mirror of
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master.git
synced 2026-02-03 02:43:26 +08:00
Merge branch 'youngyangyang04:master' into master
This commit is contained in:
194
README.md
194
README.md
@@ -4,11 +4,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
> 1. **介绍**:本项目是一套完整的刷题计划,旨在帮助大家少走弯路,循序渐进学算法,[关注作者](#关于作者)
|
||||
> 2. **PDF版本** : [「代码随想录」算法精讲 PDF 版本](https://programmercarl.com/other/algo_pdf.html) 。
|
||||
> 3. **最强八股文:**:[代码随想录知识星球精华PDF](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar_baguwen.html)
|
||||
> 4. **刷题顺序** : README已经将刷题顺序排好了,按照顺序一道一道刷就可以。
|
||||
> 5. **学习社区** : 一起学习打卡/面试技巧/如何选择offer/大厂内推/职场规则/简历修改/技术分享/程序人生。欢迎加入[「代码随想录」知识星球](https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html) 。
|
||||
> 6. **提交代码**:本项目统一使用C++语言进行讲解,但已经有Java、Python、Go、JavaScript等等多语言版本,感谢[这里的每一位贡献者](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors),如果你也想贡献代码点亮你的头像,[点击这里](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A)了解提交代码的方式。
|
||||
> 7. **转载须知** :以下所有文章皆为我([程序员Carl](https://github.com/youngyangyang04))的原创。引用本项目文章请注明出处,发现恶意抄袭或搬运,会动用法律武器维护自己的权益。让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境!
|
||||
> 3. **算法公开课** : [《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fA4y1o715) 。
|
||||
> 4. **最强八股文:**:[代码随想录知识星球精华PDF](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar_baguwen.html)
|
||||
> 5. **刷题顺序** : README已经将刷题顺序排好了,按照顺序一道一道刷就可以。
|
||||
> 6. **学习社区** : 一起学习打卡/面试技巧/如何选择offer/大厂内推/职场规则/简历修改/技术分享/程序人生。欢迎加入[「代码随想录」知识星球](https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html) 。
|
||||
> 7. **提交代码**:本项目统一使用C++语言进行讲解,但已经有Java、Python、Go、JavaScript等等多语言版本,感谢[这里的每一位贡献者](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors),如果你也想贡献代码点亮你的头像,[点击这里](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A)了解提交代码的方式。
|
||||
> 8. **转载须知** :以下所有文章皆为我([程序员Carl](https://github.com/youngyangyang04))的原创。引用本项目文章请注明出处,发现恶意抄袭或搬运,会动用法律武器维护自己的权益。让我们一起维护一个良好的技术创作环境!
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="programmercarl.com" target="_blank">
|
||||
@@ -102,6 +103,7 @@
|
||||
* [看了这么多代码,谈一谈代码风格!](./problems/前序/代码风格.md)
|
||||
* [力扣上的代码想在本地编译运行?](./problems/前序/力扣上的代码想在本地编译运行?.md)
|
||||
* [什么是核心代码模式,什么又是ACM模式?](./problems/前序/什么是核心代码模式,什么又是ACM模式?.md)
|
||||
* [刷题要不要用库函数](./problems/前序/刷力扣用不用库函数.md)
|
||||
* [ACM模式如何构造二叉树](./problems/前序/ACM模式如何构建二叉树.md)
|
||||
* [解密互联网大厂研发流程](./problems/前序/互联网大厂研发流程.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -129,45 +131,6 @@
|
||||
* [递归算法的时间与空间复杂度分析!](./problems/前序/递归算法的时间与空间复杂度分析.md)
|
||||
* [刷了这么多题,你了解自己代码的内存消耗么?](./problems/前序/刷了这么多题,你了解自己代码的内存消耗么?.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 知识星球精选
|
||||
|
||||
* [秋招面试,心态很重要!](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结3.md)
|
||||
* [秋招倒霉透顶,触底反弹!](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结2.md)
|
||||
* [无竞赛,无实习,如何秋招?](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招总结1.md)
|
||||
* [offer总决赛,何去何从!](./problems/知识星球精选/offer总决赛,何去何从.md)
|
||||
* [入职后担心代码能力跟不上!](./problems/知识星球精选/入职后担心代码能力跟不上.md)
|
||||
* [秋招进入offer决赛圈!](./problems/知识星球精选/offer对比-决赛圈.md)
|
||||
* [非科班的困扰](./problems/知识星球精选/非科班的困扰.md)
|
||||
* [offer的选择-开奖](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招开奖.md)
|
||||
* [看到代码就抵触!怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/不喜欢写代码怎么办.md)
|
||||
* [遭遇逼签,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/逼签.md)
|
||||
* [HR特意刁难非科班!](./problems/知识星球精选/HR特意刁难非科班.md)
|
||||
* [offer的选择](./problems/知识星球精选/offer的选择.md)
|
||||
* [天下乌鸦一般黑,哪家没有PUA?](./problems/知识星球精选/天下乌鸦一般黑.md)
|
||||
* [初入大三,考研VS工作](./problems/知识星球精选/初入大三选择考研VS工作.md)
|
||||
* [非科班2021秋招总结](./problems/知识星球精选/非科班2021秋招总结.md)
|
||||
* [秋招下半场依然没offer,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招下半场依然没offer.md)
|
||||
* [合适自己的就是最好的](./problems/知识星球精选/合适自己的就是最好的.md)
|
||||
* [为什么都说客户端会消失](./problems/知识星球精选/客三消.md)
|
||||
* [博士转计算机如何找工作](./problems/知识星球精选/博士转行计算机.md)
|
||||
* [不一样的七夕](./problems/知识星球精选/不一样的七夕.md)
|
||||
* [HR面注意事项](./problems/知识星球精选/HR面注意事项.md)
|
||||
* [刷题攻略要刷两遍!](./problems/知识星球精选/刷题攻略要刷两遍.md)
|
||||
* [秋招进行中的迷茫与焦虑......](./problems/知识星球精选/秋招进行中的迷茫与焦虑.md)
|
||||
* [大厂新人培养体系应该是什么样的?](./problems/知识星球精选/大厂新人培养体系.md)
|
||||
* [你的简历里「专业技能」写的够专业么?](./problems/知识星球精选/专业技能可以这么写.md)
|
||||
* [Carl看了上百份简历,总结了这些!](./problems/知识星球精选/写简历的一些问题.md)
|
||||
* [备战2022届秋招](./problems/知识星球精选/备战2022届秋招.md)
|
||||
* [技术不太好,如果选择方向](./problems/知识星球精选/技术不好如何选择技术方向.md)
|
||||
* [刷题要不要使用库函数](./problems/知识星球精选/刷力扣用不用库函数.md)
|
||||
* [关于实习的几点问题](./problems/知识星球精选/关于实习大家的疑问.md)
|
||||
* [面试中遇到了发散性问题,怎么办?](./problems/知识星球精选/面试中发散性问题.md)
|
||||
* [英语到底重不重要!](./problems/知识星球精选/英语到底重不重要.md)
|
||||
* [计算机专业要不要读研!](./problems/知识星球精选/要不要考研.md)
|
||||
* [关于提前批的一些建议](./problems/知识星球精选/关于提前批的一些建议.md)
|
||||
* [已经在实习的录友要如何准备秋招](./problems/知识星球精选/如何权衡实习与秋招复习.md)
|
||||
* [华为提前批已经开始了](./problems/知识星球精选/提前批已经开始了.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 杂谈
|
||||
|
||||
* [「代码随想录」刷题网站上线](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-6rd_g7LrVD1fuKBYk2tXQ)。
|
||||
@@ -179,77 +142,77 @@
|
||||
## 数组
|
||||
|
||||
1. [数组过于简单,但你该了解这些!](./problems/数组理论基础.md)
|
||||
2. [数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
|
||||
3. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
|
||||
4. [数组:有序数组的平方,还有序么?](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
|
||||
5. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
|
||||
6. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
|
||||
2. [数组:二分查找](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
|
||||
3. [数组:移除元素](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
|
||||
4. [数组:序数组的平方](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
|
||||
5. [数组:长度最小的子数组](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
|
||||
6. [数组:螺旋矩阵II](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
|
||||
7. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 链表
|
||||
|
||||
1. [关于链表,你该了解这些!](./problems/链表理论基础.md)
|
||||
2. [链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](./problems/0203.移除链表元素.md)
|
||||
3. [链表:一道题目考察了常见的五个操作!](./problems/0707.设计链表.md)
|
||||
4. [链表:听说过两天反转链表又写不出来了?](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
|
||||
2. [链表:移除链表元素](./problems/0203.移除链表元素.md)
|
||||
3. [链表:设计链表](./problems/0707.设计链表.md)
|
||||
4. [链表:翻转链表](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
|
||||
5. [链表:两两交换链表中的节点](./problems/0024.两两交换链表中的节点.md)
|
||||
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
|
||||
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
|
||||
8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
|
||||
8. [链表:环形链表](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
|
||||
9. [链表:总结篇!](./problems/链表总结篇.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 哈希表
|
||||
|
||||
1. [关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](./problems/哈希表理论基础.md)
|
||||
2. [哈希表:可以拿数组当哈希表来用,但哈希值不要太大](./problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md)
|
||||
2. [哈希表:有效的字母异位词](./problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md)
|
||||
3. [哈希表:查找常用字符](./problems/1002.查找常用字符.md)
|
||||
4. [哈希表:哈希值太大了,还是得用set](./problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md)
|
||||
5. [哈希表:用set来判断快乐数](./problems/0202.快乐数.md)
|
||||
6. [哈希表:map等候多时了](./problems/0001.两数之和.md)
|
||||
7. [哈希表:其实需要哈希的地方都能找到map的身影](./problems/0454.四数相加II.md)
|
||||
8. [哈希表:这道题目我做过?](./problems/0383.赎金信.md)
|
||||
9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
|
||||
10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
|
||||
11. [哈希表:总结篇!(每逢总结必经典)](./problems/哈希表总结.md)
|
||||
4. [哈希表:两个数组的交集](./problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md)
|
||||
5. [哈希表:快乐数](./problems/0202.快乐数.md)
|
||||
6. [哈希表:两数之和](./problems/0001.两数之和.md)
|
||||
7. [哈希表:四数相加II](./problems/0454.四数相加II.md)
|
||||
8. [哈希表:赎金信](./problems/0383.赎金信.md)
|
||||
9. [哈希表:三数之和](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
|
||||
10. [双指针法:四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
|
||||
11. [哈希表:总结篇!](./problems/哈希表总结.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 字符串
|
||||
|
||||
1. [字符串:这道题目,使用库函数一行代码搞定](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
|
||||
2. [字符串:简单的反转还不够!](./problems/0541.反转字符串II.md)
|
||||
1. [字符串:反转字符串](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
|
||||
2. [字符串:反转字符串II](./problems/0541.反转字符串II.md)
|
||||
3. [字符串:替换空格](./problems/剑指Offer05.替换空格.md)
|
||||
4. [字符串:花式反转还不够!](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
|
||||
5. [字符串:反转个字符串还有这个用处?](./problems/剑指Offer58-II.左旋转字符串.md)
|
||||
4. [字符串:翻转字符串里的单词](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
|
||||
5. [字符串:左旋转字符串](./problems/剑指Offer58-II.左旋转字符串.md)
|
||||
6. [帮你把KMP算法学个通透](./problems/0028.实现strStr.md)
|
||||
8. [字符串:KMP算法还能干这个!](./problems/0459.重复的子字符串.md)
|
||||
8. [字符串:重复的子字符串](./problems/0459.重复的子字符串.md)
|
||||
9. [字符串:总结篇!](./problems/字符串总结.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 双指针法
|
||||
|
||||
双指针法基本都是应用在数组,字符串与链表的题目上
|
||||
|
||||
1. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
|
||||
2. [字符串:这道题目,使用库函数一行代码搞定](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
|
||||
1. [数组:移除元素](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
|
||||
2. [字符串:反转字符串](./problems/0344.反转字符串.md)
|
||||
3. [字符串:替换空格](./problems/剑指Offer05.替换空格.md)
|
||||
4. [字符串:花式反转还不够!](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
|
||||
5. [链表:听说过两天反转链表又写不出来了?](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
|
||||
4. [字符串:翻转字符串里的单词](./problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md)
|
||||
5. [链表:翻转链表](./problems/0206.翻转链表.md)
|
||||
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
|
||||
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
|
||||
8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
|
||||
9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
|
||||
10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
|
||||
11. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
|
||||
8. [链表:环形链表](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
|
||||
9. [双指针:三数之和](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
|
||||
10. [双指针:四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
|
||||
11. [双指针:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 栈与队列
|
||||
|
||||
1. [栈与队列:来看看栈和队列不为人知的一面](./problems/栈与队列理论基础.md)
|
||||
2. [栈与队列:我用栈来实现队列怎么样?](./problems/0232.用栈实现队列.md)
|
||||
3. [栈与队列:用队列实现栈还有点别扭](./problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md)
|
||||
4. [栈与队列:系统中处处都是栈的应用](./problems/0020.有效的括号.md)
|
||||
5. [栈与队列:匹配问题都是栈的强项](./problems/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.md)
|
||||
6. [栈与队列:有没有想过计算机是如何处理表达式的?](./problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md)
|
||||
7. [栈与队列:滑动窗口里求最大值引出一个重要数据结构](./problems/0239.滑动窗口最大值.md)
|
||||
8. [栈与队列:求前 K 个高频元素和队列有啥关系?](./problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md)
|
||||
2. [栈与队列:用栈实现队列](./problems/0232.用栈实现队列.md)
|
||||
3. [栈与队列:用队列实现栈](./problems/0225.用队列实现栈.md)
|
||||
4. [栈与队列:有效的括号](./problems/0020.有效的括号.md)
|
||||
5. [栈与队列:删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](./problems/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.md)
|
||||
6. [栈与队列:逆波兰表达式求值](./problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md)
|
||||
7. [栈与队列:滑动窗口最大值](./problems/0239.滑动窗口最大值.md)
|
||||
8. [栈与队列:前K个高频元素](./problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md)
|
||||
9. [栈与队列:总结篇!](./problems/栈与队列总结.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 二叉树
|
||||
@@ -258,41 +221,41 @@
|
||||
<img src='https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20210219190809451.png' width=600 alt='二叉树大纲'> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
|
||||
2. [二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
|
||||
3. [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
|
||||
4. [二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的写法就不能统一一下么?](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
|
||||
5. [二叉树:层序遍历登场!](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
|
||||
6. [二叉树:你真的会翻转二叉树么?](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
|
||||
2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
|
||||
3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
|
||||
4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
|
||||
5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
|
||||
6. [二叉树:翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
|
||||
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
|
||||
8. [二叉树:我对称么?](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
|
||||
9. [二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
|
||||
10. [二叉树:看看这些树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
|
||||
11. [二叉树:我有多少个节点?](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
|
||||
12. [二叉树:我平衡么?](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
|
||||
13. [二叉树:找我的所有路径?](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
|
||||
8. [二叉树:对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
|
||||
9. [二叉树:二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
|
||||
10. [二叉树:二叉树的最小深度](./problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md)
|
||||
11. [二叉树:完全二叉树的节点个数](./problems/0222.完全二叉树的节点个数.md)
|
||||
12. [二叉树:平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
|
||||
13. [二叉树:二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
|
||||
14. [本周总结!二叉树系列二](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
|
||||
15. [二叉树:以为使用了递归,其实还隐藏着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
|
||||
16. [二叉树:做了这么多题目了,我的左叶子之和是多少?](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
|
||||
17. [二叉树:我的左下角的值是多少?](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
|
||||
15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
|
||||
16. [二叉树:左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
|
||||
17. [二叉树:找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
|
||||
18. [二叉树:路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
|
||||
19. [二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
|
||||
20. [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
|
||||
19. [二叉树:构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
|
||||
20. [二叉树:最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
|
||||
21. [本周小结!(二叉树系列三)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
|
||||
22. [二叉树:合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
|
||||
23. [二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
|
||||
24. [二叉树:我是不是一棵二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
|
||||
24. [二叉树:验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
|
||||
25. [二叉树:搜索树的最小绝对差](./problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md)
|
||||
26. [二叉树:我的众数是多少?](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
|
||||
26. [二叉树:二叉搜索树中的众数](./problems/0501.二叉搜索树中的众数.md)
|
||||
27. [二叉树:公共祖先问题](./problems/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.md)
|
||||
28. [本周小结!(二叉树系列四)](./problems/周总结/20201017二叉树周末总结.md)
|
||||
29. [二叉树:搜索树的公共祖先问题](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
|
||||
29. [二叉树:搜索树的最近公共祖先](./problems/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.md)
|
||||
30. [二叉树:搜索树中的插入操作](./problems/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.md)
|
||||
31. [二叉树:搜索树中的删除操作](./problems/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.md)
|
||||
32. [二叉树:修剪一棵搜索树](./problems/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.md)
|
||||
33. [二叉树:构造一棵搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
|
||||
34. [二叉树:搜索树转成累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
|
||||
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 回溯算法
|
||||
|
||||
题目分类大纲如下:
|
||||
@@ -538,29 +501,14 @@
|
||||
|
||||
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# B站算法视频讲解
|
||||
|
||||
以下为[B站「代码随想录」](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)算法讲解视频:
|
||||
|
||||
* [KMP算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd)
|
||||
* [KMP算法(代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
|
||||
* [回溯算法理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM)
|
||||
* [回溯算法之组合问题(力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)
|
||||
* [组合问题的剪枝操作(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er)
|
||||
* [组合总和(对应力扣题目:39.组合总和)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
|
||||
* [分割回文串(对应力扣题目:131.分割回文串)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6)
|
||||
* [二叉树理论基础](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Hy4y1t7ij)
|
||||
* [二叉树的递归遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wh411S7xt)
|
||||
* [二叉树的非递归遍历(一)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2)
|
||||
|
||||
(持续更新中....)
|
||||
|
||||
# 贡献者
|
||||
|
||||
[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
|
||||
|
||||
# Star 趋势
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://star-history.com/#youngyangyang04/leetcode-master&Date)
|
||||
|
||||
# 关于作者
|
||||
|
||||
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
|
||||
@@ -569,7 +517,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20220102204804.png" data-img="1" width="200" height="200"></img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/第二企业刷题活码.png" data-img="1" width="200" height="200"></img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -581,6 +530,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**来看看就知道了,你会发现相见恨晚!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="公众号"></a>
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20211026122841.png" data-img="1" width="650" height="500"></img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
pics/.DS_Store
vendored
BIN
pics/.DS_Store
vendored
Binary file not shown.
