mirror of
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master.git
synced 2026-02-02 18:39:09 +08:00
550 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
550 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
|
||
* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
|
||
* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/)
|
||
|
||
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
|
||
|
||
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
|
||
|
||
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
|
||
节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
|
||
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
|
||
|
||
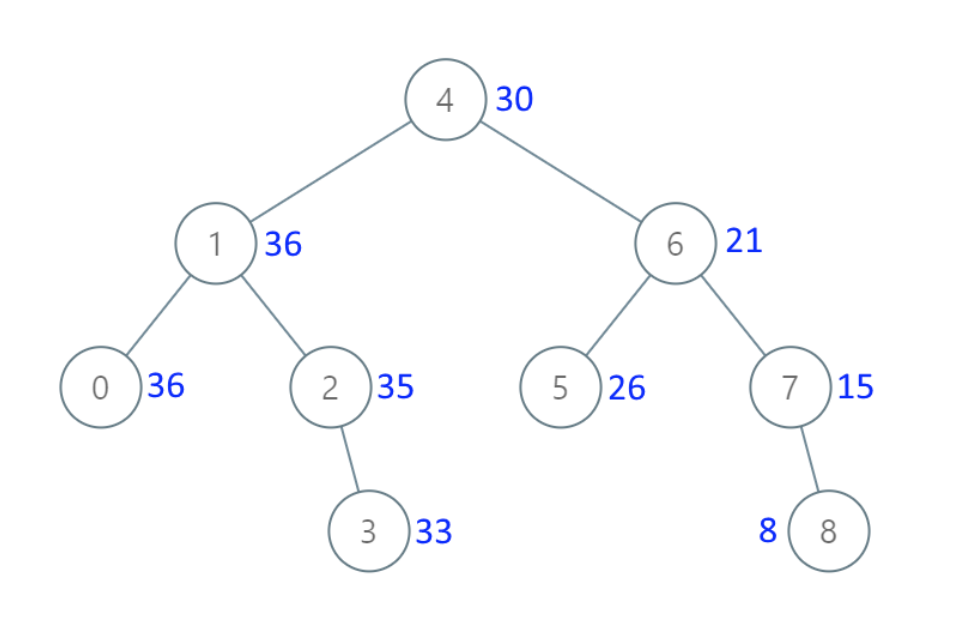
|
||
|
||
* 输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
|
||
* 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
* 输入:root = [0,null,1]
|
||
* 输出:[1,null,1]
|
||
|
||
示例 3:
|
||
* 输入:root = [1,0,2]
|
||
* 输出:[3,3,2]
|
||
|
||
示例 4:
|
||
* 输入:root = [3,2,4,1]
|
||
* 输出:[7,9,4,10]
|
||
|
||
提示:
|
||
|
||
* 树中的节点数介于 0 和 104 之间。
|
||
* 每个节点的值介于 -104 和 104 之间。
|
||
* 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
|
||
* 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
|
||
|
||
## 算法公开课
|
||
|
||
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[普大喜奔!二叉树章节已全部更完啦!| LeetCode:538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1d44y1f7wP?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
一看到累加树,相信很多小伙伴都会疑惑:如何累加?遇到一个节点,然后再遍历其他节点累加?怎么一想这么麻烦呢。
|
||
|
||
然后再发现这是一棵二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树啊,这是有序的啊。
|
||
|
||
那么有序的元素如何求累加呢?
|
||
|
||
**其实这就是一棵树,大家可能看起来有点别扭,换一个角度来看,这就是一个有序数组[2, 5, 13],求从后到前的累加数组,也就是[20, 18, 13],是不是感觉这就简单了。**
|
||
|
||
为什么变成数组就是感觉简单了呢?
