
|
||
min_left_index[i] = temp
|
||
|
||
# 记录每个柱子的右侧第一个矮一级的柱子的下标
|
||
min_right_index[size-1] = size # 初始化防止while死循环
|
||
for i in range(size-2, -1, -1):
|
||
# 以当前柱子为主心骨,向右迭代寻找次级柱子
|
||
temp = i + 1
|
||
while temp < size and heights[temp] >= heights[i]:
|
||
# 当右侧的柱子持续较高时,尝试这个高柱子自己的次级柱子(DP
|
||
temp = min_right_index[temp]
|
||
# 当找到右侧矮一级的目标柱子时
|
||
min_right_index[i] = temp
|
||
|
||
for i in range(size):
|
||
area = heights[i] * (min_right_index[i] - min_left_index[i] - 1)
|
||
result = max(area, result)
|
||
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
# 单调栈
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
# Monotonic Stack
|
||
'''
|
||
找每个柱子左右侧的第一个高度值小于该柱子的柱子
|
||
单调栈:栈顶到栈底:从大到小(每插入一个新的小数值时,都要弹出先前的大数值)
|
||
栈顶,栈顶的下一个元素,即将入栈的元素:这三个元素组成了最大面积的高度和宽度
|
||
情况一:当前遍历的元素heights[i]大于栈顶元素的情况
|
||
情况二:当前遍历的元素heights[i]等于栈顶元素的情况
|
||
情况三:当前遍历的元素heights[i]小于栈顶元素的情况
|
||
'''
|
||
|
||
# 输入数组首尾各补上一个0(与42.接雨水不同的是,本题原首尾的两个柱子可以作为核心柱进行最大面积尝试
|
||
heights.insert(0, 0)
|
||
heights.append(0)
|
||
stack = [0]
|
||
result = 0
|
||
for i in range(1, len(heights)):
|
||
# 情况一
|
||
if heights[i] > heights[stack[-1]]:
|
||
stack.append(i)
|
||
# 情况二
|
||
elif heights[i] == heights[stack[-1]]:
|
||
stack.pop()
|
||
stack.append(i)
|
||
# 情况三
|
||
else:
|
||
# 抛出所有较高的柱子
|
||
while stack and heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]]:
|
||
# 栈顶就是中间的柱子,主心骨
|
||
mid_index = stack[-1]
|
||
stack.pop()
|
||
if stack:
|
||
left_index = stack[-1]
|
||
right_index = i
|
||
width = right_index - left_index - 1
|
||
height = heights[mid_index]
|
||
result = max(result, width * height)
|
||
stack.append(i)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
# 单调栈精简
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
heights.insert(0, 0)
|
||
heights.append(0)
|
||
stack = [0]
|
||
result = 0
|
||
for i in range(1, len(heights)):
|
||
while stack and heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]]:
|
||
mid_height = heights[stack[-1]]
|
||
stack.pop()
|
||
if stack:
|
||
# area = width * height
|
||
area = (i - stack[-1] - 1) * mid_height
|
||
result = max(area, result)
|
||
stack.append(i)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go:
|
||
|
||
暴力解法
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
|
||
sum := 0
|
||
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
|
||
left, right := i, i
|
||
for left >= 0 {
|
||
if heights[left] < heights[i] {
|
||
break
|
||
}
|
||
left--
|
||
}
|
||
for right < len(heights) {
|
||
if heights[right] < heights[i] {
|
||
break
|
||
}
|
||
right++
|
||
}
|
||
w := right - left - 1
|
||
h := heights[i]
|
||
sum = max(sum, w * h)
|
||
}
|
||
return sum
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func max(x, y int) int {
|
||
if x > y {
|
||
return x
|
||
}
|
||
return y
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
双指针解法
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
|
||
size := len(heights)
|
||
minLeftIndex := make([]int, size)
|
||
minRightIndex := make([]int, size)
|
||
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minLeftIndex[0] = -1 // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for i := 1; i < size; i++ {
|
||
t := i - 1
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
|
||
for t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
|
||
t = minLeftIndex[t]
|
||
}
|
||
minLeftIndex[i] = t
|
||
}
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minRightIndex[size - 1] = size; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for i := size - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||
t := i + 1
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
|
||
for t < size && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
|
||
t = minRightIndex[t]
|
||
}
|
||
minRightIndex[i] = t
|
||
}
|
||
// 求和
|
||
result := 0
|
||
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
|
||
sum := heights[i] * (minRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1)
|
||
result = max(sum, result)
|
||
}
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func max(x, y int) int {
|
||
if x > y {
|
||
return x
|
||
}
|
||
return y
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
单调栈
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
|
||
result := 0
|
||
heights = append([]int{0}, heights...) // 数组头部加入元素0
|
||
heights = append(heights, 0) // 数组尾部加入元素0
|
||
st := []int{0}
|
||
|
||