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 两数之和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
很明显暴力的解法是两层for循环查找,时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$。
|
||||
建议看一下我录的这期视频:[梦开始的地方,Leetcode:1.两数之和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1aT41177mK),结合本题解来学习,事半功倍。
|
||||
|
||||
很明显暴力的解法是两层for循环查找,时间复杂度是O(n^2)。
|
||||
|
||||
建议大家做这道题目之前,先做一下这两道
|
||||
* [242. 有效的字母异位词](https://www.programmercarl.com/0242.有效的字母异位词.html)
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +34,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://www.programmercarl.com/0242.有效的字母异位词.html) 这道题目是用数组作为哈希表来解决哈希问题,[349. 两个数组的交集](https://www.programmercarl.com/0349.两个数组的交集.html)这道题目是通过set作为哈希表来解决哈希问题。
|
||||
|
||||
本题呢,则要使用map,那么来看一下使用数组和set来做哈希法的局限。
|
||||
|
||||
首先我在强调一下 **什么时候使用哈希法**,当我们需要查询一个元素是否出现过,或者一个元素是否在集合里的时候,就要第一时间想到哈希法。
|
||||
|
||||
本题呢,我就需要一个集合来存放我们遍历过的元素,然后在遍历数组的时候去询问这个集合,某元素是否遍历过,也就是 是否出现在这个集合。
|
||||
|
||||
那么我们就应该想到使用哈希法了。
|
||||
|
||||
因为本地,我们不仅要知道元素有没有遍历过,还有知道这个元素对应的下标,**需要使用 key value结构来存放,key来存元素,value来存下标,那么使用map正合适**。
|
||||
|
||||
再来看一下使用数组和set来做哈希法的局限。
|
||||
|
||||
* 数组的大小是受限制的,而且如果元素很少,而哈希值太大会造成内存空间的浪费。
|
||||
* set是一个集合,里面放的元素只能是一个key,而两数之和这道题目,不仅要判断y是否存在而且还要记录y的下标位置,因为要返回x 和 y的下标。所以set 也不能用。
|
||||
@@ -43,20 +54,38 @@ C++中map,有三种类型:
|
||||
|
||||
|映射 |底层实现 | 是否有序 |数值是否可以重复 | 能否更改数值|查询效率 |增删效率|
|
||||
|---|---| --- |---| --- | --- | ---|
|
||||
|std::map |红黑树 |key有序 |key不可重复 |key不可修改 | $O(\log n)$|$O(\log n)$ |
|
||||
|std::multimap | 红黑树|key有序 | key可重复 | key不可修改|$O(\log n)$ |$O(\log n)$ |
|
||||
|std::unordered_map |哈希表 | key无序 |key不可重复 |key不可修改 |$O(1)$ | $O(1)$|
|
||||
|std::map |红黑树 |key有序 |key不可重复 |key不可修改 | O(log n)|O(log n) |
|
||||
|std::multimap | 红黑树|key有序 | key可重复 | key不可修改|O(log n) |O(log n) |
|
||||
|std::unordered_map |哈希表 | key无序 |key不可重复 |key不可修改 |O(1) | O(1)|
|
||||
|
||||
std::unordered_map 底层实现为哈希表,std::map 和std::multimap 的底层实现是红黑树。
|
||||
|
||||
同理,std::map 和std::multimap 的key也是有序的(这个问题也经常作为面试题,考察对语言容器底层的理解)。 更多哈希表的理论知识请看[关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](https://www.programmercarl.com/哈希表理论基础.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
**这道题目中并不需要key有序,选择std::unordered_map 效率更高!**
|
||||
**这道题目中并不需要key有序,选择std::unordered_map 效率更高!** 使用其他语言的录友注意了解一下自己所用语言的数据结构就行。
|
||||
|
||||
解题思路动画如下:
|
||||
接下来需要明确两点:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
* **map用来做什么**
|
||||
* **map中key和value分别表示什么**
|
||||
|
||||
map目的用来存放我们访问过的元素,因为遍历数组的时候,需要记录我们之前遍历过哪些元素和对应的下表,这样才能找到与当前元素相匹配的(也就是相加等于target)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来是map中key和value分别表示什么。
|
||||
|
||||
这道题 我们需要 给出一个元素,判断这个元素是否出现过,如果出现过,返回这个元素的下标。
|
||||
|
||||
那么判断元素是否出现,这个元素就要作为key,所以数组中的元素作为key,有key对应的就是value,value用来存下标。
|
||||
|
||||
所以 map中的存储结构为 {key:数据元素,value:数组元素对应的下表}。
|
||||
|
||||
在遍历数组的时候,只需要向map去查询是否有和目前遍历元素比配的数值,如果有,就找到的匹配对,如果没有,就把目前遍历的元素放进map中,因为map存放的就是我们访问过的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
过程如下:
|
||||
|
||||
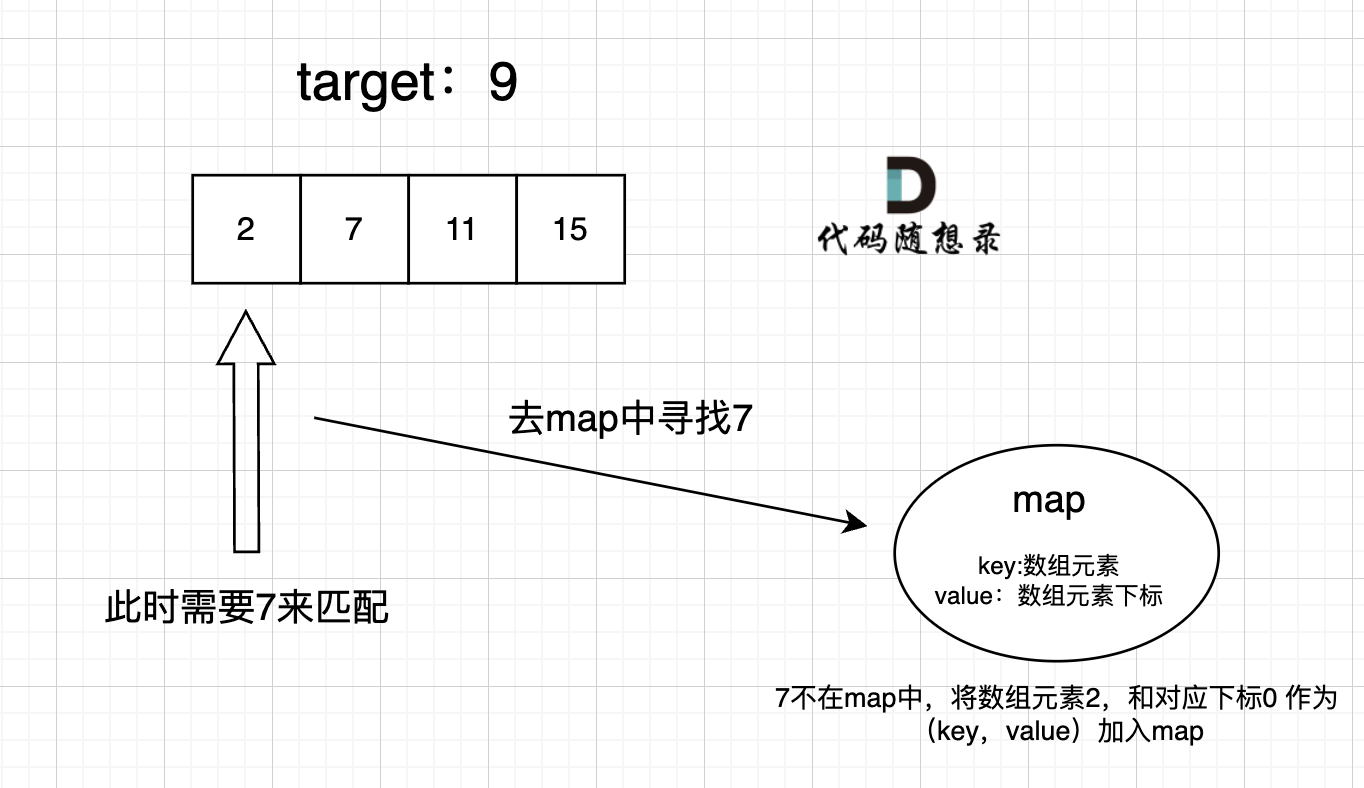
|
||||
|
||||
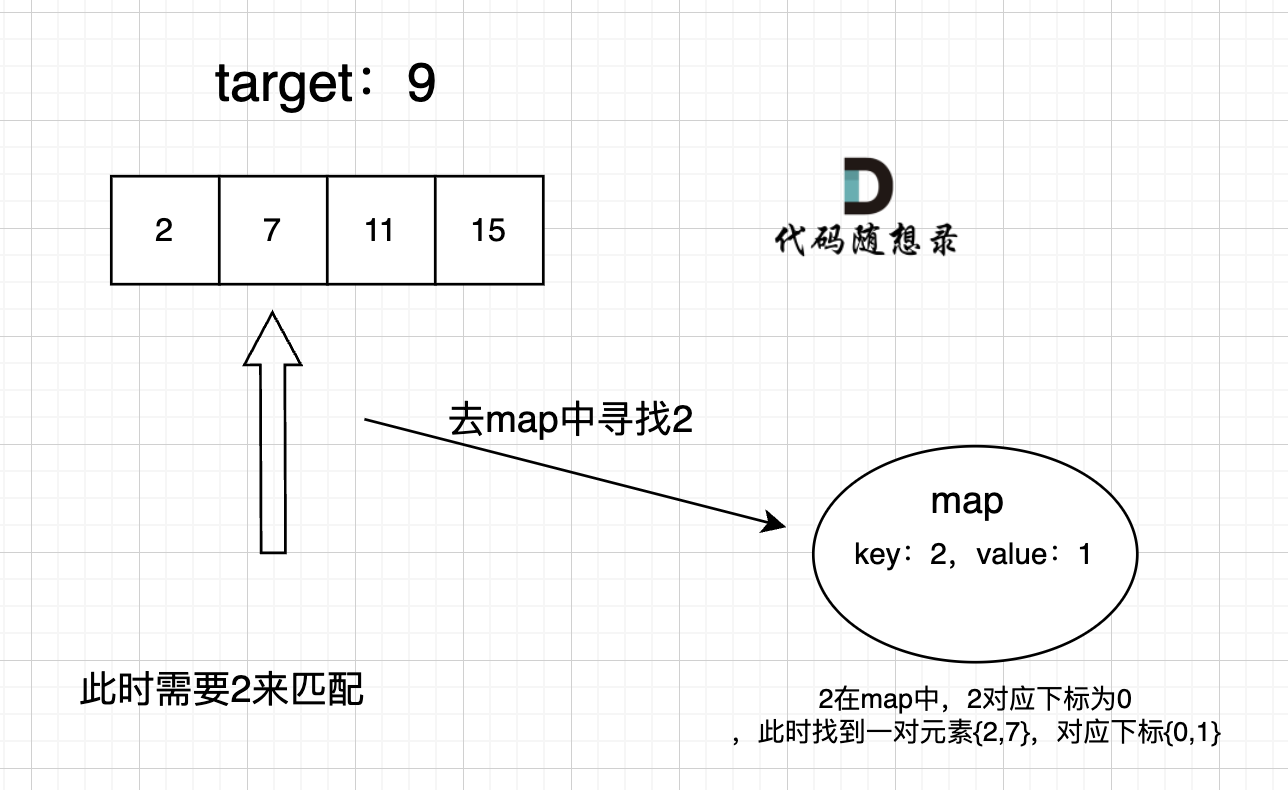
|
||||
|
||||
C++代码:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -66,18 +95,31 @@ public:
|
||||
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
|
||||
std::unordered_map <int,int> map;
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
||||
auto iter = map.find(target - nums[i]);
|
||||
// 遍历当前元素,并在map中寻找是否有匹配的key
|
||||
auto iter = map.find(target - nums[i]);
|
||||
if(iter != map.end()) {
|
||||
return {iter->second, i};
|
||||
}
|
||||
map.insert(pair<int, int>(nums[i], i));
|
||||
// 如果没找到匹配对,就把访问过的元素和下标加入到map中
|
||||
map.insert(pair<int, int>(nums[i], i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return {};
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本题其实有四个重点:
|
||||
|
||||
* 为什么会想到用哈希表
|
||||
* 哈希表为什么用map
|
||||
* 本题map是用来存什么的
|
||||
* map中的key和value用来存什么的
|
||||
|
||||
把这四点想清楚了,本题才算是理解透彻了。
|
||||
|
||||
很多录友把这道题目 通过了,但都没想清楚map是用来做什么的,以至于对代码的理解其实是 一知半解的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
@@ -221,13 +263,15 @@ php
|
||||
```php
|
||||
function twoSum(array $nums, int $target): array
|
||||
{
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < count($nums);$i++) {
|
||||
// 计算剩下的数
|
||||
$residue = $target - $nums[$i];
|
||||
// 匹配的index,有则返回index, 无则返回false
|
||||
$match_index = array_search($residue, $nums);
|
||||
if ($match_index !== false && $match_index != $i) {
|
||||
return array($i, $match_index);
|
||||
$map = [];
|
||||
foreach($nums as $i => $num) {
|
||||
if (isset($map[$target - $num])) {
|
||||
return [
|
||||
$i,
|
||||
$map[$target - $num]
|
||||
];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
$map[$num] = $i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return [];
|
||||
@@ -250,28 +294,61 @@ func twoSum(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [Int] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param Integer[] $nums
|
||||
* @param Integer $target
|
||||
* @return Integer[]
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function twoSum($nums, $target) {
|
||||
if (count($nums) == 0) {
|
||||
return [];
|
||||
}
|
||||
$table = [];
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < count($nums); $i++) {
|
||||
$temp = $target - $nums[$i];
|
||||
if (isset($table[$temp])) {
|
||||
return [$table[$temp], $i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
$table[$nums[$i]] = $i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return [];
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
// 导入包
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def twoSum(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Array[Int] = {
|
||||
// key存储值,value存储下标
|
||||
val map = new mutable.HashMap[Int, Int]()
|
||||
for (i <- nums.indices) {
|
||||
val tmp = target - nums(i) // 计算差值
|
||||
// 如果这个差值存在于map,则说明找到了结果
|
||||
if (map.contains(tmp)) {
|
||||
return Array(map.get(tmp).get, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果不包含把当前值与其下标放到map
|
||||
map.put(nums(i), i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果没有找到直接返回一个空的数组,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
new Array[Int](2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int[] TwoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
|
||||
Dictionary<int ,int> dic= new Dictionary<int,int>();
|
||||
for(int i=0;i<nums.Length;i++){
|
||||
int imp= target-nums[i];
|
||||
if(dic.ContainsKey(imp)&&dic[imp]!=i){
|
||||
return new int[]{i, dic[imp]};
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!dic.ContainsKey(nums[i])){
|
||||
dic.Add(nums[i],i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return new int[]{0, 0};
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dart:
|
||||
```dart
|
||||
List<int> twoSum(List<int> nums, int target) {
|
||||
var tmp = [];
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
var rest = target - nums[i];
|
||||
if(tmp.contains(rest)){
|
||||
return [tmp.indexOf(rest), i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
tmp.add(nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return [0 , 0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 5.最长回文子串
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 第15题. 三数之和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -29,6 +29,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
针对本题,我录制了视频讲解:[梦破碎的地方!| LeetCode:15.三数之和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1GW4y127qo),结合本题解一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
**注意[0, 0, 0, 0] 这组数据**
|
||||
|
||||
## 哈希解法
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +41,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
去重的过程不好处理,有很多小细节,如果在面试中很难想到位。
|
||||
|
||||
时间复杂度可以做到$O(n^2)$,但还是比较费时的,因为不好做剪枝操作。
|
||||
时间复杂度可以做到O(n^2),但还是比较费时的,因为不好做剪枝操作。
|
||||
|
||||
大家可以尝试使用哈希法写一写,就知道其困难的程度了。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +87,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
**其实这道题目使用哈希法并不十分合适**,因为在去重的操作中有很多细节需要注意,在面试中很难直接写出没有bug的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
而且使用哈希法 在使用两层for循环的时候,能做的剪枝操作很有限,虽然时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$,也是可以在leetcode上通过,但是程序的执行时间依然比较长 。
|
||||
而且使用哈希法 在使用两层for循环的时候,能做的剪枝操作很有限,虽然时间复杂度是O(n^2),也是可以在leetcode上通过,但是程序的执行时间依然比较长 。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我来介绍另一个解法:双指针法,**这道题目使用双指针法 要比哈希法高效一些**,那么来讲解一下具体实现的思路。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,13 +97,13 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
拿这个nums数组来举例,首先将数组排序,然后有一层for循环,i从下标0的地方开始,同时定一个下标left 定义在i+1的位置上,定义下标right 在数组结尾的位置上。
|
||||
|
||||
依然还是在数组中找到 abc 使得a + b +c =0,我们这里相当于 a = nums[i] b = nums[left] c = nums[right]。
|
||||
依然还是在数组中找到 abc 使得a + b +c =0,我们这里相当于 a = nums[i],b = nums[left],c = nums[right]。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来如何移动left 和right呢, 如果nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0 就说明 此时三数之和大了,因为数组是排序后了,所以right下标就应该向左移动,这样才能让三数之和小一些。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0 说明 此时 三数之和小了,left 就向右移动,才能让三数之和大一些,直到left与right相遇为止。
|
||||
|
||||
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$。
|
||||
时间复杂度:O(n^2)。
|
||||
|
||||
C++代码代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,13 +120,13 @@ public:
|
||||
if (nums[i] > 0) {
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 错误去重方法,将会漏掉-1,-1,2 这种情况
|
||||
// 错误去重a方法,将会漏掉-1,-1,2 这种情况
|
||||
/*
|
||||
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
// 正确去重方法
|
||||
// 正确去重a方法
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -136,17 +138,11 @@ public:
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) {
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
// 当前元素不合适了,可以去重
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1]) right--;
|
||||
} else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0) {
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
// 不合适,去重
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) left++;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) right--;
|
||||
else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0) left++;
|
||||
else {
|
||||
result.push_back(vector<int>{nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
|
||||
// 去重逻辑应该放在找到一个三元组之后
|
||||
// 去重逻辑应该放在找到一个三元组之后,对b 和 c去重
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -162,6 +158,78 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 去重逻辑的思考
|
||||
|
||||
### a的去重
|
||||
|
||||
说道去重,其实主要考虑三个数的去重。 a, b ,c, 对应的就是 nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]
|
||||
|
||||
a 如果重复了怎么办,a是nums里遍历的元素,那么应该直接跳过去。
|
||||
|
||||
但这里有一个问题,是判断 nums[i] 与 nums[i + 1]是否相同,还是判断 nums[i] 与 nums[i-1] 是否相同。
|
||||
|
||||
有同学可能想,这不都一样吗。
|
||||
|
||||
其实不一样!