|
||
|
||
因为数组大家都知道怎么遍历啊,从后向前,挨个累加就完事了,这换成了二叉搜索树,看起来就别扭了一些是不是。
|
||
|
||
那么知道如何遍历这个二叉树,也就迎刃而解了,**从树中可以看出累加的顺序是右中左,所以我们需要反中序遍历这个二叉树,然后顺序累加就可以了**。
|
||
|
||
### 递归
|
||
|
||
遍历顺序如图所示:
|
||
|
||
|
||
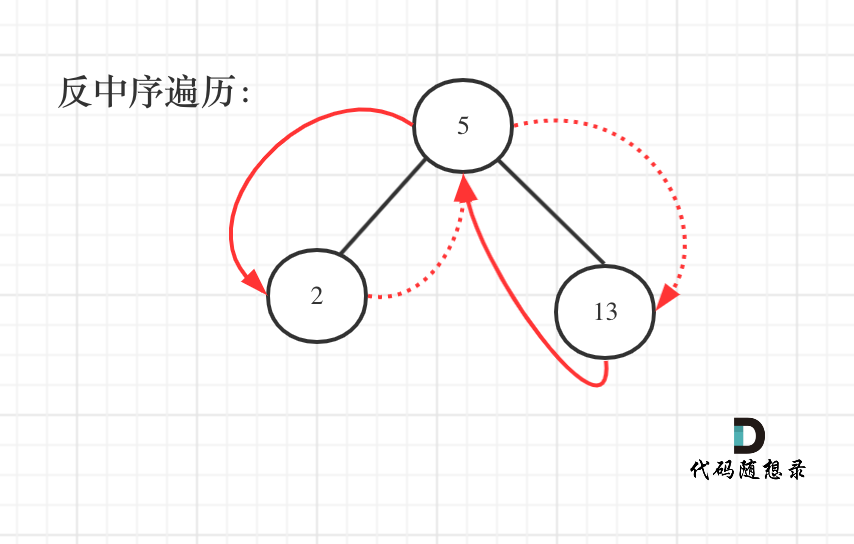
|
||
|
||
本题依然需要一个pre指针记录当前遍历节点cur的前一个节点,这样才方便做累加。
|
||
|
||
pre指针的使用技巧,我们在[二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](https://programmercarl.com/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.html)和[二叉树:我的众数是多少?](https://programmercarl.com/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.html)都提到了,这是常用的操作手段。
|
||
|
||
* 递归函数参数以及返回值
|
||
|
||
这里很明确了,不需要递归函数的返回值做什么操作了,要遍历整棵树。
|
||
|
||
同时需要定义一个全局变量pre,用来保存cur节点的前一个节点的数值,定义为int型就可以了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int pre = 0; // 记录前一个节点的数值
|
||
void traversal(TreeNode* cur)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 确定终止条件
|
||
|
||
遇空就终止。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
if (cur == NULL) return;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 确定单层递归的逻辑
|
||
|
||
注意**要右中左来遍历二叉树**, 中节点的处理逻辑就是让cur的数值加上前一个节点的数值。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
traversal(cur->right); // 右
|
||
cur->val += pre; // 中
|
||
pre = cur->val;
|
||
traversal(cur->left); // 左
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
递归法整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
int pre = 0; // 记录前一个节点的数值
|
||
void traversal(TreeNode* cur) { // 右中左遍历
|
||
if (cur == NULL) return;
|
||
traversal(cur->right);
|
||
cur->val += pre;
|
||
pre = cur->val;
|
||
traversal(cur->left);
|
||
}
|
||
public:
|
||
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
pre = 0;
|
||
traversal(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 迭代法
|
||
|
||
迭代法其实就是中序模板题了,在[二叉树:前中后序迭代法](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的迭代遍历.html)和[二叉树:前中后序统一方式迭代法](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的统一迭代法.html)可以选一种自己习惯的写法。
|
||
|
||
这里我给出其中的一种,代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
int pre; // 记录前一个节点的数值
|
||
void traversal(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
TreeNode* cur = root;
|
||
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
|
||
if (cur != NULL) {
|
||
st.push(cur);
|
||
cur = cur->right; // 右
|
||
} else {
|
||
cur = st.top(); // 中
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
cur->val += pre;
|
||
pre = cur->val;
|
||
cur = cur->left; // 左
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
public:
|
||
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
pre = 0;
|
||
traversal(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
经历了前面各种二叉树增删改查的洗礼之后,这道题目应该比较简单了。
|
||
|
||
**好了,二叉树已经接近尾声了,接下来就是要对二叉树来一个大总结了**。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
int sum;
|
||
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
|
||
sum = 0;
|
||
convertBST1(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 按右中左顺序遍历,累加即可
|
||
public void convertBST1(TreeNode root) {
|
||
if (root == null) {
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
convertBST1(root.right);
|
||
sum += root.val;
|
||
root.val = sum;
|
||
convertBST1(root.left);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
**迭代**
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
//DFS iteraion統一迭代法
|
||
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
|
||
int pre = 0;
|
||
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
|
||
if(root == null) //edge case check
|
||
return null;
|
||
|
||
stack.add(root);
|
||
|
||