// 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
|
||
for i := 1; i < len(heights); i++ {
|
||
if heights[i] > heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||
st = append(st, i)
|
||
} else if heights[i] == heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||
st = st[:len(st)-1]
|
||
st = append(st, i)
|
||
} else {
|
||
for len(st) > 0 && heights[i] < heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||
mid := st[len(st)-1]
|
||
st = st[:len(st)-1]
|
||
if len(st) > 0 {
|
||
left := st[len(st)-1]
|
||
right := i
|
||
w := right - left - 1
|
||
h := heights[mid]
|
||
result = max(result, w * h)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
st = append(st, i)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func max(x, y int) int {
|
||
if x > y {
|
||
return x
|
||
}
|
||
return y
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
单调栈精简
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
|
||
max := 0
|
||
// 使用切片实现栈
|
||
stack := make([]int, 0)
|
||
// 数组头部加入0
|
||
heights = append([]int{0}, heights...)
|
||
// 数组尾部加入0
|
||
heights = append(heights, 0)
|
||
// 初始化栈,序号从0开始
|
||
stack = append(stack, 0)
|
||
for i := 1; i < len(heights); i ++ {
|
||
// 结束循环条件为:当即将入栈元素>top元素,也就是形成非单调递增的趋势
|
||
for heights[stack[len(stack) - 1]] > heights[i] {
|
||
// mid 是top
|
||
mid := stack[len(stack) - 1]
|
||
// 出栈
|
||
stack = stack[0 : len(stack) - 1]
|
||
// left是top的下一位元素,i是将要入栈的元素
|
||
left := stack[len(stack) - 1]
|
||
// 高度x宽度
|
||
tmp := heights[mid] * (i - left - 1)
|
||
if tmp > max {
|
||
max = tmp
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
stack = append(stack, i)
|
||
}
|
||
return max
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### JavaScript:
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
//双指针 js中运行速度最快
|
||
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
|
||
const len = heights.length;
|
||
const minLeftIndex = new Array(len);
|
||
const maxRightIndex = new Array(len);
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
minLeftIndex[0] = -1; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for(let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
|
||
let t = i - 1;
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
|
||
while (t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]) {
|
||
t = minLeftIndex[t];
|
||
}
|
||
minLeftIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
|
||
maxRightIndex[len - 1] = len; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
|
||
for(let i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--){
|
||
let t = i + 1;
|
||
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
|
||
while (t <= n && heights[t] > heights[i]) {
|
||
t = maxRightIndex[t];
|
||
}
|
||
maxRightIndex[i] = t;
|
||
}
|
||
// 求和
|
||
let maxArea = 0;
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++){
|
||
let sum = heights[i] * (maxRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1);
|
||
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea , sum);
|
||
}
|
||
return maxArea;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
//单调栈
|
||
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
|
||
let maxArea = 0;
|
||
const stack = [0];
|
||
heights.push(0);
|
||
const n = heights.length;
|
||
|
||
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
|
||
let top = stack.at(-1);
|
||
// 情况三
|
||
if (heights[top] < heights[i]) {
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
// 情况二
|
||
if (heights[top] === heights[i]) {
|
||
stack.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
// 情况一
|
||
if (heights[top] > heights[i]) {
|
||
while (stack.length > 0 && heights[top] > heights[i]) {
|
||
// 栈顶元素出栈,并保存栈顶bar的索引
|
||
const h = heights[stack.pop()];
|
||
const left = stack.at(-1) ?? -1;
|
||
const w = i - left - 1;
|
||
// 计算面积,并取最大面积
|
||
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, w * h);
|
||
top = stack.at(-1);
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return maxArea;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
//单调栈 简洁
|
||
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
|
||
let maxArea = 0;
|
||
const stack = [];
|
||
heights = [0,...heights,0]; // 数组头部加入元素0 数组尾部加入元素0
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < heights.length; i++){ // 只用考虑情况一 当前遍历的元素heights[i]小于栈顶元素heights[stack[stack.length-1]]]的情况
|
||
while(heights[i] < heights[stack[stack.length-1]]){// 当前bar比栈顶bar矮