|
||||
|
||||
都是和 nums[i]进行比较,是比较它的前一个,还是比较他的后一个。
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们的写法是 这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```C++
|
||||
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) { // 去重操作
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
那就我们就把 三元组中出现重复元素的情况直接pass掉了。 例如{-1, -1 ,2} 这组数据,当遍历到第一个-1 的时候,判断 下一个也是-1,那这组数据就pass了。
|
||||
|
||||
**我们要做的是 不能有重复的三元组,但三元组内的元素是可以重复的!**
|
||||
|
||||
所以这里是有两个重复的维度。
|
||||
|
||||
那么应该这么写:
|
||||
|
||||
```C++
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这么写就是当前使用 nums[i],我们判断前一位是不是一样的元素,在看 {-1, -1 ,2} 这组数据,当遍历到 第一个 -1 的时候,只要前一位没有-1,那么 {-1, -1 ,2} 这组数据一样可以收录到 结果集里。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个非常细节的思考过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### b与c的去重
|
||||
|
||||
很多同学写本题的时候,去重的逻辑多加了 对right 和left 的去重:(代码中注释部分)
|
||||
|
||||
```C++
|
||||
while (right > left) {
|
||||
if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) {
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
// 去重 right
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1]) right--;
|
||||
} else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0) {
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
// 去重 left
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) left++;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但细想一下,这种去重其实对提升程序运行效率是没有帮助的。
|
||||
|
||||
拿right去重为例,即使不加这个去重逻辑,依然根据 `while (right > left) ` 和 `if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0)` 去完成right-- 的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
多加了 ` while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1]) right--;` 这一行代码,其实就是把 需要执行的逻辑提前执行了,但并没有减少 判断的逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
最直白的思考过程,就是right还是一个数一个数的减下去的,所以在哪里减的都是一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
所以这种去重 是可以不加的。 仅仅是 把去重的逻辑提前了而已。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 思考题
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -312,57 +380,109 @@ func threeSum(nums []int)[][]int{
|
||||
|
||||
javaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var threeSum = function(nums) {
|
||||
const res = [], len = nums.length
|
||||
// 将数组排序
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
|
||||
let l = i + 1, r = len - 1, iNum = nums[i]
|
||||
// 数组排过序,如果第一个数大于0直接返回res
|
||||
if (iNum > 0) return res
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
if (iNum == nums[i - 1]) continue
|
||||
while(l < r) {
|
||||
let lNum = nums[l], rNum = nums[r], threeSum = iNum + lNum + rNum
|
||||
// 三数之和小于0,则左指针向右移动
|
||||
if (threeSum < 0) l++
|
||||
else if (threeSum > 0) r--
|
||||
else {
|
||||
res.push([iNum, lNum, rNum])
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while(l < r && nums[l] == nums[l + 1]){
|
||||
l++
|
||||
}
|
||||
while(l < r && nums[r] == nums[r - 1]) {
|
||||
r--
|
||||
}
|
||||
l++
|
||||
r--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
解法二:nSum通用解法。递归
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* nsum通用解法,支持2sum,3sum,4sum...等等
|
||||
* 时间复杂度分析:
|
||||
* 1. n = 2时,时间复杂度O(NlogN),排序所消耗的时间。、
|
||||
* 2. n > 2时,时间复杂度为O(N^n-1),即N的n-1次方,至少是2次方,此时可省略排序所消耗的时间。举例:3sum为O(n^2),4sum为O(n^3)
|
||||
* @param {number[]} nums
|
||||
* @return {number[][]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// 循环内不考虑去重
|
||||
var threeSum = function(nums) {
|
||||
const len = nums.length;
|
||||
if(len < 3) return [];
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
const resSet = new Set();
|
||||
for(let i = 0; i < len - 2; i++) {
|
||||
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
|
||||
let l = i + 1, r = len - 1;
|
||||
while(l < r) {
|
||||
const sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r];
|
||||
if(sum < 0) { l++; continue };
|
||||
if(sum > 0) { r--; continue };
|
||||
resSet.add(`${nums[i]},${nums[l]},${nums[r]}`);
|
||||
l++;
|
||||
r--;
|
||||
var threeSum = function (nums) {
|
||||
// nsum通用解法核心方法
|
||||
function nSumTarget(nums, n, start, target) {
|
||||
// 前提:nums要先排序好
|
||||
let res = [];
|
||||
if (n === 2) {
|
||||
res = towSumTarget(nums, start, target);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (let i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
// 递归求(n - 1)sum
|
||||
let subRes = nSumTarget(
|
||||
nums,
|
||||
n - 1,
|
||||
i + 1,
|
||||
target - nums[i]
|
||||
);
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < subRes.length; j++) {
|
||||
res.push([nums[i], ...subRes[j]]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 跳过相同元素
|
||||
while (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Array.from(resSet).map(i => i.split(","));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 去重优化
|
||||
var threeSum = function(nums) {
|
||||
const len = nums.length;
|
||||
if(len < 3) return [];
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
const res = [];
|
||||
for(let i = 0; i < len - 2; i++) {
|
||||
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
|
||||
// a去重
|
||||
if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue;
|
||||
let l = i + 1, r = len - 1;
|
||||
while(l < r) {
|
||||
const sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r];
|
||||
if(sum < 0) { l++; continue };
|
||||
if(sum > 0) { r--; continue };
|
||||
res.push([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]])
|
||||
// b c 去重
|
||||
while(l < r && nums[l] === nums[++l]);
|
||||
while(l < r && nums[r] === nums[--r]);
|
||||
function towSumTarget(nums, start, target) {
|
||||
// 前提:nums要先排序好
|
||||
let res = [];
|
||||
let len = nums.length;
|
||||
let left = start;
|
||||
let right = len - 1;
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
let sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
|
||||
if (sum < target) {
|
||||
while (nums[left] === nums[left + 1]) left++;
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
} else if (sum > target) {
|
||||
while (nums[right] === nums[right - 1]) right--;
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 相等
|
||||
res.push([nums[left], nums[right]]);
|
||||
// 跳过相同元素
|
||||
while (nums[left] === nums[left + 1]) left++;
|
||||
while (nums[right] === nums[right - 1]) right--;
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
// n = 3,此时求3sum之和
|
||||
return nSumTarget(nums, 3, 0, 0);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
@@ -373,6 +493,9 @@ function threeSum(nums: number[]): number[][] {
|
||||
right: number = length - 1;
|
||||
let resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (nums[i]>0) {
|
||||
return resArr; //nums经过排序后,只要nums[i]>0, 此后的nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]均大于0,可以提前终止循环。
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -502,6 +625,71 @@ func threeSum(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
// 哈希解法
|
||||
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn three_sum(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut nums = nums;
|
||||
nums.sort();
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
for i in 0..len {
|
||||
if nums[i] > 0 { break; }
|
||||
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] { continue; }
|
||||
let mut set = HashSet::new();
|
||||
for j in (i + 1)..len {
|
||||
if j > i + 2 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1] && nums[j] == nums[j - 2] { continue; }
|
||||
let c = 0 - (nums[i] + nums[j]);
|
||||
if set.contains(&c) {
|
||||
result.push(vec![nums[i], nums[j], c]);
|
||||
set.remove(&c);
|
||||
} else { set.insert(nums[j]); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
// 双指针法
|
||||
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn three_sum(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut nums = nums;
|
||||
nums.sort();
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
for i in 0..len {
|
||||
if nums[i] > 0 { return result; }
|
||||
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] { continue; }
|
||||
let (mut left, mut right) = (i + 1, len - 1);
|
||||
while left < right {
|
||||
if nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0 {
|
||||
right -= 1;
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1] { right -= 1; }
|
||||
} else if nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0 {
|
||||
left += 1;
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1] { left += 1; }
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result.push(vec![nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]]);
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
right -= 1;
|
||||
left += 1;
|
||||
while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1] { right -= 1; }
|
||||
while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1] { left += 1; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
```C
|
||||
//qsort辅助cmp函数
|
||||
@@ -634,6 +822,49 @@ public class Solution
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
// 导包
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||||
import scala.util.control.Breaks.{break, breakable}
|
||||
|
||||
def threeSum(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
// 定义结果集,最后需要转换为List
|
||||
val res = ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
val nums_tmp = nums.sorted // 对nums进行排序
|
||||
for (i <- nums_tmp.indices) {
|
||||
// 如果要排的第一个数字大于0,直接返回结果
|
||||
if (nums_tmp(i) > 0) {
|
||||
return res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果i大于0并且和前一个数字重复,则跳过本次循环,相当于continue
|
||||
breakable {
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums_tmp(i) == nums_tmp(i - 1)) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var left = i + 1
|
||||
var right = nums_tmp.length - 1
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
var sum = nums_tmp(i) + nums_tmp(left) + nums_tmp(right) // 求三数之和
|
||||
if (sum < 0) left += 1
|
||||
else if (sum > 0) right -= 1
|
||||
else {
|
||||
res += List(nums_tmp(i), nums_tmp(left), nums_tmp(right)) // 如果等于0 添加进结果集
|
||||
// 为了避免重复,对left和right进行移动
|
||||
while (left < right && nums_tmp(left) == nums_tmp(left + 1)) left += 1
|
||||
while (left < right && nums_tmp(right) == nums_tmp(right - 1)) right -= 1
|
||||
left += 1
|
||||
right -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终返回需要转换为List,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 17.电话号码的字母组合
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -420,6 +420,83 @@ var letterCombinations = function(digits) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function letterCombinations(digits: string): string[] {
|
||||
if (digits === '') return [];
|
||||
const strMap: { [index: string]: string[] } = {
|
||||
1: [],
|
||||
2: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
|
||||
3: ['d', 'e', 'f'],
|
||||
4: ['g', 'h', 'i'],
|
||||
5: ['j', 'k', 'l'],
|
||||
6: ['m', 'n', 'o'],
|
||||
7: ['p', 'q', 'r', 's'],
|
||||
8: ['t', 'u', 'v'],
|
||||
9: ['w', 'x', 'y', 'z'],
|
||||
}
|
||||
const resArr: string[] = [];
|
||||
function backTracking(digits: string, curIndex: number, route: string[]): void {
|
||||
if (curIndex === digits.length) {
|
||||
resArr.push(route.join(''));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let tempArr: string[] = strMap[digits[curIndex]];
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = tempArr.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
route.push(tempArr[i]);
|
||||
backTracking(digits, curIndex + 1, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
backTracking(digits, 0, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<String>, s: &mut String, map: &[&str; 10], digits: &String, index: usize) {
|
||||
let len = digits.len();
|
||||
if len == index {
|
||||
result.push(s.to_string());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 在保证不会越界的情况下使用unwrap()将Some()中的值提取出来
|
||||
let digit= digits.chars().nth(index).unwrap().to_digit(10).unwrap() as usize;
|
||||
let letters = map[digit];
|
||||
for i in letters.chars() {
|
||||
s.push(i);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, s, &map, &digits, index+1);
|
||||
s.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn letter_combinations(digits: String) -> Vec<String> {
|
||||
if digits.len() == 0 {
|
||||
return vec![];
|
||||
}
|
||||
const MAP: [&str; 10] = [
|
||||
"",
|
||||
"",
|
||||
"abc",
|
||||
"def",
|
||||
"ghi",
|
||||
"jkl",
|
||||
"mno",
|
||||
"pqrs",
|
||||
"tuv",
|
||||
"wxyz"
|
||||
];
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut s: String = String::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut s, &MAP, &digits, 0);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -523,6 +600,37 @@ func letterCombinations(_ digits: String) -> [String] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def letterCombinations(digits: String): List[String] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
if(digits == "") return result.toList // 如果参数为空,返回空结果集的List形式
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Char]()
|
||||
// 数字和字符的映射关系
|
||||
val map = Array[String]("", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz")
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(index: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (index == digits.size) {
|
||||
result.append(path.mkString) // mkString语法:将数组类型直接转换为字符串
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var digit = digits(index) - '0' // 这里使用toInt会报错!必须 -'0'
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until map(digit).size) {
|
||||
path.append(map(digit)(i))
|
||||
backtracking(index + 1)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 第18题. 四数之和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
题意:给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素 a,b,c 和 d ,使得 a + b + c + d 的值与 target 相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -29,17 +29,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
针对本题,我录制了视频讲解:[难在去重和剪枝!| LeetCode:18. 四数之和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DS4y147US),结合本题解一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
四数之和,和[15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html)是一个思路,都是使用双指针法, 基本解法就是在[15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html) 的基础上再套一层for循环。
|
||||
|
||||
但是有一些细节需要注意,例如: 不要判断`nums[k] > target` 就返回了,三数之和 可以通过 `nums[i] > 0` 就返回了,因为 0 已经是确定的数了,四数之和这道题目 target是任意值。(大家亲自写代码就能感受出来)
|
||||
但是有一些细节需要注意,例如: 不要判断`nums[k] > target` 就返回了,三数之和 可以通过 `nums[i] > 0` 就返回了,因为 0 已经是确定的数了,四数之和这道题目 target是任意值。比如:数组是`[-4, -3, -2, -1]`,`target`是`-10`,不能因为`-4 > -10`而跳过。但是我们依旧可以去做剪枝,逻辑变成`nums[i] > target && (nums[i] >=0 || target >= 0)`就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
[15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html)的双指针解法是一层for循环num[i]为确定值,然后循环内有left和right下标作为双指针,找到nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == 0。
|
||||
|
||||
四数之和的双指针解法是两层for循环nums[k] + nums[i]为确定值,依然是循环内有left和right下标作为双指针,找出nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == target的情况,三数之和的时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$,四数之和的时间复杂度是$O(n^3)$ 。
|
||||
四数之和的双指针解法是两层for循环nums[k] + nums[i]为确定值,依然是循环内有left和right下标作为双指针,找出nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == target的情况,三数之和的时间复杂度是O(n^2),四数之和的时间复杂度是O(n^3) 。
|
||||
|
||||
那么一样的道理,五数之和、六数之和等等都采用这种解法。
|
||||
|
||||
对于[15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html)双指针法就是将原本暴力$O(n^3)$的解法,降为$O(n^2)$的解法,四数之和的双指针解法就是将原本暴力$O(n^4)$的解法,降为$O(n^3)$的解法。
|
||||
对于[15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html)双指针法就是将原本暴力O(n^3)的解法,降为O(n^2)的解法,四数之和的双指针解法就是将原本暴力O(n^4)的解法,降为O(n^3)的解法。
|
||||
|
||||
之前我们讲过哈希表的经典题目:[454.四数相加II](https://programmercarl.com/0454.四数相加II.html),相对于本题简单很多,因为本题是要求在一个集合中找出四个数相加等于target,同时四元组不能重复。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,14 +49,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
我们来回顾一下,几道题目使用了双指针法。
|
||||
|
||||
双指针法将时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$的解法优化为 $O(n)$的解法。也就是降一个数量级,题目如下:
|
||||
双指针法将时间复杂度:O(n^2)的解法优化为 O(n)的解法。也就是降一个数量级,题目如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* [27.移除元素](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html)
|
||||
* [15.三数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0015.三数之和.html)
|
||||
* [18.四数之和](https://programmercarl.com/0018.四数之和.html)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
操作链表:
|
||||
链表相关双指针题目:
|
||||
|
||||
* [206.反转链表](https://programmercarl.com/0206.翻转链表.html)
|
||||
* [19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点](https://programmercarl.com/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.html)
|
||||
@@ -72,16 +73,21 @@ public:
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> result;
|
||||
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
|
||||
for (int k = 0; k < nums.size(); k++) {
|
||||
// 这种剪枝是错误的,这道题目target 是任意值
|
||||
// if (nums[k] > target) {
|
||||
// return result;
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
// 剪枝处理
|
||||
if (nums[k] > target && nums[k] >= 0) {
|
||||
break; // 这里使用break,统一通过最后的return返回
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 对nums[k]去重
|
||||
if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = k + 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
||||
// 正确去重方法
|
||||
// 2级剪枝处理
|
||||
if (nums[k] + nums[i] > target && nums[k] + nums[i] >= 0) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 对nums[i]去重
|
||||
if (i > k + 1 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -89,18 +95,14 @@ public:
|
||||
int right = nums.size() - 1;
|
||||
while (right > left) {
|
||||
// nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target 会溢出
|
||||
if (nums[k] + nums[i] > target - (nums[left] + nums[right])) {
|
||||
if ((long) nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target) {
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
// 当前元素不合适了,可以去重
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1]) right--;
|
||||
// nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target 会溢出
|
||||
} else if (nums[k] + nums[i] < target - (nums[left] + nums[right])) {
|
||||
} else if ((long) nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target) {
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
// 不合适,去重
|
||||
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) left++;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result.push_back(vector<int>{nums[k], nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
|
||||
// 去重逻辑应该放在找到一个四元组之后
|
||||
// 对nums[left]和nums[right]去重
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
|
||||
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -135,6 +137,11 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
// nums[i] > target 直接返回, 剪枝操作
|
||||
if (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] > target) {
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -148,7 +155,7 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
int left = j + 1;
|
||||
int right = nums.length - 1;
|
||||
while (right > left) {
|
||||
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
|
||||
long sum = (long) nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
|
||||
if (sum > target) {
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
} else if (sum < target) {
|
||||
@@ -518,5 +525,93 @@ public class Solution
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn four_sum(nums: Vec<i32>, target: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut nums = nums;
|
||||
nums.sort();
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
for k in 0..len {
|
||||
// 剪枝
|
||||
if nums[k] > target && (nums[k] > 0 || target > 0) { break; }
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
if k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1] { continue; }
|
||||
for i in (k + 1)..len {
|
||||
// 剪枝
|
||||
if nums[k] + nums[i] > target && (nums[k] + nums[i] >= 0 || target >= 0) { break; }
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
if i > k + 1 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] { continue; }
|
||||
let (mut left, mut right) = (i + 1, len - 1);
|
||||
while left < right {
|
||||
if nums[k] + nums[i] > target - (nums[left] + nums[right]) {
|
||||
right -= 1;
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right + 1] { right -= 1; }
|
||||
} else if nums[k] + nums[i] < target - (nums[left] + nums[right]) {
|
||||
left += 1;
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1] { left += 1; }
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result.push(vec![nums[k], nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]]);
|
||||
// 去重
|
||||
while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1] { right -= 1; }
|
||||
while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1] { left += 1; }
|
||||
left += 1;
|
||||
right -= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
// 导包
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||||
import scala.util.control.Breaks.{break, breakable}
|
||||
def fourSum(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
val res = ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
val nums_tmp = nums.sorted // 先排序
|
||||
for (i <- nums_tmp.indices) {
|
||||
breakable {
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums_tmp(i) == nums_tmp(i - 1)) {
|
||||
break // 如果该值和上次的值相同,跳过本次循环,相当于continue
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (j <- i + 1 until nums_tmp.length) {
|
||||
breakable {
|
||||
if (j > i + 1 && nums_tmp(j) == nums_tmp(j - 1)) {
|
||||
break // 同上
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 双指针
|
||||
var (left, right) = (j + 1, nums_tmp.length - 1)
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
var sum = nums_tmp(i) + nums_tmp(j) + nums_tmp(left) + nums_tmp(right)
|
||||
if (sum == target) {
|
||||
// 满足要求,直接加入到集合里面去
|
||||
res += List(nums_tmp(i), nums_tmp(j), nums_tmp(left), nums_tmp(right))
|
||||
while (left < right && nums_tmp(left) == nums_tmp(left + 1)) left += 1
|
||||
while (left < right && nums_tmp(right) == nums_tmp(right - 1)) right -= 1
|
||||
left += 1
|
||||
right -= 1
|
||||
} else if (sum < target) left += 1
|
||||
else right -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终返回的res要转换为List,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,13 +33,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法公开课:[链表遍历学清楚! | LeetCode:19.删除链表倒数第N个节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1U7Gf),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
双指针的经典应用,如果要删除倒数第n个节点,让fast移动n步,然后让fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向链表末尾。删掉slow所指向的节点就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
思路是这样的,但要注意一些细节。
|
||||
|
||||
分为如下几步:
|
||||
|
||||
* 首先这里我推荐大家使用虚拟头结点,这样方面处理删除实际头结点的逻辑,如果虚拟头结点不清楚,可以看这篇: [链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](https://programmercarl.com/0203.移除链表元素.html)
|
||||
* 首先这里我推荐大家使用虚拟头结点,这样方便处理删除实际头结点的逻辑,如果虚拟头结点不清楚,可以看这篇: [链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](https://programmercarl.com/0203.移除链表元素.html)
|
||||
|
||||
* 定义fast指针和slow指针,初始值为虚拟头结点,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -188,18 +191,20 @@ TypeScript:
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let newHead: ListNode | null = new ListNode(0, head);
|
||||
let slowNode: ListNode | null = newHead,
|
||||
fastNode: ListNode | null = newHead;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next;
|
||||
//根据leetcode题目的定义可推断这里快慢指针均不需要定义为ListNode | null。
|
||||
let slowNode: ListNode = newHead;
|
||||
let fastNode: ListNode = newHead;
|
||||
|
||||
while(n--) {
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next!; //由虚拟头节点前进n个节点时,fastNode.next可推断不为null。
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (fastNode.next) {
|
||||
while(fastNode.next) { //遍历直至fastNode.next = null, 即尾部节点。 此时slowNode指向倒数第n个节点。
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next;
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode.next;
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
|
||||
}
|
||||
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
|
||||
return newHead.next;
|
||||
};
|
||||
slowNode.next = slowNode.next!.next; //倒数第n个节点可推断其next节点不为空。
|
||||
return newHead.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
版本二(计算节点总数法):
|
||||
@@ -290,5 +295,51 @@ func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
|
||||
// 设置虚拟头节点
|
||||
$dummyHead = new ListNode();
|
||||
$dummyHead->next = $head;
|
||||
|
||||
$slow = $fast = $dummyHead;
|
||||
while($n-- && $fast != null){
|
||||
$fast = $fast->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// fast 再走一步,让 slow 指向删除节点的上一个节点
|
||||
$fast = $fast->next;
|
||||
while ($fast != NULL) {
|
||||
$fast = $fast->next;
|
||||
$slow = $slow->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
$slow->next = $slow->next->next;
|
||||
return $dummyHead->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode, n: Int): ListNode = {
|
||||
val dummy = new ListNode(-1, head) // 定义虚拟头节点
|
||||
var fast = head // 快指针从头开始走
|
||||
var slow = dummy // 慢指针从虚拟头开始头
|
||||
// 因为参数 n 是不可变量,所以不能使用 while(n>0){n-=1}的方式
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until n) {
|
||||
fast = fast.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 快指针和满指针一起走,直到fast走到null
|
||||
while (fast != null) {
|
||||
slow = slow.next
|
||||
fast = fast.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 删除slow的下一个节点
|
||||
slow.next = slow.next.next
|
||||
// 返回虚拟头节点的下一个
|
||||
dummy.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 20. 有效的括号
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,6 +41,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[栈的拿手好戏!| LeetCode:20. 有效的括号](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1AF411w78g),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 题外话
|
||||
|
||||
**括号匹配是使用栈解决的经典问题。**
|
||||
@@ -79,8 +82,10 @@ cd a/b/c/../../
|
||||
|
||||
1. 第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了 ,所以不匹配。
|
||||
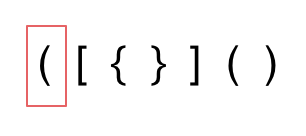
|
||||
|
||||
2. 第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上。