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
|
||
TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
|
||
//curr != null的狀況,只負責存node到stack中
|
||
if(curr != null){
|
||
stack.pop();
|
||
if(curr.left != null) //左
|
||
stack.add(curr.left);
|
||
stack.add(curr); //中
|
||
stack.add(null);
|
||
if(curr.right != null) //右
|
||
stack.add(curr.right);
|
||
}else{
|
||
//curr == null的狀況,只負責做單層邏輯
|
||
stack.pop();
|
||
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
|
||
temp.val += pre;
|
||
pre = temp.val;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
递归法(版本一)
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
|
||
self.pre = 0 # 记录前一个节点的数值
|
||
self.traversal(root)
|
||
return root
|
||
def traversal(self, cur):
|
||
if cur is None:
|
||
return
|
||
self.traversal(cur.right)
|
||
cur.val += self.pre
|
||
self.pre = cur.val
|
||
self.traversal(cur.left)
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
递归法(版本二)
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
self.count = 0
|
||
|
||
def convertBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||
if root == None:
|
||
return
|
||
'''
|
||
倒序累加替换:
|
||
'''
|
||
# 右
|
||
self.convertBST(root.right)
|
||
|
||
# 中
|
||
# 中节点:用当前root的值加上pre的值
|
||
self.count += root.val
|
||
|
||
root.val = self.count
|
||
|
||
# 左
|
||
self.convertBST(root.left)
|
||
|
||
return root
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
迭代法(版本一)
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
self.pre = 0 # 记录前一个节点的数值
|
||
|
||
def traversal(self, root):
|
||
stack = []
|
||
cur = root
|
||
while cur or stack:
|
||
if cur:
|
||
stack.append(cur)
|
||
cur = cur.right # 右
|
||
else:
|
||
cur = stack.pop() # 中
|
||
cur.val += self.pre
|
||
self.pre = cur.val
|
||
cur = cur.left # 左
|
||
|
||
def convertBST(self, root):
|
||
self.pre = 0
|
||
self.traversal(root)
|
||
return root
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
迭代法(版本二)
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def convertBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||
if not root: return root
|
||
stack = []
|
||
result = []
|
||
cur = root
|
||
pre = 0
|
||
while cur or stack:
|
||
if cur:
|
||
stack.append(cur)
|
||
cur = cur.right
|
||
else:
|
||
cur = stack.pop()
|
||
cur.val+= pre
|
||
pre = cur.val
|
||
cur =cur.left
|
||
return root
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go
|
||
|
||
弄一个sum暂存其和值
|
||
```go
|
||
var pre int
|
||
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
|
||
pre = 0
|
||
traversal(root)
|
||
return root
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func traversal(cur *TreeNode) {
|
||
if cur == nil {
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
traversal(cur.Right)
|
||
cur.Val += pre
|
||
pre = cur.Val
|
||
traversal(cur.Left)
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### JavaScript
|
||
|
||
递归
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var convertBST = function(root) {
|
||
let pre = 0;
|
||
const ReverseInOrder = (cur) => {
|
||
if(cur) {
|
||
ReverseInOrder(cur.right);
|
||
cur.val += pre;
|
||
pre = cur.val;
|
||
ReverseInOrder(cur.left);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
ReverseInOrder(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var convertBST = function (root) {
|
||
let pre = 0;
|
||
let cur = root;
|
||
let stack = [];
|
||
while (cur !== null || stack.length !== 0) {
|
||
while (cur !== null) {
|
||
stack.push(cur);
|
||
cur = cur.right;
|
||
}
|
||
cur = stack.pop();
|
||
cur.val += pre;