|
||
const stackTopIndex = stack.pop();// 栈顶元素出栈,并保存栈顶bar的索引
|
||
let w = i - stack[stack.length -1] - 1;
|
||
let h = heights[stackTopIndex]
|
||
// 计算面积,并取最大面积
|
||
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, w * h);
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(i);// 当前bar比栈顶bar高了,入栈
|
||
}
|
||
return maxArea;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
### TypeScript:
|
||
|
||
> 暴力法(会超时):
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||
for (let i = 0, length = heights.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||
// 左开右开
|
||
let left: number = i - 1,
|
||
right: number = i + 1;
|
||
while (left >= 0 && heights[left] >= heights[i]) {
|
||
left--;
|
||
}
|
||
while (right < length && heights[right] >= heights[i]) {
|
||
right++;
|
||
}
|
||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, heights[i] * (right - left - 1));
|
||
}
|
||
return resMax;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 双指针预处理:
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||
const length: number = heights.length;
|
||
const leftHeightDp: number[] = [],
|
||
rightHeightDp: number[] = [];
|
||
leftHeightDp[0] = -1;
|
||
rightHeightDp[length - 1] = length;
|
||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||
let j = i - 1;
|
||
while (j >= 0 && heights[i] <= heights[j]) {
|
||
j = leftHeightDp[j];
|
||
}
|
||
leftHeightDp[i] = j;
|
||
}
|
||
for (let i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
let j = i + 1;
|
||
while (j < length && heights[i] <= heights[j]) {
|
||
j = rightHeightDp[j];
|
||
}
|
||
rightHeightDp[i] = j;
|
||
}
|
||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||
let area = heights[i] * (rightHeightDp[i] - leftHeightDp[i] - 1);
|
||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, area);
|
||
}
|
||
return resMax;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 单调栈:
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||
heights.push(0);
|
||
const length: number = heights.length;
|
||
// 栈底->栈顶:严格单调递增
|
||
const stack: number[] = [];
|
||
stack.push(0);
|
||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||
let top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||
if (heights[top] < heights[i]) {
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
} else if (heights[top] === heights[i]) {
|
||
stack.pop();
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
} else {
|
||
while (stack.length > 0 && heights[top] > heights[i]) {
|
||
let mid = stack.pop();
|
||
let left = stack.length > 0 ? stack[stack.length - 1] : -1;
|
||
let w = i - left - 1;
|
||
let h = heights[mid];
|
||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, w * h);
|
||
top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return resMax;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Rust:
|
||
|
||
双指针预处理
|
||
```rust
|
||
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn largest_rectangle_area(v: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||
let n = v.len();
|
||
let mut left_smaller_idx = vec![-1; n];
|
||
let mut right_smaller_idx = vec![n as i32; n];
|
||
for i in 1..n {
|
||
let mut mid = i as i32 - 1;
|
||
while mid >= 0 && v[mid as usize] >= v[i] {
|
||
mid = left_smaller_idx[mid as usize];
|
||
}
|
||
left_smaller_idx[i] = mid;
|
||
}
|
||
for i in (0..n-1).rev() {
|
||
let mut mid = i + 1;
|
||
while mid < n && v[mid] >= v[i] {
|
||
mid = right_smaller_idx[mid] as usize;
|
||
}
|
||
right_smaller_idx[i] = mid as i32;
|
||
}
|
||
let mut res = 0;
|
||
for (idx, &e) in v.iter().enumerate() {
|
||
res = res.max((right_smaller_idx[idx] - left_smaller_idx[idx] - 1) * e);
|
||
}
|
||
dbg!(res)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
单调栈
|
||
```rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn largest_rectangle_area1(mut v: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||
v.insert(0, 0); // 便于使第一个元素能够有左侧<=它的值
|
||
v.push(0); // 便于在结束处理最后一个元素后清空残留在栈中的值
|
||
let mut res = 0;
|
||
let mut stack = vec![]; // 递增的栈
|
||
for (idx, &e) in v.iter().enumerate() {
|
||
while !stack.is_empty() && v[*stack.last().unwrap()] > e {
|
||
let pos = stack.pop().unwrap();
|
||
let prev_pos = *stack.last().unwrap();
|
||
let s = (idx - prev_pos - 1) as i32 * v[pos];
|
||
res = res.max(s);
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(idx);
|
||
}
|
||
res
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|