|
||||
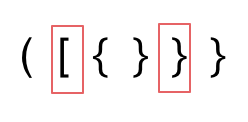
|
||||
|
||||
3. 第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
|
||||
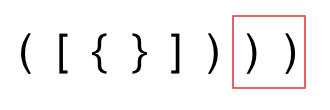
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -110,7 +115,8 @@ cd a/b/c/../../
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool isValid(string s) {
|
||||
stack<int> st;
|
||||
if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // 如果s的长度为奇数,一定不符合要求
|
||||
stack<char> st;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
|
||||
if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');
|
||||
else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');
|
||||
@@ -124,6 +130,7 @@ public:
|
||||
return st.empty();
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
技巧性的东西没有固定的学习方法,还是要多看多练,自己灵活运用了。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -401,5 +408,90 @@ bool isValid(char * s){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public bool IsValid(string s) {
|
||||
var len = s.Length;
|
||||
if(len % 2 == 1) return false; // 字符串长度为单数,直接返回 false
|
||||
// 初始化栈
|
||||
var stack = new Stack<char>();
|
||||
// 遍历字符串
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
|
||||
// 当字符串为左括号时,进栈对应的右括号
|
||||
if(s[i] == '('){
|
||||
stack.Push(')');
|
||||
}else if(s[i] == '['){
|
||||
stack.Push(']');
|
||||
}else if(s[i] == '{'){
|
||||
stack.Push('}');
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 当字符串为右括号时,当栈为空(无左括号) 或者 出栈字符不是当前的字符
|
||||
else if(stack.Count == 0 || stack.Pop() != s[i])
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果栈不为空,例如“((()”,右括号少于左括号,返回false
|
||||
if (stack.Count > 0)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
// 上面的校验都满足,则返回true
|
||||
else
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splstack.php
|
||||
class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
function isValid($s){
|
||||
$stack = new SplStack();
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
|
||||
if ($s[$i] == "(") {
|
||||
$stack->push(')');
|
||||
} else if ($s[$i] == "{") {
|
||||
$stack->push('}');
|
||||
} else if ($s[$i] == "[") {
|
||||
$stack->push(']');
|
||||
// 2、遍历匹配过程中,发现栈内没有要匹配的字符 return false
|
||||
// 3、遍历匹配过程中,栈已为空,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false
|
||||
} else if ($stack->isEmpty() || $stack->top() != $s[$i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
} else {//$stack->top() == $s[$i]
|
||||
$stack->pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 1、遍历完,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的括号没有被匹配,return false
|
||||
return $stack->isEmpty();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def isValid(s: String): Boolean = {
|
||||
if(s.length % 2 != 0) return false // 如果字符串长度是奇数直接返回false
|
||||
val stack = mutable.Stack[Char]()
|
||||
// 循环遍历字符串
|
||||
for (i <- s.indices) {
|
||||
val c = s(i)
|
||||
if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') stack.push(c)
|
||||
else if(stack.isEmpty) return false // 如果没有(、[、{则直接返回false
|
||||
// 以下三种情况,不满足则直接返回false
|
||||
else if(c==')' && stack.pop() != '(') return false
|
||||
else if(c==']' && stack.pop() != '[') return false
|
||||
else if(c=='}' && stack.pop() != '{') return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果为空则正确匹配,否则还有余孽就不匹配
|
||||
stack.isEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +18,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法公开课:[帮你把链表细节学清楚! | LeetCode:24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目正常模拟就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
建议使用虚拟头结点,这样会方便很多,要不然每次针对头结点(没有前一个指针指向头结点),还要单独处理。
|
||||
@@ -63,8 +66,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
## 拓展
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -254,20 +257,19 @@ TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
|
||||
const dummyHead: ListNode = new ListNode(0, head);
|
||||
let cur: ListNode = dummyHead;
|
||||
while(cur.next !== null && cur.next.next !== null) {
|
||||
const tem: ListNode = cur.next;
|
||||
const tem1: ListNode = cur.next.next.next;
|
||||
|
||||
cur.next = cur.next.next; // step 1
|
||||
cur.next.next = tem; // step 2
|
||||
cur.next.next.next = tem1; // step 3
|
||||
|
||||
cur = cur.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dummyHead.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const dummyNode: ListNode = new ListNode(0, head);
|
||||
let curNode: ListNode | null = dummyNode;
|
||||
while (curNode && curNode.next && curNode.next.next) {
|
||||
let firstNode: ListNode = curNode.next,
|
||||
secNode: ListNode = curNode.next.next,
|
||||
thirdNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next.next.next;
|
||||
curNode.next = secNode;
|
||||
secNode.next = firstNode;
|
||||
firstNode.next = thirdNode;
|
||||
curNode = firstNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dummyNode.next;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
@@ -311,7 +313,72 @@ func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
|
||||
return dummyHead.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 虚拟头节点
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def swapPairs(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
var dummy = new ListNode(0, head) // 虚拟头节点
|
||||
var pre = dummy
|
||||
var cur = head
|
||||
// 当pre的下一个和下下个都不为空,才进行两两转换
|
||||
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null) {
|
||||
var tmp: ListNode = cur.next.next // 缓存下一次要进行转换的第一个节点
|
||||
pre.next = cur.next // 步骤一
|
||||
cur.next.next = cur // 步骤二
|
||||
cur.next = tmp // 步骤三
|
||||
// 下面是准备下一轮的交换
|
||||
pre = cur
|
||||
cur = tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终返回dummy虚拟头节点的下一个,return可以省略
|
||||
dummy.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
//虚拟头结点
|
||||
function swapPairs($head) {
|
||||
if ($head == null || $head->next == null) {
|
||||
return $head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
$dummyNode = new ListNode(0, $head);
|
||||
$preNode = $dummyNode; //虚拟头结点
|
||||
$curNode = $head;
|
||||
$nextNode = $head->next;
|
||||
while($curNode && $nextNode) {
|
||||
$nextNextNode = $nextNode->next; //存下一个节点
|
||||
$nextNode->next = $curNode; //交换curHead 和 nextHead
|
||||
$curNode->next = $nextNextNode;
|
||||
$preNode->next = $nextNode; //上一个节点的下一个指向指向nextHead
|
||||
|
||||
//更新当前的几个指针
|
||||
$preNode = $preNode->next->next;
|
||||
$curNode = $nextNextNode;
|
||||
$nextNode = $nextNextNode->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return $dummyNode->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//递归版本
|
||||
function swapPairs($head)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// 终止条件
|
||||
if ($head === null || $head->next === null) {
|
||||
return $head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//结果要返回的头结点
|
||||
$next = $head->next;
|
||||
$head->next = $this->swapPairs($next->next); //当前头结点->next指向更新
|
||||
$next->next = $head; //当前第二个节点的->next指向更新
|
||||
return $next; //返回翻转后的头结点
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 27. 移除元素
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,6 +28,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
针对本题,我录制了视频讲解:[数组中移除元素并不容易!LeetCode:27. 移除元素](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12A4y1Z7LP),结合本题解一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
有的同学可能说了,多余的元素,删掉不就得了。
|
||||
|
||||
**要知道数组的元素在内存地址中是连续的,不能单独删除数组中的某个元素,只能覆盖。**
|
||||
@@ -75,13 +77,23 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
双指针法(快慢指针法): **通过一个快指针和慢指针在一个for循环下完成两个for循环的工作。**
|
||||
|
||||
定义快慢指针
|
||||
|
||||
* 快指针:寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
|
||||
* 慢指针:指向更新 新数组下标的位置
|
||||
|
||||
很多同学这道题目做的很懵,就是不理解 快慢指针究竟都是什么含义,所以一定要明确含义,后面的思路就更容易理解了。
|
||||
|
||||
删除过程如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
很多同学不了解
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**双指针法(快慢指针法)在数组和链表的操作中是非常常见的,很多考察数组、链表、字符串等操作的面试题,都使用双指针法。**
|
||||
|
||||
后序都会一一介绍到,本题代码如下:
|
||||
后续都会一一介绍到,本题代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
@@ -104,8 +116,6 @@ public:
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
旧文链接:[数组:就移除个元素很难么?](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html)
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 相向双指针方法,基于元素顺序可以改变的题目描述改变了元素相对位置,确保了移动最少元素
|
||||
@@ -136,7 +146,7 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 相关题目推荐
|
||||
|
||||
* 26.删除排序数组中的重复项
|
||||
@@ -144,10 +154,6 @@ public:
|
||||
* 844.比较含退格的字符串
|
||||
* 977.有序数组的平方
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -155,46 +161,59 @@ Java:
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
|
||||
|
||||
// 快慢指针
|
||||
int fastIndex = 0;
|
||||
int slowIndex;
|
||||
for (slowIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
|
||||
int slowIndex = 0;
|
||||
for (int fastIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
|
||||
if (nums[fastIndex] != val) {
|
||||
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
|
||||
slowIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slowIndex;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//相向双指针法
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
|
||||
int left = 0;
|
||||
int right = nums.length - 1;
|
||||
while(right >= 0 && nums[right] == val) right--; //将right移到从右数第一个值不为val的位置
|
||||
while(left <= right) {
|
||||
if(nums[left] == val) { //left位置的元素需要移除
|
||||
//将right位置的元素移到left(覆盖),right位置移除
|
||||
nums[left] = nums[right];
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
while(right >= 0 && nums[right] == val) right--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return left;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python3
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
"""双指针法
|
||||
时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def removeElement(cls, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
|
||||
fast = slow = 0
|
||||
|
||||
while fast < len(nums):
|
||||
|
||||
if nums[fast] != val:
|
||||
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
|
||||
slow += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# 当 fast 指针遇到要删除的元素时停止赋值
|
||||
# slow 指针停止移动, fast 指针继续前进
|
||||
fast += 1
|
||||
|
||||
return slow
|
||||
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
|
||||
if nums is None or len(nums)==0:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
l=0
|
||||
r=len(nums)-1
|
||||
while l<r:
|
||||
while(l<r and nums[l]!=val):
|
||||
l+=1
|
||||
while(l<r and nums[r]==val):
|
||||
r-=1
|
||||
nums[l], nums[r]=nums[r], nums[l]
|
||||
print(nums)
|
||||
if nums[l]==val:
|
||||
return l
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return l+1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -209,6 +228,7 @@ func removeElement(nums []int, val int) int {
|
||||
res++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
nums=nums[:res]
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -281,10 +301,8 @@ func removeElement(_ nums: inout [Int], _ val: Int) -> Int {
|
||||
|
||||
for fastIndex in 0..<nums.count {
|
||||
if val != nums[fastIndex] {
|
||||
if slowIndex != fastIndex {
|
||||
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex]
|
||||
}
|
||||
slowIndex += 1
|
||||
slowIndex += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slowIndex
|
||||
@@ -331,5 +349,47 @@ int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
fun removeElement(nums: IntArray, `val`: Int): Int {
|
||||
var slowIndex = 0 // 初始化慢指针
|
||||
for (fastIndex in nums.indices) {
|
||||
if (nums[fastIndex] != `val`) nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex] // 在慢指针所在位置存储未被删除的元素
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slowIndex
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def removeElement(nums: Array[Int], `val`: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var slow = 0
|
||||
for (fast <- 0 until nums.length) {
|
||||
if (`val` != nums(fast)) {
|
||||
nums(slow) = nums(fast)
|
||||
slow += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
slow
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int RemoveElement(int[] nums, int val) {
|
||||
int slow = 0;
|
||||
for (int fast = 0; fast < nums.Length; fast++) {
|
||||
if (val != nums[fast]) {
|
||||
nums[slow++] = nums[fast];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slow;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 28. 实现 strStr()
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-strstr/)
|
||||
|
||||
实现 strStr() 函数。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -685,7 +685,21 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python3:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
//暴力解法:
|
||||
class Solution(object):
|
||||
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:type haystack: str
|
||||
:type needle: str
|
||||
:rtype: int
|
||||
"""
|
||||
m,n=len(haystack),len(needle)
|
||||
for i in range(m):
|
||||
if haystack[i:i+n]==needle:
|
||||
return i
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
// 方法一
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
@@ -1059,5 +1073,231 @@ func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 前缀表右移
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
|
||||
|
||||
let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
|
||||
guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
|
||||
|
||||
var j = 0
|
||||
var next = [Int].init(repeating: 0, count: p.count)
|
||||
getNext(&next, p)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in 0 ..< s.count {
|
||||
|
||||
while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s[i] == p[j] {
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if j == p.count {
|
||||
return i - p.count + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 前缀表后移一位,首位用 -1 填充
|
||||
func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], _ needle: [Character]) {
|
||||
|
||||
guard needle.count > 1 else { return }
|
||||
|
||||
var j = 0
|
||||
next[0] = j
|
||||
|
||||
for i in 1 ..< needle.count-1 {
|
||||
|
||||
while j > 0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if needle[i] == needle[j] {
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
next[i] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
next.removeLast()
|
||||
next.insert(-1, at: 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 前缀表统一不减一
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
|
||||
func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
|
||||
|
||||
let s = Array(haystack), p = Array(needle)
|
||||
guard p.count != 0 else { return 0 }
|
||||
|
||||
var j = 0
|
||||
var next = [Int](repeating: 0, count: needle.count)
|
||||
// KMP
|
||||
getNext(&next, needle: p)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in 0 ..< s.count {
|
||||
while j > 0 && s[i] != p[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s[i] == p[j] {
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if j == p.count {
|
||||
return i - p.count + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//前缀表
|
||||
func getNext(_ next: inout [Int], needle: [Character]) {
|
||||
|
||||
var j = 0
|
||||
next[0] = j
|
||||
|
||||
for i in 1 ..< needle.count {
|
||||
|
||||
while j>0 && needle[i] != needle[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if needle[i] == needle[j] {
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
next[i] = j
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
|
||||
> 前缀表统一减一
|
||||
```php
|
||||
function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
|
||||
if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
|
||||
$next= [];
|
||||
$this->getNext($next,$needle);
|
||||
|
||||
$j = -1;
|
||||
for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
|
||||
while($j >= 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j + 1]) {
|
||||
$j = $next[$j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j + 1]) {
|
||||
$j++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($j == (strlen($needle) - 1) ) {
|
||||
return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getNext(&$next, $s){
|
||||
$j = -1;
|
||||
$next[0] = $j;
|
||||
for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
|
||||
while ($j >= 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j + 1]) {
|
||||
$j = $next[$j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($s[$i] == $s[$j + 1]) {
|
||||
$j++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
$next[$i] = $j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 前缀表统一不减一
|
||||
```php
|
||||
function strStr($haystack, $needle) {
|
||||
if (strlen($needle) == 0) return 0;
|
||||
$next= [];
|
||||
$this->getNext($next,$needle);
|
||||
|
||||
$j = 0;
|
||||
for ($i = 0;$i < strlen($haystack); $i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
|
||||
while($j > 0 && $haystack[$i] != $needle[$j]) {
|
||||
$j = $next[$j-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($haystack[$i] == $needle[$j]) {
|
||||
$j++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($j == strlen($needle)) {
|
||||
return ($i - strlen($needle) + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getNext(&$next, $s){
|
||||
$j = 0;
|
||||
$next[0] = $j;
|
||||
for($i = 1; $i < strlen($s); $i++) { // 注意i从1开始
|
||||
while ($j > 0 && $s[$i] != $s[$j]) {
|
||||
$j = $next[$j-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ($s[$i] == $s[$j]) {
|
||||
$j++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
$next[$i] = $j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
> 前缀表统一不减一
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn get_next(next: &mut Vec<usize>, s: &Vec<char>) {
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
let mut j = 0;
|
||||
for i in 1..len {
|
||||
while j > 0 && s[i] != s[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s[i] == s[j] {
|
||||
j += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
next[i] = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
|
||||
let (haystack_len, needle_len) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
|
||||
if haystack_len == 0 { return 0; }
|
||||
if haystack_len < needle_len { return -1;}
|
||||
let (haystack, needle) = (haystack.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>(), needle.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>());
|
||||
let mut next: Vec<usize> = vec![0; haystack_len];
|
||||
Self::get_next(&mut next, &needle);
|
||||
let mut j = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..haystack_len {
|
||||
while j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j] {
|
||||
j = next[j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if haystack[i] == needle[j] {
|
||||
j += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j == needle_len {
|
||||
return (i - needle_len + 1) as i32;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 31.下一个排列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-permutation/)
|
||||
|
||||
实现获取 下一个排列 的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -116,6 +116,48 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
> 优化时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1)
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
|
||||
// 1.从后向前获取逆序区域的前一位
|
||||
int index = findIndex(nums);
|
||||
// 判断数组是否处于最小组合状态
|
||||
if(index != 0){
|
||||
// 2.交换逆序区域刚好大于它的最小数字
|
||||
exchange(nums,index);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 3.把原来的逆序区转为顺序
|
||||
reverse(nums,index);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static int findIndex(int [] nums){
|
||||
for(int i = nums.length-1;i>0;i--){
|
||||
if(nums[i]>nums[i-1]){
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
public static void exchange(int [] nums, int index){
|
||||
int head = nums[index-1];
|
||||
for(int i = nums.length-1;i>0;i--){
|
||||
if(head < nums[i]){
|
||||
nums[index-1] = nums[i];
|
||||
nums[i] = head;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
public static void reverse(int [] nums, int index){
|
||||
for(int i = index,j = nums.length-1;i<j;i++,j--){
|
||||
int temp = nums[i];
|
||||
nums[i] = nums[j];
|
||||
nums[j] = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
>直接使用sorted()不符合题意
|
||||
@@ -136,10 +178,10 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
>另一种思路
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
'''
|
||||
抛砖引玉:因题目要求“必须原地修改,只允许使用额外常数空间”,python内置sorted函数以及数组切片+sort()无法使用。
|
||||
故选择另一种算法暂且提供一种python思路
|
||||
'''
|
||||
'''
|
||||
抛砖引玉:因题目要求“必须原地修改,只允许使用额外常数空间”,python内置sorted函数以及数组切片+sort()无法使用。
|
||||
故选择另一种算法暂且提供一种python思路
|
||||
'''
|
||||
def nextPermutation(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
|
||||
@@ -153,9 +195,9 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
break
|
||||
self.reverse(nums, i, length-1)
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# 若正常结束循环,则对原数组直接翻转
|
||||
self.reverse(nums, 0, length-1)
|
||||
if n == 1:
|
||||
# 若正常结束循环,则对原数组直接翻转
|
||||
self.reverse(nums, 0, length-1)
|
||||
|
||||
def reverse(self, nums: List[int], low: int, high: int) -> None:
|
||||
while low < high:
|
||||
@@ -164,20 +206,20 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
high -= 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
>上一版本简化版
|
||||
'''python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution(object):
|
||||
def nextPermutation(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
|
||||
n = len(nums)
|
||||
i = n-2
|
||||
while i >= 0 and nums[i] >= nums[i+1]:
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if i > -1: // i==-1,不存在下一个更大的排列
|
||||
j = n-1
|
||||
while j >= 0 and nums[j] <= nums[i]:
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
start, end = i+1, n-1
|
||||
while start < end:
|
||||
nums[start], nums[end] = nums[end], nums[start]
|
||||
@@ -185,11 +227,31 @@ class Solution(object):
|
||||
end -= 1
|
||||
|
||||
return nums
|
||||
'''
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
//卡尔的解法
|
||||
func nextPermutation(nums []int) {
|
||||
for i:=len(nums)-1;i>=0;i--{
|
||||
for j:=len(nums)-1;j>i;j--{
|
||||
if nums[j]>nums[i]{
|
||||
//交换
|
||||
nums[j],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[j]
|
||||
reverse(nums,0+i+1,len(nums)-1)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
reverse(nums,0,len(nums)-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
//对目标切片指定区间的反转方法
|
||||
func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
|
||||
for i,j:=begin,end;i<j;i,j=i+1,j-1{
|
||||
a[i],a[j]=a[j],a[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
|
||||
|
||||
如果数组中不存在目标值 target,返回 [-1, -1]。
|
||||
@@ -482,5 +485,150 @@ var searchRange = function(nums, target) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function searchRange(nums: number[], target: number): number[] {
|
||||
const leftBoard: number = getLeftBorder(nums, target);
|
||||
const rightBoard: number = getRightBorder(nums, target);
|
||||
// target 在nums区间左侧或右侧
|
||||
if (leftBoard === (nums.length - 1) || rightBoard === 0) return [-1, -1];
|
||||
// target 不存在与nums范围内
|
||||
if (rightBoard - leftBoard <= 1) return [-1, -1];
|
||||
// target 存在于nums范围内
|
||||
return [leftBoard + 1, rightBoard - 1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
// 查找第一个大于target的元素下标
|
||||
function getRightBorder(nums: number[], target: number): number {
|
||||
let left: number = 0,
|
||||
right: number = nums.length - 1;
|
||||
// 0表示target在nums区间的左边
|
||||
let rightBoard: number = 0;
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
|
||||
if (nums[mid] <= target) {
|
||||
// 右边界一定在mid右边(不含mid)
|
||||
left = mid + 1;
|
||||
rightBoard = left;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 右边界在mid左边(含mid)
|
||||
right = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return rightBoard;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 查找第一个小于target的元素下标
|
||||
function getLeftBorder(nums: number[], target: number): number {
|
||||
let left: number = 0,
|
||||
right: number = nums.length - 1;
|
||||
// length-1表示target在nums区间的右边
|
||||
let leftBoard: number = nums.length - 1;
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
|
||||
if (nums[mid] >= target) {
|
||||
// 左边界一定在mid左边(不含mid)
|
||||
right = mid - 1;
|
||||
leftBoard = right;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 左边界在mid右边(含mid)
|
||||
left = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return leftBoard;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def searchRange(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Array[Int] = {
|
||||
var left = getLeftBorder(nums, target)
|
||||
var right = getRightBorder(nums, target)
|
||||
if (left == -2 || right == -2) return Array(-1, -1)
|
||||
if (right - left > 1) return Array(left + 1, right - 1)
|
||||
Array(-1, -1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 寻找左边界
|
||||
def getLeftBorder(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var leftBorder = -2
|
||||
var left = 0
|
||||
var right = nums.length - 1
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
var mid = left + (right - left) / 2
|
||||
if (nums(mid) >= target) {
|
||||
right = mid - 1
|
||||
leftBorder = right
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
left = mid + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
leftBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 寻找右边界
|
||||
def getRightBorder(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var rightBorder = -2
|
||||
var left = 0
|
||||
var right = nums.length - 1
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
var mid = left + (right - left) / 2
|
||||
if (nums(mid) <= target) {
|
||||
left = mid + 1
|
||||
rightBorder = left
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
right = mid - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
rightBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Kotlin
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
fun searchRange(nums: IntArray, target: Int): IntArray {
|
||||
var index = binarySearch(nums, target)
|
||||
// 没找到,返回[-1, -1]
|
||||