|
||
pre = cur.val;
|
||
cur = cur.left;
|
||
}
|
||
return root;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### C
|
||
|
||
递归
|
||
```c
|
||
int pre;
|
||
void traversal(struct TreeNode* node) {
|
||
if(!node)
|
||
return ;
|
||
traversal(node->right);
|
||
node->val = node->val + pre;
|
||
pre = node->val;
|
||
traversal(node->left);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
struct TreeNode* convertBST(struct TreeNode* root){
|
||
pre = 0;
|
||
traversal(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### TypeScript
|
||
|
||
> 递归法
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function convertBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
|
||
let pre: number = 0;
|
||
function recur(root: TreeNode | null): void {
|
||
if (root === null) return;
|
||
recur(root.right);
|
||
root.val += pre;
|
||
pre = root.val;
|
||
recur(root.left);
|
||
}
|
||
recur(root);
|
||
return root;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 迭代法
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function convertBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
|
||
const helperStack: TreeNode[] = [];
|
||
let curNode: TreeNode | null = root;
|
||
let pre: number = 0;
|
||
while (curNode !== null || helperStack.length > 0) {
|
||
while (curNode !== null) {
|
||
helperStack.push(curNode);
|
||
curNode = curNode.right;
|
||
}
|
||
curNode = helperStack.pop()!;
|
||
curNode.val += pre;
|
||
pre = curNode.val;
|
||
curNode = curNode.left;
|
||
}
|
||
return root;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Scala
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def convertBST(root: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||
var sum = 0
|
||
def convert(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
|
||
if (node == null) return
|
||
convert(node.right)
|
||
sum += node.value
|
||
node.value = sum
|
||
convert(node.left)
|
||
}
|
||
convert(root)
|
||
root
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Rust
|
||
|
||
递归:
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
|
||
let mut pre = 0;
|
||
Self::traversal(&root, &mut pre);
|
||
root
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn traversal(cur: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, pre: &mut i32) {
|
||
if cur.is_none() {
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
let mut node = cur.as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut();
|
||
Self::traversal(&node.right, pre);
|
||
*pre += node.val;
|
||
node.val = *pre;
|
||
Self::traversal(&node.left, pre);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代:
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
|
||
let mut cur = root.clone();
|
||
let mut stack = vec![];
|
||
let mut pre = 0;
|
||
while !stack.is_empty() || cur.is_some() {
|
||
while let Some(node) = cur {
|
||
cur = node.borrow().right.clone();
|
||
stack.push(node);
|
||
}
|
||
if let Some(node) = stack.pop() {
|
||
pre += node.borrow().val;
|
||
node.borrow_mut().val = pre;
|
||
cur = node.borrow().left.clone();
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
root
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### C#
|
||
```csharp
|
||
// 递归
|
||
public class Solution
|
||
{
|
||
int pre = 0;
|
||
public TreeNode ConvertBST(TreeNode root)
|
||
{
|
||
if (root == null) return null;
|
||
ConvertBST(root.right);
|
||
root.val += pre;
|
||
pre = root.val;
|
||
ConvertBST(root.left);
|
||
return root;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|