if (index == -1) return intArrayOf(-1, -1)
|
||||
var left = index
|
||||
var right = index
|
||||
// 寻找左边界
|
||||
while (left - 1 >=0 && nums[left - 1] == target){
|
||||
left--
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 寻找右边界
|
||||
while (right + 1 <nums.size && nums[right + 1] == target){
|
||||
right++
|
||||
}
|
||||
return intArrayOf(left, right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 二分查找常规写法
|
||||
fun binarySearch(nums: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
|
||||
var left = 0;
|
||||
var right = nums.size - 1
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
var middle = left + (right - left)/2
|
||||
if (nums[middle] > target) {
|
||||
right = middle - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
if (nums[middle] < target) {
|
||||
left = middle + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
return middle
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 没找到,返回-1
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 35.搜索插入位置
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -73,8 +73,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
效率如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -135,14 +135,14 @@ public:
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之前 [0, -1]
|
||||
// 目标值等于数组中某一个元素 return middle;
|
||||
// 目标值插入数组中的位置 [left, right],return right + 1
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之后的情况 [left, right], return right + 1
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之后的情况 [left, right], 因为是右闭区间,所以 return right + 1
|
||||
return right + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(\log n)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(log n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
效率如下:
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -178,7 +178,7 @@ public:
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之前 [0,0)
|
||||
// 目标值等于数组中某一个元素 return middle
|
||||
// 目标值插入数组中的位置 [left, right) ,return right 即可
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之后的情况 [left, right),return right 即可
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之后的情况 [left, right),因为是右开区间,所以 return right
|
||||
return right;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@@ -226,7 +226,32 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//第二种二分法:左闭右开
|
||||
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
|
||||
int left = 0;
|
||||
int right = nums.length;
|
||||
while (left < right) { //左闭右开 [left, right)
|
||||
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
|
||||
if (nums[middle] > target) {
|
||||
right = middle; // target 在左区间,在[left, middle)中
|
||||
} else if (nums[middle] < target) {
|
||||
left = middle + 1; // target 在右区间,在 [middle+1, right)中
|
||||
} else { // nums[middle] == target
|
||||
return middle; // 数组中找到目标值的情况,直接返回下标
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之前 [0,0)
|
||||
// 目标值插入数组中的位置 [left, right) ,return right 即可
|
||||
// 目标值在数组所有元素之后的情况 [left, right),因为是右开区间,所以 return right
|
||||
return right;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Golang:
|
||||
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
// 第一种二分法
|
||||
func searchInsert(nums []int, target int) int {
|
||||
@@ -283,6 +308,28 @@ var searchInsert = function (nums, target) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// 第一种二分法
|
||||
function searchInsert(nums: number[], target: number): number {
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
let left: number = 0,
|
||||
right: number = length - 1;
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
const mid: number = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
|
||||
if (nums[mid] < target) {
|
||||
left = mid + 1;
|
||||
} else if (nums[mid] === target) {
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
right = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return right + 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
@@ -316,8 +363,52 @@ func searchInsert(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> Int {
|
||||
return right + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def searchInsert(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var left = 0
|
||||
var right = nums.length - 1
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
var mid = left + (right - left) / 2
|
||||
if (target == nums(mid)) {
|
||||
return mid
|
||||
} else if (target > nums(mid)) {
|
||||
left = mid + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
right = mid - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
right + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PHP
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// 二分法(1):[左闭右闭]
|
||||
function searchInsert($nums, $target)
|
||||
{
|
||||
$n = count($nums);
|
||||
$l = 0;
|
||||
$r = $n - 1;
|
||||
while ($l <= $r) {
|
||||
$mid = floor(($l + $r) / 2);
|
||||
if ($nums[$mid] > $target) {
|
||||
// 下次搜索在左区间:[$l,$mid-1]
|
||||
$r = $mid - 1;
|
||||
} else if ($nums[$mid] < $target) {
|
||||
// 下次搜索在右区间:[$mid+1,$r]
|
||||
$l = $mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 命中返回
|
||||
return $mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $r + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 37. 解数独
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sudoku-solver/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sudoku-solver/)
|
||||
|
||||
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -439,6 +439,101 @@ var solveSudoku = function(board) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function isValid(col: number, row: number, val: string, board: string[][]): boolean {
|
||||
let n: number = board.length;
|
||||
// 列向检查
|
||||
for (let rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < n; rowIndex++) {
|
||||
if (board[rowIndex][col] === val) return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 横向检查
|
||||
for (let colIndex = 0; colIndex < n; colIndex++) {
|
||||
if (board[row][colIndex] === val) return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 九宫格检查
|
||||
const startX = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3;
|
||||
const startY = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3;
|
||||
for (let rowIndex = startY; rowIndex < startY + 3; rowIndex++) {
|
||||
for (let colIndex = startX; colIndex < startX + 3; colIndex++) {
|
||||
if (board[rowIndex][colIndex] === val) return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function solveSudoku(board: string[][]): void {
|
||||
let n: number = 9;
|
||||
backTracking(n, board);
|
||||
function backTracking(n: number, board: string[][]): boolean {
|
||||
for (let row = 0; row < n; row++) {
|
||||
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
|
||||
if (board[row][col] === '.') {
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
if (isValid(col, row, String(i), board)) {
|
||||
board[row][col] = String(i);
|
||||
if (backTracking(n, board) === true) return true;
|
||||
board[row][col] = '.';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn is_valid(row: usize, col: usize, val: char, board: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) -> bool{
|
||||
for i in 0..9 {
|
||||
if board[row][i] == val { return false; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j in 0..9 {
|
||||
if board[j][col] == val {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
let start_row = (row / 3) * 3;
|
||||
let start_col = (col / 3) * 3;
|
||||
for i in start_row..(start_row + 3) {
|
||||
for j in start_col..(start_col + 3) {
|
||||
if board[i][j] == val { return false; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn backtracking(board: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) -> bool{
|
||||
for i in 0..board.len() {
|
||||
for j in 0..board[0].len() {
|
||||
if board[i][j] != '.' { continue; }
|
||||
for k in '1'..='9' {
|
||||
if Self::is_valid(i, j, k, board) {
|
||||
board[i][j] = k;
|
||||
if Self::backtracking(board) { return true; }
|
||||
board[i][j] = '.';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn solve_sudoku(board: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) {
|
||||
Self::backtracking(board);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
@@ -553,5 +648,100 @@ func solveSudoku(_ board: inout [[Character]]) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
详细写法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
|
||||
backtracking(board)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Boolean = {
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until 9) {
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until 9) {
|
||||
if (board(i)(j) == '.') { // 必须是为 . 的数字才放数字
|
||||
for (k <- '1' to '9') { // 这个位置放k是否合适
|
||||
if (isVaild(i, j, k, board)) {
|
||||
board(i)(j) = k
|
||||
if (backtracking(board)) return true // 找到了立刻返回
|
||||
board(i)(j) = '.' // 回溯
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false // 9个数都试完了,都不行就返回false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
true // 遍历完所有的都没返回false,说明找到了
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def isVaild(x: Int, y: Int, value: Char, board: Array[Array[Char]]): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 行
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until 9 ) {
|
||||
if (board(i)(y) == value) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 列
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until 9) {
|
||||
if (board(x)(j) == value) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 宫
|
||||
var row = (x / 3) * 3
|
||||
var col = (y / 3) * 3
|
||||
for (i <- row until row + 3) {
|
||||
for (j <- col until col + 3) {
|
||||
if (board(i)(j) == value) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
遵循Scala至简原则写法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
|
||||
backtracking(board)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 双重for循环 + 循环守卫
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until 9; j <- 0 until 9 if board(i)(j) == '.') {
|
||||
// 必须是为 . 的数字才放数字,使用循环守卫判断该位置是否可以放置当前循环的数字
|
||||
for (k <- '1' to '9' if isVaild(i, j, k, board)) { // 这个位置放k是否合适
|
||||
board(i)(j) = k
|
||||
if (backtracking(board)) return true // 找到了立刻返回
|
||||
board(i)(j) = '.' // 回溯
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false // 9个数都试完了,都不行就返回false
|
||||
}
|
||||
true // 遍历完所有的都没返回false,说明找到了
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def isVaild(x: Int, y: Int, value: Char, board: Array[Array[Char]]): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 行,循环守卫进行判断
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until 9 if board(i)(y) == value) return false
|
||||
// 列,循环守卫进行判断
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until 9 if board(x)(j) == value) return false
|
||||
// 宫,循环守卫进行判断
|
||||
var row = (x / 3) * 3
|
||||
var col = (y / 3) * 3
|
||||
for (i <- row until row + 3; j <- col until col + 3 if board(i)(j) == value) return false
|
||||
true // 最终没有返回false,就说明该位置可以填写true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 39. 组合总和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -291,7 +291,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
|
||||
sum_ += candidates[i]
|
||||
self.path.append(candidates[i])
|
||||
self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i) # 因为无限制重复选取,所以不是i-1
|
||||
self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i) # 因为无限制重复选取,所以不是i+1
|
||||
sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯
|
||||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -370,18 +370,17 @@ func backtracking(startIndex,sum,target int,candidates,trcak []int,res *[][]int)
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var combinationSum = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
const res = [], path = [];
|
||||
candidates.sort(); // 排序
|
||||
candidates.sort((a,b)=>a-b); // 排序
|
||||
backtracking(0, 0);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
function backtracking(j, sum) {
|
||||
if (sum > target) return;
|
||||
if (sum === target) {
|
||||
res.push(Array.from(path));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(let i = j; i < candidates.length; i++ ) {
|
||||
const n = candidates[i];
|
||||
if(n > target - sum) continue;
|
||||
if(n > target - sum) break;
|
||||
path.push(n);
|
||||
sum += n;
|
||||
backtracking(i, sum);
|
||||
@@ -392,7 +391,63 @@ var combinationSum = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function combinationSum(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
function backTracking(
|
||||
candidates: number[], target: number,
|
||||
startIndex: number, route: number[], curSum: number
|
||||
): void {
|
||||
if (curSum > target) return;
|
||||
if (curSum === target) {
|
||||
resArr.push(route.slice());
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex, length = candidates.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let tempVal: number = candidates[i];
|
||||
route.push(tempVal);
|
||||
backTracking(candidates, target, i, route, curSum + tempVal);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
backTracking(candidates, target, 0, [], 0);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, candidates: &Vec<i32>, target: i32, mut sum: i32, start_index: usize) {
|
||||
if sum == target {
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in start_index..candidates.len() {
|
||||
if sum + candidates[i] <= target {
|
||||
sum += candidates[i];
|
||||
path.push(candidates[i]);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, candidates, target, sum, i);
|
||||
sum -= candidates[i];
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn combination_sum(candidates: Vec<i32>, target: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &candidates, target, 0, 0);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
@@ -476,5 +531,35 @@ func combinationSum(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def combinationSum(candidates: Array[Int], target: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(sum: Int, index: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (sum == target) {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList) // 如果正好等于target,就添加到结果集
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 应该是从当前索引开始的,而不是从0
|
||||
// 剪枝优化:添加循环守卫,当sum + c(i) <= target的时候才循环,才可以进入下一次递归
|
||||
for (i <- index until candidates.size if sum + candidates(i) <= target) {
|
||||
path.append(candidates(i))
|
||||
backtracking(sum + candidates(i), i)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0, 0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 40.组合总和II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -508,22 +508,27 @@ func backtracking(startIndex,sum,target int,candidates,trcak []int,res *[][]int)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
const res = []; path = [], len = candidates.length;
|
||||
candidates.sort();
|
||||
candidates.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
|
||||
backtracking(0, 0);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
function backtracking(sum, i) {
|
||||
if (sum > target) return;
|
||||
if (sum === target) {
|
||||
res.push(Array.from(path));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let f = -1;
|
||||
for(let j = i; j < len; j++) {
|
||||
const n = candidates[j];
|
||||
if(n > target - sum || n === f) continue;
|
||||
if(j > i && candidates[j] === candidates[j-1]){
|
||||
//若当前元素和前一个元素相等
|
||||
//则本次循环结束,防止出现重复组合
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//如果当前元素值大于目标值-总和的值
|
||||
//由于数组已排序,那么该元素之后的元素必定不满足条件
|
||||
//直接终止当前层的递归
|
||||
if(n > target - sum) break;
|
||||
path.push(n);
|
||||
sum += n;
|
||||
f = n;
|
||||
backtracking(sum, j + 1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
sum -= n;
|
||||
@@ -532,6 +537,7 @@ var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
**使用used去重**
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
let res = [];
|
||||
@@ -562,6 +568,72 @@ var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function combinationSum2(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
|
||||
candidates.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
function backTracking(
|
||||
candidates: number[], target: number,
|
||||
curSum: number, startIndex: number, route: number[]
|
||||
) {
|
||||
if (curSum > target) return;
|
||||
if (curSum === target) {
|
||||
resArr.push(route.slice());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex, length = candidates.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] === candidates[i - 1]) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let tempVal: number = candidates[i];
|
||||
route.push(tempVal);
|
||||
backTracking(candidates, target, curSum + tempVal, i + 1, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
backTracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, candidates: &Vec<i32>, target: i32, mut sum: i32, start_index: usize, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
|
||||
if sum == target {
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in start_index..candidates.len() {
|
||||
if sum + candidates[i] <= target {
|
||||
if i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false { continue; }
|
||||
sum += candidates[i];
|
||||
path.push(candidates[i]);
|
||||
used[i] = true;
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, candidates, target, sum, i + 1, used);
|
||||
used[i] = false;
|
||||
sum -= candidates[i];
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn combination_sum2(candidates: Vec<i32>, target: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut used: Vec<bool> = vec![false; candidates.len()];
|
||||
let mut candidates = candidates;
|
||||
candidates.sort();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &candidates, target, 0, 0, &mut used);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -656,5 +728,37 @@ func combinationSum2(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def combinationSum2(candidates: Array[Int], target: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var res = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
var candidate = candidates.sorted
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(sum: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (sum == target) {
|
||||
res.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex until candidate.size if sum + candidate(i) <= target) {
|
||||
if (!(i > startIndex && candidate(i) == candidate(i - 1))) {
|
||||
path.append(candidate(i))
|
||||
backtracking(sum + candidate(i), i + 1)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0, 0)
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 42. 接雨水
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -640,8 +640,44 @@ func min(a,b int)int{
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈解法
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func trap(height []int) int {
|
||||
if len(height) <= 2 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
st := make([]int, 1, len(height)) // 切片模拟单调栈,st存储的是高度数组下标
|
||||
var res int
|
||||
for i := 1; i < len(height); i++ {
|
||||
if height[i] < height[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||||
st = append(st, i)
|
||||
} else if height[i] == height[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||||
st = st[:len(st)-1] // 比较的新元素和栈顶的元素相等,去掉栈中的,入栈新元素下标
|
||||
st = append(st, i)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for len(st) != 0 && height[i] > height[st[len(st)-1]] {
|
||||
top := st[len(st)-1]
|
||||
st = st[:len(st)-1]
|
||||
if len(st) != 0 {
|
||||
tmp := (min(height[i], height[st[len(st)-1]]) - height[top]) * (i - st[len(st)-1] - 1)
|
||||
res += tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
st = append(st, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
func min(x, y int) int {
|
||||
if x >= y {
|
||||
return y
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
@@ -744,6 +780,91 @@ var trap = function(height) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
双指针法:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function trap(height: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = height.length;
|
||||
let resVal: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let leftMaxHeight: number = height[i],
|
||||
rightMaxHeight: number = height[i];
|
||||
let leftIndex: number = i - 1,
|
||||
rightIndex: number = i + 1;
|
||||
while (leftIndex >= 0) {
|
||||
if (height[leftIndex] > leftMaxHeight)
|
||||
leftMaxHeight = height[leftIndex];
|
||||
leftIndex--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (rightIndex < length) {
|
||||
if (height[rightIndex] > rightMaxHeight)
|
||||
rightMaxHeight = height[rightIndex];
|
||||
rightIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
resVal += Math.min(leftMaxHeight, rightMaxHeight) - height[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resVal;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function trap(height: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = height.length;
|
||||
const leftMaxHeightDp: number[] = [],
|
||||
rightMaxHeightDp: number[] = [];
|
||||
leftMaxHeightDp[0] = height[0];
|
||||
rightMaxHeightDp[length - 1] = height[length - 1];
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
leftMaxHeightDp[i] = Math.max(height[i], leftMaxHeightDp[i - 1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||||
rightMaxHeightDp[i] = Math.max(height[i], rightMaxHeightDp[i + 1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
let resVal: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
resVal += Math.min(leftMaxHeightDp[i], rightMaxHeightDp[i]) - height[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resVal;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function trap(height: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = height.length;
|
||||
const stack: number[] = [];
|
||||
stack.push(0);
|
||||
let resVal: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||||
if (height[top] > height[i]) {
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
} else if (height[top] === height[i]) {
|
||||
stack.pop();
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
while (stack.length > 0 && height[top] < height[i]) {
|
||||
let mid = stack.pop();
|
||||
if (stack.length > 0) {
|
||||
let left = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||||
let h = Math.min(height[left], height[i]) - height[mid];
|
||||
let w = i - left - 1;
|
||||
resVal += h * w;
|
||||
top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resVal;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C:
|
||||
|
||||
一种更简便的双指针方法:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 45.跳跃游戏II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -217,18 +217,26 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func jump(nums []int) int {
|
||||
dp:=make([]int ,len(nums))
|
||||
dp[0]=0
|
||||
dp := make([]int, len(nums))
|
||||
dp[0] = 0//初始第一格跳跃数一定为0
|
||||
|
||||
for i:=1;i<len(nums);i++{
|
||||
dp[i]=i
|
||||
for j:=0;j<i;j++{
|
||||
if nums[j]+j>i{
|
||||
dp[i]=min(dp[j]+1,dp[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[len(nums)-1]
|
||||
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
|
||||
dp[i] = i
|
||||
for j := 0; j < i; j++ {
|
||||
if nums[j] + j >= i {//nums[j]为起点,j为往右跳的覆盖范围,这行表示从j能跳到i
|
||||
dp[i] = min(dp[j] + 1, dp[i])//更新最小能到i的跳跃次数
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[len(nums)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -250,8 +258,103 @@ var jump = function(nums) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function jump(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
let curFarthestIndex: number = 0,
|
||||
nextFarthestIndex: number = 0;
|
||||
let curIndex: number = 0;
|
||||
let stepNum: number = 0;
|
||||
while (curIndex < length - 1) {
|
||||
nextFarthestIndex = Math.max(nextFarthestIndex, curIndex + nums[curIndex]);
|
||||
if (curIndex === curFarthestIndex) {
|
||||
curFarthestIndex = nextFarthestIndex;
|
||||
stepNum++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
curIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return stepNum;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def jump(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
if (nums.length == 0) return 0
|
||||
var result = 0 // 记录走的最大步数
|
||||
var curDistance = 0 // 当前覆盖最远距离下标
|
||||
var nextDistance = 0 // 下一步覆盖最远距离下标
|
||||
for (i <- nums.indices) {
|
||||
nextDistance = math.max(nums(i) + i, nextDistance) // 更新下一步覆盖最远距离下标
|
||||
if (i == curDistance) {
|
||||
if (curDistance != nums.length - 1) {
|
||||
result += 1
|
||||
curDistance = nextDistance
|
||||
if (nextDistance >= nums.length - 1) return result
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
//版本一
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b:i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn jump(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
if nums.len() == 0 { return 0; }
|
||||
let mut cur_distance: i32 = 0;
|
||||
let mut ans: i32 = 0;
|
||||
let mut next_distance: i32 = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..nums.len() {
|
||||
next_distance = Self::max(nums[i] + i as i32, next_distance);
|
||||
if i as i32 == cur_distance {
|
||||
if cur_distance != (nums.len() - 1) as i32 {
|
||||
ans += 1;
|
||||
cur_distance = next_distance;
|
||||
if next_distance == (nums.len() - 1) as i32 { break; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
else { break; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
//版本二
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b:i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn jump(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut cur_distance: i32 = 0;
|
||||
let mut ans: i32 = 0;
|
||||
let mut next_distance: i32 = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..nums.len() - 1 {
|
||||
next_distance = Self::max(nums[i] + i as i32, next_distance);
|
||||
if i as i32 == cur_distance {
|
||||
cur_distance = next_distance;
|
||||
ans += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 46.全排列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -331,6 +331,64 @@ var permute = function(nums) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function permute(nums: number[]): number[][] {
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
const helperSet: Set<number> = new Set();
|
||||
backTracking(nums, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTracking(nums: number[], route: number[]): void {
|
||||
if (route.length === nums.length) {
|
||||
resArr.push([...route]);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let tempVal: number;
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
tempVal = nums[i];
|
||||
if (!helperSet.has(tempVal)) {
|
||||
route.push(tempVal);
|
||||
helperSet.add(tempVal);
|
||||
backTracking(nums, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
helperSet.delete(tempVal);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, nums: &Vec<i32>, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
if path.len() == len {
|
||||
result.push(path.clone());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in 0..len {
|
||||
if used[i] == true { continue; }
|
||||
used[i] = true;
|
||||
path.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, nums, used);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
used[i] = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn permute(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut used = vec![false; nums.len()];
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &nums, &mut used);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -428,6 +486,36 @@ func permute(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def permute(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(used: Array[Boolean]): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == nums.size) {
|
||||
// 如果path的长度和nums相等,那么可以添加到结果集
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 添加循环守卫,只有当当前数字没有用过的情况下才进入回溯
|
||||
for (i <- nums.indices if used(i) == false) {
|
||||
used(i) = true
|
||||
path.append(nums(i))
|
||||
backtracking(used) // 回溯
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
used(i) = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(new Array[Boolean](nums.size)) // 调用方法
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回结果集的List形式
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 47.全排列 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -268,7 +268,7 @@ var permuteUnique = function (nums) {
|
||||
|
||||
function backtracing( used) {
|
||||
if (path.length === nums.length) {
|
||||
result.push(path.slice())
|
||||
result.push([...path])
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
@@ -292,6 +292,34 @@ var permuteUnique = function (nums) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function permuteUnique(nums: number[]): number[][] {
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
const usedArr: boolean[] = new Array(nums.length).fill(false);
|
||||
backTracking(nums, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTracking(nums: number[], route: number[]): void {
|
||||
if (route.length === nums.length) {
|
||||
resArr.push([...route]);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1] && usedArr[i - 1] === false) continue;
|
||||
if (usedArr[i] === false) {
|
||||
route.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
usedArr[i] = true;
|
||||
backTracking(nums, route);
|
||||
usedArr[i] = false;
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
@@ -323,6 +351,40 @@ func permuteUnique(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, nums: &Vec<i32>, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
if path.len() == len {
|
||||
result.push(path.clone());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in 0..len {
|
||||
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false { continue; }
|
||||
if used[i] == false {
|
||||
used[i] = true;
|
||||
path.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, nums, used);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
used[i] = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn permute_unique(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut used = vec![false; nums.len()];
|
||||
let mut nums= nums;
|
||||
nums.sort();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &nums, &mut used);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//临时数组
|
||||
@@ -394,5 +456,43 @@ int** permuteUnique(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumn
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def permuteUnique(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
var num = nums.sorted // 首先对数据进行排序
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(used: Array[Boolean]): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == num.size) {
|
||||
// 如果path的size等于num了,那么可以添加到结果集
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 循环守卫,当前元素没被使用过就进入循环体
|
||||
for (i <- num.indices if used(i) == false) {
|
||||
// 当前索引为0,不存在和前一个数字相等可以进入回溯
|
||||
// 当前索引值和上一个索引不相等,可以回溯
|
||||
// 前一个索引对应的值没有被选,可以回溯
|
||||
// 因为Scala没有continue,只能将逻辑反过来写
|
||||
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && num(i) != num(i - 1)) || used(i-1) == false) {
|
||||
used(i) = true
|
||||
path.append(num(i))
|
||||
backtracking(used)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
used(i) = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(new Array[Boolean](nums.length))
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 第51题. N皇后
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens/)
|
||||
|
||||
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -129,7 +129,6 @@ for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
// 检查列
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
|
||||
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
|
||||
@@ -178,7 +177,6 @@ void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
// 检查列
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
|
||||
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
|
||||
@@ -458,6 +456,58 @@ var solveNQueens = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function solveNQueens(n: number): string[][] {
|
||||
const board: string[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(_ => new Array(n).fill('.'));
|
||||
const resArr: string[][] = [];
|
||||
backTracking(n, 0, board);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTracking(n: number, rowNum: number, board: string[][]): void {
|
||||
if (rowNum === n) {
|
||||
resArr.push(transformBoard(board));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
if (isValid(i, rowNum, board) === true) {
|
||||
board[rowNum][i] = 'Q';
|
||||
backTracking(n, rowNum + 1, board);
|
||||
board[rowNum][i] = '.';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
function isValid(col: number, row: number, board: string[][]): boolean {
|
||||
const n: number = board.length;
|
||||
if (col < 0 || col >= n || row < 0 || row >= n) return false;
|
||||
// 检查列
|
||||
for (let row of board) {
|
||||
if (row[col] === 'Q') return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 检查45度方向
|
||||
let x: number = col,
|
||||
y: number = row;
|
||||
while (y >= 0 && x < n) {
|
||||
if (board[y--][x++] === 'Q') return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 检查135度方向
|
||||
x = col;
|
||||
y = row;
|
||||
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0) {
|
||||
if (board[y--][x--] === 'Q') return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function transformBoard(board: string[][]): string[] {
|
||||
const resArr = [];
|
||||
for (let row of board) {
|
||||
resArr.push(row.join(''));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
@@ -509,6 +559,56 @@ func solveNQueens(_ n: Int) -> [[String]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn is_valid(row: usize, col: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>, n: usize) -> bool {
|
||||
let mut i = 0 as usize;
|
||||
while i < row {
|
||||
if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' { return false; }
|
||||
i += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 - 1);
|
||||
while i >= 0 && j >= 0 {
|
||||
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
|
||||
i -= 1;
|
||||
j -= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 + 1);
|
||||
while i >= 0 && j < n as i32 {
|
||||
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
|
||||
i -= 1;
|
||||
j += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>, n: usize, row: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) {
|
||||
if row == n {
|
||||
let mut chessboard_clone: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
|
||||
for i in chessboard {
|
||||
chessboard_clone.push(i.iter().collect::<String>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
result.push(chessboard_clone);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for col in 0..n {
|
||||
if Self::is_valid(row, col, chessboard, n) {
|
||||
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, n, row + 1, chessboard);
|
||||
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn solve_n_queens(n: i32) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut chessboard: Vec<Vec<char>> = vec![vec!['.'; n as usize]; n as usize];
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, n as usize, 0, &mut chessboard);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
char ***ans;
|
||||
@@ -634,5 +734,77 @@ char *** solveNQueens(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def solveNQueens(n: Int): List[List[String]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[String]]()
|
||||
|
||||
def judge(x: Int, y: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 正上方
|
||||
var xx = x
|
||||
while (xx >= 0) {
|
||||
if (maze(xx)(y)) return false
|
||||
xx -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 左边
|
||||
var yy = y
|
||||
while (yy >= 0) {
|
||||
if (maze(x)(yy)) return false
|
||||
yy -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 左上方
|
||||
xx = x
|
||||
yy = y
|
||||
while (xx >= 0 && yy >= 0) {
|
||||
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
|
||||
xx -= 1
|
||||
yy -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
xx = x
|
||||
yy = y
|
||||
// 右上方
|
||||
while (xx >= 0 && yy < n) {
|
||||
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
|
||||
xx -= 1
|
||||
yy += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(row: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Unit = {
|
||||
if (row == n) {
|
||||
// 将结果转换为题目所需要的形式
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
for (x <- maze) {
|
||||
var tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
for (y <- x) {
|
||||
if (y == true) tmp.append("Q")
|
||||
else tmp.append(".")
|
||||
}
|
||||
path.append(tmp.mkString)
|
||||
}
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until n) {
|
||||
// 判断这个位置是否可以放置皇后
|
||||
if (judge(row, j, maze)) {
|
||||
maze(row)(j) = true
|
||||
backtracking(row + 1, maze)
|
||||
maze(row)(j) = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0, Array.ofDim[Boolean](n, n))
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 52. N皇后II
|
||||
|
||||
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens-ii/
|
||||
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
想看:[51.N皇后](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lU_QwCMj6g60nh8m98GAWg) ,基本没有区别
|
||||
详看:[51.N皇后](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lU_QwCMj6g60nh8m98GAWg) ,基本没有区别
|
||||
|
||||
# C++代码
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -144,7 +144,61 @@ var totalNQueens = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// 0-该格为空,1-该格有皇后
|
||||
type GridStatus = 0 | 1;
|
||||
function totalNQueens(n: number): number {
|
||||
let resCount: number = 0;
|
||||
const chess: GridStatus[][] = new Array(n).fill(0)
|
||||
.map(_ => new Array(n).fill(0));
|
||||
backTracking(chess, n, 0);
|
||||
return resCount;
|
||||
function backTracking(chess: GridStatus[][], n: number, startRowIndex: number): void {
|
||||
if (startRowIndex === n) {
|
||||
resCount++;
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
if (checkValid(chess, startRowIndex, j, n) === true) {
|
||||
chess[startRowIndex][j] = 1;
|
||||
backTracking(chess, n, startRowIndex + 1);
|
||||
chess[startRowIndex][j] = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
function checkValid(chess: GridStatus[][], i: number, j: number, n: number): boolean {
|
||||
// 向上纵向检查
|
||||
let tempI: number = i - 1,
|
||||
tempJ: number = j;
|
||||
while (tempI >= 0) {
|
||||
if (chess[tempI][tempJ] === 1) return false;
|
||||
tempI--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 斜向左上检查
|
||||
tempI = i - 1;
|
||||
tempJ = j - 1;
|
||||
while (tempI >= 0 && tempJ >= 0) {
|
||||
if (chess[tempI][tempJ] === 1) return false;
|
||||
tempI--;
|
||||
tempJ--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 斜向右上检查
|
||||
tempI = i - 1;
|
||||
tempJ = j + 1;
|
||||
while (tempI >= 0 && tempJ < n) {
|
||||
if (chess[tempI][tempJ] === 1) return false;
|
||||
tempI--;
|
||||
tempJ++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//path[i]为在i行,path[i]列上存在皇后
|
||||
int *path;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 53. 最大子序和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ public:
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
@@ -195,7 +195,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
|
||||
@@ -211,7 +211,21 @@ func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
|
||||
return maxSum
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn max_sub_array(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut max_sum = i32::MIN;
|
||||
let mut curr = 0;
|
||||
for n in nums.iter() {
|
||||
curr += n;
|
||||
max_sum = max_sum.max(curr);
|
||||
curr = curr.max(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
max_sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript:
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
|
||||
@@ -231,6 +245,129 @@ var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### C:
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
|
||||
int maxVal = INT_MIN;
|
||||
int subArrSum = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i) {
|
||||
subArrSum += nums[i];
|
||||
// 若当前局部和大于之前的最大结果,对结果进行更新
|
||||
maxVal = subArrSum > maxVal ? subArrSum : maxVal;
|
||||
// 若当前局部和为负,对结果无益。则从nums[i+1]开始应重新计算。
|
||||
subArrSum = subArrSum < 0 ? 0 : subArrSum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return maxVal;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 解题思路:动态规划:
|
||||
* 1. dp数组:dp[i]表示从0到i的子序列中最大序列和的值
|
||||
* 2. 递推公式:dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i])
|
||||
若dp[i-1]<0,对最后结果无益。dp[i]则为nums[i]。
|
||||
* 3. dp数组初始化:dp[0]的最大子数组和为nums[0]
|
||||
* 4. 推导顺序:从前往后遍历
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
|
||||
|
||||
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
|
||||
int dp[numsSize];
|
||||
// dp[0]最大子数组和为nums[0]
|
||||
dp[0] = nums[0];
|
||||
// 若numsSize为1,应直接返回nums[0]
|
||||
int subArrSum = nums[0];
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
|
||||
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
// 若dp[i]大于之前记录的最大值,进行更新
|
||||
if(dp[i] > subArrSum)
|
||||
subArrSum = dp[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return subArrSum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
**贪心**
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
let curSum: number = 0;
|
||||
let resMax: number = -Infinity;
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
curSum += nums[i];
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(curSum, resMax);
|
||||
if (curSum < 0) curSum = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**动态规划**
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// 动态规划
|
||||
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length = nums.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
dp[0] = nums[0];
|
||||
let resMax: number = nums[0];
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
**贪心**
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxSubArray(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var result = Int.MinValue
|
||||
var count = 0
|
||||
for (i <- nums.indices) {
|
||||
count += nums(i) // count累加
|
||||
if (count > result) result = count // 记录最大值
|
||||
if (count <= 0) count = 0 // 一旦count为负,则count归0
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**动态规划**
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxSubArray(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var dp = new Array[Int](nums.length)
|
||||
var result = nums(0)
|
||||
dp(0) = nums(0)
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until nums.length) {
|
||||
dp(i) = math.max(nums(i), dp(i - 1) + nums(i))
|
||||
result = math.max(result, dp(i)) // 更新最大值
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 53. 最大子序和
|
||||
# 53. 最大子序和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -187,6 +187,41 @@ const maxSubArray = nums => {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxSubArray(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var dp = new Array[Int](nums.length)
|
||||
var result = nums(0)
|
||||
dp(0) = nums(0)
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until nums.length) {
|
||||
dp(i) = math.max(nums(i), dp(i - 1) + nums(i))
|
||||
result = math.max(result, dp(i)) // 更新最大值
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]:以nums[i]结尾的最大和
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = []
|
||||
dp[0] = nums[0];
|
||||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 54.螺旋矩阵
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,49 +128,10 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
## 类似题目
|
||||
|
||||
* [59.螺旋矩阵II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
|
||||
* [剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/)
|
||||
* [59.螺旋矩阵II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
|
||||
* [剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
|
||||
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
|
||||
left, right, up, down = 0, n - 1, 0, m - 1 # 定位四个方向的边界,闭区间
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
for i in range(left, right + 1): # 上边,从左到右
|
||||
res.append(matrix[up][i])
|
||||
up += 1 # 上边界下移
|
||||
|
||||
if len(res) >= m * n: # 判断是否已经遍历完
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(up, down + 1): # 右边,从上到下
|
||||
res.append(matrix[i][right])
|
||||
right -= 1 # 右边界左移
|
||||
|
||||
if len(res) >= m * n:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1): # 下边,从右到左
|
||||
res.append(matrix[down][i])
|
||||
down -= 1 # 下边界上移
|
||||
|
||||
if len(res) >= m * n:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(down, up - 1, -1): # 左边,从下到上
|
||||
res.append(matrix[i][left])
|
||||
left += 1 # 左边界右移
|
||||
|
||||
if len(res) >= m * n:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 55. 跳跃游戏
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -154,6 +154,82 @@ var canJump = function(nums) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: usize, b: usize) -> usize {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn can_jump(nums: Vec<i32>) -> bool {
|
||||
let mut cover = 0;
|
||||
if (nums.len() == 1) { return true; }
|
||||
let mut i = 0;
|
||||
while i <= cover {
|
||||
cover = Self::max(i + nums[i] as usize, cover);
|
||||
if cover >= nums.len() - 1 { return true; }
|
||||
i += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
|
||||
|
||||
bool canJump(int* nums, int numsSize){
|
||||
int cover = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
// 只可能获取cover范围中的步数,所以i<=cover
|
||||
for(i = 0; i <= cover; ++i) {
|
||||
// 更新cover为从i出发能到达的最大值/cover的值中较大值
|
||||
cover = max(i + nums[i], cover);
|
||||
|
||||
// 若更新后cover可以到达最后的元素,返回true
|
||||
if(cover >= numsSize - 1)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function canJump(nums: number[]): boolean {
|
||||
let farthestIndex: number = 0;
|
||||
let cur: number = 0;
|
||||
while (cur <= farthestIndex) {
|
||||
farthestIndex = Math.max(farthestIndex, cur + nums[cur]);
|
||||
if (farthestIndex >= nums.length - 1) return true;
|
||||
cur++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def canJump(nums: Array[Int]): Boolean = {
|
||||
var cover = 0
|
||||
if (nums.length == 1) return true // 如果只有一个元素,那么必定到达
|
||||
var i = 0
|
||||
while (i <= cover) { // i表示下标,当前只能够走cover步
|
||||
cover = math.max(i + nums(i), cover)
|
||||
if (cover >= nums.length - 1) return true // 说明可以覆盖到终点,直接返回
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
false // 如果上面没有返回就是跳不到
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 56. 合并区间
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-intervals/)
|
||||
|
||||
给出一个区间的集合,请合并所有重叠的区间。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,9 +22,6 @@
|
||||
* 解释: 区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
|
||||
* 注意:输入类型已于2019年4月15日更改。 请重置默认代码定义以获取新方法签名。
|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
* intervals[i][0] <= intervals[i][1]
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +93,7 @@ public:
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> result;
|
||||
if (intervals.size() == 0) return result;
|
||||
// 排序的参数使用了lamda表达式
|
||||
// 排序的参数使用了lambda表达式
|
||||
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){return a[0] < b[0];});
|
||||
|
||||
result.push_back(intervals[0]);
|
||||
@@ -112,8 +109,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n\log n)$ ,有一个快排
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$,我没有算result数组(返回值所需容器占的空间)
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(nlog n) ,有一个快排
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(n),有一个快排,最差情况(倒序)时,需要n次递归调用。因此确实需要O(n)的栈空间
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
@@ -136,24 +133,38 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
时间复杂度 : O(NlogN) 排序需要O(NlogN)
|
||||
空间复杂度 : O(logN) java 的内置排序是快速排序 需要 O(logN)空间
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
|
||||
List<int[]> res = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
Arrays.sort(intervals, (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1[0], o2[0]));
|
||||
|
||||
//按照左边界排序
|
||||
Arrays.sort(intervals, (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x[0], y[0]));
|
||||
//initial start 是最小左边界
|
||||
int start = intervals[0][0];
|
||||
int rightmostRightBound = intervals[0][1];
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (intervals[i][0] > intervals[i - 1][1]) {
|
||||
res.add(new int[]{start, intervals[i - 1][1]});
|
||||
//如果左边界大于最大右边界
|
||||
if (intervals[i][0] > rightmostRightBound) {
|
||||
//加入区间 并且更新start
|
||||
res.add(new int[]{start, rightmostRightBound});
|
||||
start = intervals[i][0];
|
||||
rightmostRightBound = intervals[i][1];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
intervals[i][1] = Math.max(intervals[i][1], intervals[i - 1][1]);
|
||||
//更新最大右边界
|
||||
rightmostRightBound = Math.max(rightmostRightBound, intervals[i][1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.add(new int[]{start, intervals[intervals.length - 1][1]});
|
||||
res.add(new int[]{start, rightmostRightBound});
|
||||
return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// 版本2
|
||||
@@ -266,7 +277,83 @@ var merge = function(intervals) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function merge(intervals: number[][]): number[][] {
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
|
||||
resArr[0] = [...intervals[0]]; // 避免修改原intervals
|
||||
for (let i = 1, length = intervals.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let interval: number[] = intervals[i];
|
||||
let last: number[] = resArr[resArr.length - 1];
|
||||
if (interval[0] <= last[1]) {
|
||||
last[1] = Math.max(interval[1], last[1]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
resArr.push([...intervals[i]]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def merge(intervals: Array[Array[Int]]): Array[Array[Int]] = {
|
||||
var res = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Array[Int]]()
|
||||
|
||||
// 排序
|
||||
var interval = intervals.sortWith((a, b) => {
|
||||
a(0) < b(0)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
var left = interval(0)(0)
|
||||
var right = interval(0)(1)
|
||||
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until interval.length) {
|
||||
if (interval(i)(0) <= right) {
|
||||
left = math.min(left, interval(i)(0))
|
||||
right = math.max(right, interval(i)(1))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res.append(Array[Int](left, right))
|
||||
left = interval(i)(0)
|
||||
right = interval(i)(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(Array[Int](left, right))
|
||||
res.toArray // 返回res的Array形式
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn merge(intervals: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut intervals = intervals;
|
||||
let mut result = Vec::new();
|
||||
if intervals.len() == 0 { return result; }
|
||||
intervals.sort_by(|a, b| a[0].cmp(&b[0]));
|
||||
result.push(intervals[0].clone());
|
||||
for i in 1..intervals.len() {
|
||||
if result.last_mut().unwrap()[1] >= intervals[i][0] {
|
||||
result.last_mut().unwrap()[1] = Self::max(result.last_mut().unwrap()[1], intervals[i][1]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result.push(intervals[i].clone());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 59.螺旋矩阵II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n^2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,13 +24,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
为了利于录友们理解,我特意录制了视频,[拿下螺旋矩阵!LeetCode:59.螺旋矩阵II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SL4y1N7mV),结合视频一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目可以说在面试中出现频率较高的题目,**本题并不涉及到什么算法,就是模拟过程,但却十分考察对代码的掌控能力。**
|
||||
|
||||
要如何画出这个螺旋排列的正方形矩阵呢?
|
||||
|
||||
相信很多同学刚开始做这种题目的时候,上来就是一波判断猛如虎。
|
||||
|
||||
结果运行的时候各种问题,然后开始各种修修补补,最后发现改了这里哪里有问题,改了那里这里又跑不起来了。
|
||||
结果运行的时候各种问题,然后开始各种修修补补,最后发现改了这里那里有问题,改了那里这里又跑不起来了。
|
||||
|
||||
大家还记得我们在这篇文章[数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废](https://programmercarl.com/0704.二分查找.html)中讲解了二分法,提到如果要写出正确的二分法一定要坚持**循环不变量原则**。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +49,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
可以发现这里的边界条件非常多,在一个循环中,如此多的边界条件,如果不按照固定规则来遍历,那就是**一进循环深似海,从此offer是路人**。
|
||||
|
||||
这里一圈下来,我们要画每四条边,这四条边怎么画,每画一条边都要坚持一致的左闭右开,或者左开又闭的原则,这样这一圈才能按照统一的规则画下来。
|
||||
这里一圈下来,我们要画每四条边,这四条边怎么画,每画一条边都要坚持一致的左闭右开,或者左开右闭的原则,这样这一圈才能按照统一的规则画下来。
|
||||
|
||||
那么我按照左闭右开的原则,来画一圈,大家看一下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +61,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学做这道题目之所以一直写不好,代码越写越乱。
|
||||
|
||||
就是因为在画每一条边的时候,一会左开又闭,一会左闭右闭,一会又来左闭右开,岂能不乱。
|
||||
就是因为在画每一条边的时候,一会左开右闭,一会左闭右闭,一会又来左闭右开,岂能不乱。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下,已经详细注释了每一步的目的,可以看出while循环里判断的情况是很多的,代码里处理的原则也是统一的左闭右开。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -74,7 +76,7 @@ public:
|
||||
int loop = n / 2; // 每个圈循环几次,例如n为奇数3,那么loop = 1 只是循环一圈,矩阵中间的值需要单独处理
|
||||
int mid = n / 2; // 矩阵中间的位置,例如:n为3, 中间的位置就是(1,1),n为5,中间位置为(2, 2)
|
||||
int count = 1; // 用来给矩阵中每一个空格赋值
|
||||
int offset = 1; // 每一圈循环,需要控制每一条边遍历的长度
|
||||
int offset = 1; // 需要控制每一条边遍历的长度,每次循环右边界收缩一位
|
||||
int i,j;
|
||||
while (loop --) {
|
||||
i = startx;
|
||||
@@ -82,11 +84,11 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
// 下面开始的四个for就是模拟转了一圈
|
||||
// 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
|
||||
for (j = starty; j < starty + n - offset; j++) {
|
||||
for (j = starty; j < n - offset; j++) {
|
||||
res[startx][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
|
||||
for (i = startx; i < startx + n - offset; i++) {
|
||||
for (i = startx; i < n - offset; i++) {
|
||||
res[i][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +105,7 @@ public:
|
||||
starty++;
|
||||
|
||||
// offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
|
||||
offset += 2;
|
||||
offset += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 如果n为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
|
||||
@@ -130,57 +132,37 @@ Java:
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
|
||||
int loop = 0; // 控制循环次数
|
||||
int[][] res = new int[n][n];
|
||||
int start = 0; // 每次循环的开始点(start, start)
|
||||
int count = 1; // 定义填充数字
|
||||
int i, j;
|
||||
|
||||
// 循环次数
|
||||
int loop = n / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义每次循环起始位置
|
||||
int startX = 0;
|
||||
int startY = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义偏移量
|
||||
int offset = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义填充数字
|
||||
int count = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// 定义中间位置
|
||||
int mid = n / 2;
|
||||
while (loop > 0) {
|
||||
int i = startX;
|
||||
int j = startY;
|
||||
|
||||
while (loop++ < n / 2) { // 判断边界后,loop从1开始
|
||||
// 模拟上侧从左到右
|
||||
for (; j<startY + n -offset; ++j) {
|
||||
res[startX][j] = count++;
|
||||
for (j = start; j < n - loop; j++) {
|
||||
res[start][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 模拟右侧从上到下
|
||||
for (; i<startX + n -offset; ++i) {
|
||||
for (i = start; i < n - loop; i++) {
|
||||
res[i][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 模拟下侧从右到左
|
||||
for (; j > startY; j--) {
|
||||
for (; j >= loop; j--) {
|
||||
res[i][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 模拟左侧从下到上
|
||||
for (; i > startX; i--) {
|
||||
for (; i >= loop; i--) {
|
||||
res[i][j] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
loop--;
|
||||
|
||||
startX += 1;
|
||||
startY += 1;
|
||||
|
||||
offset += 2;
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (n % 2 == 1) {
|
||||
res[mid][mid] = count;
|
||||
res[start][start] = count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
@@ -246,11 +228,11 @@ var generateMatrix = function(n) {
|
||||
res[row][col] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 下行从右到左(左闭右开)
|
||||
for (; col > startX; col--) {
|
||||
for (; col > startY; col--) {
|
||||
res[row][col] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 左列做下到上(左闭右开)
|
||||
for (; row > startY; row--) {
|
||||
for (; row > startX; row--) {
|
||||
res[row][col] = count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -564,6 +546,82 @@ int** generateMatrix(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||||
return ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def generateMatrix(n: Int): Array[Array[Int]] = {
|
||||
var res = Array.ofDim[Int](n, n) // 定义一个n*n的二维矩阵
|
||||
var num = 1 // 标志当前到了哪个数字
|
||||
var i = 0 // 横坐标
|
||||
var j = 0 // 竖坐标
|
||||
|
||||
while (num <= n * n) {
|
||||
// 向右:当j不越界,并且下一个要填的数字是空白时
|
||||
while (j < n && res(i)(j) == 0) {
|
||||
res(i)(j) = num // 当前坐标等于num
|
||||
num += 1 // num++
|
||||
j += 1 // 竖坐标+1
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += 1 // 下移一行
|
||||
j -= 1 // 左移一列
|
||||
|
||||
// 剩下的都同上
|
||||
|
||||
// 向下
|
||||
while (i < n && res(i)(j) == 0) {
|
||||
res(i)(j) = num
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
|
||||
// 向左
|
||||
while (j >= 0 && res(i)(j) == 0) {
|
||||
res(i)(j) = num
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
|
||||
// 向上
|
||||
while (i >= 0 && res(i)(j) == 0) {
|
||||
res(i)(j) = num
|
||||
num += 1
|
||||
i -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
j += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n) {
|
||||
int[][] answer = new int[n][];
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
|
||||
answer[i] = new int[n];
|
||||
int start = 0;
|
||||
int end = n - 1;
|
||||
int tmp = 1;
|
||||
while(tmp < n * n)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[start][i] = tmp++;
|
||||
for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[i][end] = tmp++;
|
||||
for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[end][i] = tmp++;
|
||||
for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[i][start] = tmp++;
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
end--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(n % 2 == 1) answer[n / 2][n / 2] = tmp;
|
||||
return answer;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 62.不同路径
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths/)
|
||||
|
||||
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -273,7 +273,7 @@ public:
|
||||
return dp[m-1][n-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -347,7 +347,59 @@ var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function uniquePaths(m: number, n: number): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][j]: 到达(i, j)的路径数
|
||||
dp[0][*]: 1;
|
||||
dp[*][0]: 1;
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i][j]: dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(m).fill(0).map(_ => []);
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
dp[0][i] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn unique_paths(m: i32, n: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let m = m as usize;
|
||||
let n = n as usize;
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
|
||||
for i in 0..m {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j in 0..n {
|
||||
dp[0][j] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in 1..m {
|
||||
for j in 1..n {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[m-1][n-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//初始化dp数组
|
||||
int **initDP(int m, int n) {
|
||||
@@ -384,5 +436,21 @@ int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def uniquePaths(m: Int, n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var dp = Array.ofDim[Int](m, n)
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until m) dp(i)(0) = 1
|
||||
for (j <- 1 until n) dp(0)(j) = 1
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until m; j <- 1 until n) {
|
||||
dp(i)(j) = dp(i - 1)(j) + dp(i)(j - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp(m - 1)(n - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 63. 不同路径 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ dp[i][j] :表示从(0 ,0)出发,到(i, j) 有dp[i][j]条不同的路
|
||||
|
||||
所以代码为:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0) { // 当(i, j)没有障碍的时候,再推导dp[i][j]
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0) { // 当(i, j)没有障碍的时候,再推导dp[i
|
||||
|
||||
在[62.不同路径](https://programmercarl.com/0062.不同路径.html)不同路径中我们给出如下的初始化:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0)); // 初始值为0
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
|
||||
@@ -138,6 +138,8 @@ public:
|
||||
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) {
|
||||
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
|
||||
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) //如果在起点或终点出现了障碍,直接返回0
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0; i++) dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n && obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
|
||||
@@ -184,8 +186,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n × m)$,n、m 分别为obstacleGrid 长度和宽度
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(m)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n × m),n、m 分别为obstacleGrid 长度和宽度
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(m)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
@@ -352,7 +354,74 @@ var uniquePathsWithObstacles = function(obstacleGrid) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][j]: 到达(i, j)的路径数
|
||||
dp[0][*]: 用u表示第一个障碍物下标,则u之前为1,u之后(含u)为0
|
||||
dp[*][0]: 同上
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i][j]: obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1 ? 0 : dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const m: number = obstacleGrid.length;
|
||||
const n: number = obstacleGrid[0].length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(m).fill(0).map(_ => new Array(n).fill(0));
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] === 0; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n && obstacleGrid[0][i] === 0; i++) {
|
||||
dp[0][i] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1) continue;
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn unique_paths_with_obstacles(obstacle_grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let m: usize = obstacle_grid.len();
|
||||
let n: usize = obstacle_grid[0].len();
|
||||
if obstacle_grid[0][0] == 1 || obstacle_grid[m-1][n-1] == 1 {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
|
||||
for i in 0..m {
|
||||
if obstacle_grid[i][0] == 1 {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else { dp[i][0] = 1; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j in 0..n {
|
||||
if obstacle_grid[0][j] == 1 {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else { dp[0][j] = 1; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in 1..m {
|
||||
for j in 1..n {
|
||||
if obstacle_grid[i][j] == 1 {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[m-1][n-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//初始化dp数组
|
||||
int **initDP(int m, int n, int** obstacleGrid) {
|
||||
@@ -407,5 +476,37 @@ int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int** obstacleGrid, int obstacleGridSize, int* obst
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.util.control.Breaks._
|
||||
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: Array[Array[Int]]): Int = {
|
||||
var (m, n) = (obstacleGrid.length, obstacleGrid(0).length)
|
||||
var dp = Array.ofDim[Int](m, n)
|
||||
|
||||
// 比如break、continue这些流程控制需要使用breakable
|
||||
breakable(
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until m) {
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid(i)(0) != 1) dp(i)(0) = 1
|
||||
else break()
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
breakable(
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until n) {
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid(0)(j) != 1) dp(0)(j) = 1
|
||||
else break()
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until m; j <- 1 until n; if obstacleGrid(i)(j) != 1) {
|
||||
dp(i)(j) = dp(i - 1)(j) + dp(i)(j - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dp(m - 1)(n - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
# 70. 爬楼梯
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/)
|
||||
|
||||
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -308,7 +308,58 @@ var climbStairs = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 爬2阶
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function climbStairs(n: number): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]: i阶楼梯的方法种数
|
||||
dp[1]: 1;
|
||||
dp[2]: 2;
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
dp[1] = 1;
|
||||
dp[2] = 2;
|
||||
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 爬m阶
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function climbStairs(n: number): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
一次可以爬m阶
|
||||
dp[i]: i阶楼梯的方法种数
|
||||
dp[1]: 1;
|
||||
dp[2]: 2;
|
||||
dp[3]: dp[2] + dp[1];
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + ... + dp[max(i - m, 1)]; 从i-1加到max(i-m, 1)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const m: number = 2; // 本题m为2
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
|
||||
dp[1] = 1;
|
||||
dp[2] = 2;
|
||||
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
const end: number = Math.max(i - m, 1);
|
||||
for (let j = i - 1; j >= end; j--) {
|
||||
dp[i] += dp[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int climbStairs(int n){
|
||||
//若n<=2,返回n
|
||||
@@ -350,6 +401,38 @@ int climbStairs(int n){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def climbStairs(n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
if (n <= 2) return n
|
||||
var dp = new Array[Int](n + 1)
|
||||
dp(1) = 1
|
||||
dp(2) = 2
|
||||
for (i <- 3 to n) {
|
||||
dp(i) = dp(i - 1) + dp(i - 2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
优化空间复杂度:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def climbStairs(n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
if (n <= 2) return n
|
||||
var (a, b) = (1, 2)
|
||||
for (i <- 3 to n) {
|
||||
var tmp = a + b
|
||||
a = b
|
||||
b = tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
b // 最终返回b
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 70. 爬楼梯
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/)
|
||||
|
||||
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -199,6 +199,28 @@ var climbStairs = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function climbStairs(n: number): number {
|
||||
const m: number = 2; // 本题m为2
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
|
||||
dp[0] = 1;
|
||||
// 遍历背包
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
// 遍历物品
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
|
||||
if (j <= i) {
|
||||
dp[i] += dp[i - j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 72. 编辑距离
|
||||
# 72. 编辑距离
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/edit-distance/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -327,5 +327,42 @@ const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][j]: word1前i个字符,word2前j个字符,最少操作数
|
||||
dp[0][0]=0:表示word1前0个字符为'', word2前0个字符为''
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length1: number = word1.length,
|
||||
length2: number = word2.length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
|
||||
.map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i <= length1; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i <= length2; i++) {
|
||||
dp[0][i] = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
|
||||
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = Math.min(
|
||||
dp[i - 1][j],
|
||||
dp[i][j - 1],
|
||||
dp[i - 1][j - 1]
|
||||
) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[length1][length2];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 第77题. 组合
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combinations/ )
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/ )
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
也可以直接看我的B站视频:[带你学透回溯算法-组合问题(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv#reply3733925949)
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本题这是回溯法的经典题目。
|
||||
@@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ vector<vector<int>> result; // 存放符合条件结果的集合
|
||||
vector<int> path; // 用来存放符合条件结果
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其实不定义这两个全局遍历也是可以的,把这两个变量放进递归函数的参数里,但函数里参数太多影响可读性,所以我定义全局变量了。
|
||||
其实不定义这两个全局变量也是可以的,把这两个变量放进递归函数的参数里,但函数里参数太多影响可读性,所以我定义全局变量了。
|
||||
|
||||
函数里一定有两个参数,既然是集合n里面取k的数,那么n和k是两个int型的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -232,7 +232,7 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
|
||||
|
||||
**对比一下本题的代码,是不是发现有点像!** 所以有了这个模板,就有解题的大体方向,不至于毫无头绪。
|
||||
|
||||
# 总结
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
组合问题是回溯法解决的经典问题,我们开始的时候给大家列举一个很形象的例子,就是n为100,k为50的话,直接想法就需要50层for循环。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -242,7 +242,7 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
|
||||
|
||||
接着用回溯法三部曲,逐步分析了函数参数、终止条件和单层搜索的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
# 剪枝优化
|
||||
## 剪枝优化
|
||||
|
||||
我们说过,回溯法虽然是暴力搜索,但也有时候可以有点剪枝优化一下的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -324,7 +324,7 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 剪枝总结
|
||||
## 剪枝总结
|
||||
|
||||
本篇我们准对求组合问题的回溯法代码做了剪枝优化,这个优化如果不画图的话,其实不好理解,也不好讲清楚。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -334,10 +334,10 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 其他语言版本
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Java:
|
||||
### Java:
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
@@ -366,6 +366,8 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
Python2:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution(object):
|
||||
@@ -395,7 +397,6 @@ class Solution(object):
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||||
@@ -432,7 +433,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## javascript
|
||||
### javascript
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝:
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
@@ -456,7 +457,7 @@ const combineHelper = (n, k, startIndex) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function combine(n: number, k: number): number[][] {
|
||||
@@ -479,7 +480,7 @@ function combine(n: number, k: number): number[][] {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
var res [][]int
|
||||
func combine(n int, k int) [][]int {
|
||||
@@ -534,7 +535,57 @@ func backtrack(n,k,start int,track []int){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, n: i32, k: i32, startIndex: i32) {
|
||||
let len= path.len() as i32;
|
||||
if len == k{
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in startIndex..= n {
|
||||
path.push(i);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, n, k, i+1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn combine(n: i32, k: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, n, k, 1);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, n: i32, k: i32, startIndex: i32) {
|
||||
let len= path.len() as i32;
|
||||
if len == k{
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 此处剪枝
|
||||
for i in startIndex..= n - (k - len) + 1 {
|
||||
path.push(i);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, n, k, i+1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn combine(n: i32, k: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, n, k, 1);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
@@ -642,7 +693,7 @@ int** combine(int n, int k, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Swift
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
@@ -672,5 +723,63 @@ func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
暴力:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable // 导包
|
||||
def combine(n: Int, k: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]() // 存放结果集
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() //存放符合条件的结果
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(n: Int, k: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == k) {
|
||||
// 如果path的size == k就达到题目要求,添加到结果集,并返回
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to n) { // 遍历从startIndex到n
|
||||
path.append(i) // 先把数字添加进去
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1) // 进行下一步回溯
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, 1) // 执行回溯
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回result的List形式,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable // 导包
|
||||
def combine(n: Int, k: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]() // 存放结果集
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() //存放符合条件的结果
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(n: Int, k: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == k) {
|
||||
// 如果path的size == k就达到题目要求,添加到结果集,并返回
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 剪枝优化
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
|
||||
path.append(i) // 先把数字添加进去
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1) // 进行下一步回溯
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, 1) // 执行回溯
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回result的List形式,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
文中的回溯法是可以剪枝优化的,本篇我们继续来看一下题目77. 组合。
|
||||
|
||||
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combinations/
|
||||
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/
|
||||
|
||||
**看本篇之前,需要先看[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)**。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -261,6 +261,32 @@ function combine(n: number, k: number): number[][] {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, n: i32, k: i32, startIndex: i32) {
|
||||
let len= path.len() as i32;
|
||||
if len == k{
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 此处剪枝
|
||||
for i in startIndex..= n - (k - len) + 1 {
|
||||
path.push(i);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, n, k, i+1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn combine(n: i32, k: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, n, k, 1);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -346,5 +372,34 @@ func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable // 导包
|
||||
def combine(n: Int, k: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]() // 存放结果集
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() //存放符合条件的结果
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(n: Int, k: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == k) {
|
||||
// 如果path的size == k就达到题目要求,添加到结果集,并返回
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 剪枝优化
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
|
||||
path.append(i) // 先把数字添加进去
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1) // 进行下一步回溯
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, 1) // 执行回溯
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回result的List形式,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 78.子集
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ var subsets = function(nums) {
|
||||
let result = []
|
||||
let path = []
|
||||
function backtracking(startIndex) {
|
||||
result.push(path.slice())
|
||||
result.push([...path])
|
||||
for(let i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
|
||||
path.push(nums[i])
|
||||
backtracking(i + 1)
|
||||
@@ -272,7 +272,52 @@ var subsets = function(nums) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
backTracking(nums, 0, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTracking(nums: number[], startIndex: number, route: number[]): void {
|
||||
resArr.push([...route]);
|
||||
let length = nums.length;
|
||||
if (startIndex === length) return;
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
route.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
backTracking(nums, i + 1, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, nums: &Vec<i32>, start_index: usize) {
|
||||
result.push(path.clone());
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
// if start_index >= len { return; }
|
||||
for i in start_index..len {
|
||||
path.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, nums, i + 1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn subsets(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &nums, 0);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
@@ -352,6 +397,60 @@ func subsets(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
思路一: 使用本题解思路
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def subsets(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList) // 存放结果
|
||||
if (startIndex >= nums.size) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex until nums.size) {
|
||||
path.append(nums(i)) // 添加元素
|
||||
backtracking(i + 1)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1) // 删除
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
思路二: 将原问题转换为二叉树,针对每一个元素都有**选或不选**两种选择,直到遍历到最后,所有的叶子节点即为本题的答案:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def subsets(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(path: mutable.ListBuffer[Int], startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (startIndex == nums.length) {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
path.append(nums(startIndex))
|
||||
backtracking(path, startIndex + 1) // 选择元素
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
backtracking(path, startIndex + 1) // 不选择元素
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(mutable.ListBuffer[Int](), 0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -486,5 +486,95 @@ var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
|
||||
return maxArea;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 双指针法(会超时):
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = heights.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
// 左开右开
|
||||
let left: number = i - 1,
|
||||
right: number = i + 1;
|
||||
while (left >= 0 && heights[left] >= heights[i]) {
|
||||
left--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (right < length && heights[right] >= heights[i]) {
|
||||
right++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, heights[i] * (right - left - 1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划预处理:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = heights.length;
|
||||
const leftHeightDp: number[] = [],
|
||||
rightHeightDp: number[] = [];
|
||||
leftHeightDp[0] = -1;
|
||||
rightHeightDp[length - 1] = length;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let j = i - 1;
|
||||
while (j >= 0 && heights[i] <= heights[j]) {
|
||||
j = leftHeightDp[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
leftHeightDp[i] = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||||
let j = i + 1;
|
||||
while (j < length && heights[i] <= heights[j]) {
|
||||
j = rightHeightDp[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
rightHeightDp[i] = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let area = heights[i] * (rightHeightDp[i] - leftHeightDp[i] - 1);
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, area);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 单调栈:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
|
||||
heights.push(0);
|
||||
const length: number = heights.length;
|
||||
// 栈底->栈顶:严格单调递增
|
||||
const stack: number[] = [];
|
||||
stack.push(0);
|
||||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||||
if (heights[top] < heights[i]) {
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
} else if (heights[top] === heights[i]) {
|
||||
stack.pop();
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
while (stack.length > 0 && heights[top] > heights[i]) {
|
||||
let mid = stack.pop();
|
||||
let left = stack.length > 0 ? stack[stack.length - 1] : -1;
|
||||
let w = i - left - 1;
|
||||
let h = heights[mid];
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, w * h);
|
||||
top = stack[stack.length - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 90.子集II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -261,6 +261,33 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
self.path.pop()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python3
|
||||
```python3
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
path = []
|
||||
nums.sort() # 去重需要先对数组进行排序
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(nums, startIndex):
|
||||
# 终止条件
|
||||
res.append(path[:])
|
||||
if startIndex == len(nums):
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# for循环
|
||||
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
|
||||
# 数层去重
|
||||
if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i-1]: # 去重
|
||||
continue
|
||||
path.append(nums[i])
|
||||
backtracking(nums, i+1)
|
||||
path.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(nums, 0)
|
||||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
@@ -299,7 +326,7 @@ var subsetsWithDup = function(nums) {
|
||||
return a - b
|
||||
})
|
||||
function backtracing(startIndex, sortNums) {
|
||||
result.push(path.slice(0))
|
||||
result.push([...path])
|
||||
if(startIndex > nums.length - 1) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -318,6 +345,58 @@ var subsetsWithDup = function(nums) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function subsetsWithDup(nums: number[]): number[][] {
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
backTraking(nums, 0, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTraking(nums: number[], startIndex: number, route: number[]): void {
|
||||
resArr.push([...route]);
|
||||
let length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
if (startIndex === length) return;
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (i > startIndex && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue;
|
||||
route.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
backTraking(nums, i + 1, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, nums: &Vec<i32>, start_index: usize, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
|
||||
result.push(path.clone());
|
||||
let len = nums.len();
|
||||
// if start_index >= len { return; }
|
||||
for i in start_index..len {
|
||||
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false { continue; }
|
||||
path.push(nums[i]);
|
||||
used[i] = true;
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, nums, i + 1, used);
|
||||
used[i] = false;
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn subsets_with_dup(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut used = vec![false; nums.len()];
|
||||
let mut nums = nums;
|
||||
nums.sort();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, &nums, 0, &mut used);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -387,7 +466,7 @@ int** subsetsWithDup(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColum
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Swift
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
func subsetsWithDup(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
@@ -412,6 +491,63 @@ func subsetsWithDup(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
不使用userd数组:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def subsetsWithDup(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
var num = nums.sorted // 排序
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
if (startIndex >= num.size){
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex until num.size) {
|
||||
// 同一树层重复的元素不进入回溯
|
||||
if (!(i > startIndex && num(i) == num(i - 1))) {
|
||||
path.append(num(i))
|
||||
backtracking(i + 1)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用Set去重:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def subsetsWithDup(nums: Array[Int]): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.Set[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var num = nums.sorted
|
||||
def backtracking(path: mutable.ListBuffer[Int], startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (startIndex == num.length) {
|
||||
result.add(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
path.append(num(startIndex))
|
||||
backtracking(path, startIndex + 1) // 选择
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
backtracking(path, startIndex + 1) // 不选择
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(mutable.ListBuffer[Int](), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 93.复原IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/restore-ip-addresses/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -227,7 +227,7 @@ private:
|
||||
public:
|
||||
vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
|
||||
result.clear();
|
||||
if (s.size() > 12) return result; // 算是剪枝了
|
||||
if (s.size() < 4 || s.size() > 12) return result; // 算是剪枝了
|
||||
backtracking(s, 0, 0);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -444,7 +444,7 @@ var restoreIpAddresses = function(s) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(let j = i; j < s.length; j++) {
|
||||
const str = s.substr(i, j - i + 1);
|
||||
const str = s.slice(i, j + 1);
|
||||
if(str.length > 3 || +str > 255) break;
|
||||
if(str.length > 1 && str[0] === "0") break;
|
||||
path.push(str);
|
||||
@@ -455,6 +455,45 @@ var restoreIpAddresses = function(s) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isValidIpSegment(str: string): boolean {
|
||||
let resBool: boolean = true;
|
||||
let tempVal: number = Number(str);
|
||||
if (
|
||||
str.length === 0 || isNaN(tempVal) ||
|
||||
tempVal > 255 || tempVal < 0 ||
|
||||
(str.length > 1 && str[0] === '0')
|
||||
) {
|
||||
resBool = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resBool;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function restoreIpAddresses(s: string): string[] {
|
||||
const resArr: string[] = [];
|
||||
backTracking(s, 0, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
function backTracking(s: string, startIndex: number, route: string[]): void {
|
||||
let length: number = s.length;
|
||||
if (route.length === 4 && startIndex >= length) {
|
||||
resArr.push(route.join('.'));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (route.length === 4 || startIndex >= length) return;
|
||||
let tempStr: string = '';
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex + 1; i <= Math.min(length, startIndex + 3); i++) {
|
||||
tempStr = s.slice(startIndex, i);
|
||||
if (isValidIpSegment(tempStr)) {
|
||||
route.push(s.slice(startIndex, i));
|
||||
backTracking(s, i, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
回溯(对于前导 0的IP(特别注意s[startIndex]=='0'的判断,不应该写成s[startIndex]==0,因为s截取出来不是数字))
|
||||
@@ -497,6 +536,53 @@ func isNormalIp(s string,startIndex,end int)bool{
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn is_valid(s: &Vec<char>, start: usize, end: usize) -> bool {
|
||||
if start > end { return false; }
|
||||
if s[start] == '0' && start != end { return false; }
|
||||
let mut num = 0;
|
||||
for i in start..=end {
|
||||
if s[i] > '9' || s[i] < '0' { return false; }
|
||||
if let Some(digit) = s[i].to_digit(10) { num = num * 10 + digit; }
|
||||
if num > 255 { return false; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<String>, s: &mut Vec<char>, start_index: usize, mut point_num: usize) {
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
if point_num == 3 {
|
||||
if Self::is_valid(s, start_index, len - 1) {
|
||||
result.push(s.iter().collect::<String>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in start_index..len {
|
||||
if Self::is_valid(s, start_index, i) {
|
||||
point_num += 1;
|
||||
s.insert(i + 1, '.');
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, s, i + 2, point_num);
|
||||
point_num -= 1;
|
||||
s.remove(i + 1);
|
||||
} else { break; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn restore_ip_addresses(s: String) -> Vec<String> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
if len < 4 || len > 12 { return result; }
|
||||
let mut s = s.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut s, 0, 0);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//记录结果
|
||||
@@ -620,6 +706,48 @@ func restoreIpAddresses(_ s: String) -> [String] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def restoreIpAddresses(s: String): List[String] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
if (s.size < 4 || s.length > 12) return result.toList
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断IP中的一个字段是否为正确的
|
||||
def isIP(sub: String): Boolean = {
|
||||
if (sub.size > 1 && sub(0) == '0') return false
|
||||
if (sub.toInt > 255) return false
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (startIndex >= s.size) {
|
||||
if (path.size == 4) {
|
||||
result.append(path.mkString(".")) // mkString方法可以把集合里的数据以指定字符串拼接
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// subString
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex until startIndex + 3 if i < s.size) {
|
||||
var subString = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1)
|
||||
if (isIP(subString)) { // 如果合法则进行下一轮
|
||||
path.append(subString)
|
||||
backtracking(i + 1)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 96.不同的二叉搜索树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数 n,求以 1 ... n 为节点组成的二叉搜索树有多少种?
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -227,7 +227,51 @@ const numTrees =(n) => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function numTrees(n: number): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]: i个节点对应的种树
|
||||
dp[0]: -1; 无意义;
|
||||
dp[1]: 1;
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: 2 * dp[i - 1] +
|
||||
(dp[1] * dp[i - 2] + dp[2] * dp[i - 3] + ... + dp[i - 2] * dp[1]); 从1加到i-2
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
dp[0] = -1; // 表示无意义
|
||||
dp[1] = 1;
|
||||
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = 2 * dp[i - 1];
|
||||
for (let j = 1, end = i - 1; j < end; j++) {
|
||||
dp[i] += dp[j] * dp[end - j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn num_trees(n: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let n = n as usize;
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![0; n + 1];
|
||||
dp[0] = 1;
|
||||
for i in 1..=n {
|
||||
for j in 1..=i {
|
||||
dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//开辟dp数组
|
||||
int *initDP(int n) {
|
||||
@@ -256,5 +300,22 @@ int numTrees(int n){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def numTrees(n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var dp = new Array[Int](n + 1)
|
||||
dp(0) = 1
|
||||
for (i <- 1 to n) {
|
||||
for (j <- 1 to i) {
|
||||
dp(i) += dp(j - 1) * dp(i - j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 98.验证二叉搜索树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
|
||||
@@ -408,7 +408,28 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 遵循Carl的写法,只添加了节点判断的部分
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
|
||||
# method 2
|
||||
que, pre = [], None
|
||||
while root or que:
|
||||
while root:
|
||||
que.append(root)
|
||||
root = root.left
|
||||
root = que.pop()
|
||||
# 对第一个节点只做记录,对后面的节点进行比较
|
||||
if pre is None:
|
||||
pre = root.val
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if pre >= root.val: return False
|
||||
pre = root.val
|
||||
root = root.right
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
import "math"
|
||||
@@ -568,7 +589,50 @@ function isValidBST(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
辅助数组解决:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def isValidBST(root: TreeNode): Boolean = {
|
||||
var arr = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
// 递归中序遍历二叉树,将节点添加到arr
|
||||
def traversal(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
|
||||
if (node == null) return
|
||||
traversal(node.left)
|
||||
arr.append(node.value)
|
||||
traversal(node.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
traversal(root)
|
||||
// 这个数组如果是升序就代表是二叉搜索树
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until arr.size) {
|
||||
if (arr(i) <= arr(i - 1)) return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
递归中解决:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def isValidBST(root: TreeNode): Boolean = {
|
||||
var flag = true
|
||||
var preValue:Long = Long.MinValue // 这里要使用Long类型
|
||||
|
||||
def traversal(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
|
||||
if (node == null || flag == false) return
|
||||
traversal(node.left)
|
||||
if (node.value > preValue) preValue = node.value
|
||||
else flag = false
|
||||
traversal(node.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
traversal(root)
|
||||
flag
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 100. 相同的树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/same-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个二叉树,编写一个函数来检验它们是否相同。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -240,6 +240,60 @@ Go:
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 递归法
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var isSameTree = function (p, q) {
|
||||
if (p == null && q == null)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
if (p == null || q == null)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
if (p.val != q.val)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 递归法-先序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
if (p === null && q === null) return true;
|
||||
if (p === null || q === null) return false;
|
||||
if (p.val !== q.val) return false;
|
||||
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 迭代法-层序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
const queue1: (TreeNode | null)[] = [],
|
||||
queue2: (TreeNode | null)[] = [];
|
||||
queue1.push(p);
|
||||
queue2.push(q);
|
||||
while (queue1.length > 0 && queue2.length > 0) {
|
||||
const node1 = queue1.shift(),
|
||||
node2 = queue2.shift();
|
||||
if (node1 === null && node2 === null) continue;
|
||||
if (
|
||||
(node1 === null || node2 === null) ||
|
||||
node1!.val !== node2!.val
|
||||
) return false;
|
||||
queue1.push(node1!.left);
|
||||
queue1.push(node1!.right);
|
||||
queue2.push(node2!.left);
|
||||
queue2.push(node2!.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 101. 对称二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -238,7 +238,7 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 总结
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
这次我们又深度剖析了一道二叉树的“简单题”,大家会发现,真正的把题目搞清楚其实并不简单,leetcode上accept了和真正掌握了还是有距离的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -248,7 +248,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
如果已经做过这道题目的同学,读完文章可以再去看看这道题目,思考一下,会有不一样的发现!
|
||||
|
||||
# 相关题目推荐
|
||||
## 相关题目推荐
|
||||
|
||||
这两道题目基本和本题是一样的,只要稍加修改就可以AC。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -437,38 +437,28 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
层序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
层次遍历
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
|
||||
if not root: return True
|
||||
que, cnt = [[root.left, root.right]], 1
|
||||
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
que = [root]
|
||||
while que:
|
||||
nodes, tmp, sign = que.pop(), [], False
|
||||
for node in nodes:
|
||||
if not node:
|
||||
tmp.append(None)
|
||||
tmp.append(None)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if node.left:
|
||||
tmp.append(node.left)
|
||||
sign = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
tmp.append(None)
|
||||
if node.right:
|
||||
tmp.append(node.right)
|
||||
sign = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
tmp.append(None)
|
||||
p1, p2 = 0, len(nodes) - 1
|
||||
while p1 < p2:
|
||||
if (not nodes[p1] and nodes[p2]) or (nodes[p1] and not nodes[p2]): return False
|
||||
elif nodes[p1] and nodes[p2] and nodes[p1].val != nodes[p2].val: return False
|
||||
p1 += 1
|
||||
p2 -= 1
|
||||
if sign: que.append(tmp)
|
||||
cnt += 1
|
||||
this_level_length = len(que)
|
||||
for i in range(this_level_length // 2):
|
||||
# 要么其中一个是None但另外一个不是
|
||||
if (not que[i] and que[this_level_length - 1 - i]) or (que[i] and not que[this_level_length - 1 - i]):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
# 要么两个都不是None
|
||||
if que[i] and que[i].val != que[this_level_length - 1 - i].val:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
for i in range(this_level_length):
|
||||
if not que[i]: continue
|
||||
que.append(que[i].left)
|
||||
que.append(que[i].right)
|
||||
que = que[this_level_length:]
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -760,5 +750,25 @@ func isSymmetric3(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Bool {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def isSymmetric(root: TreeNode): Boolean = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return true // 如果等于空直接返回true
|
||||
def compare(left: TreeNode, right: TreeNode): Boolean = {
|
||||
if (left == null && right == null) return true // 如果左右都为空,则为true
|
||||
if (left == null && right != null) return false // 如果左空右不空,不对称,返回false
|
||||
if (left != null && right == null) return false // 如果左不空右空,不对称,返回false
|
||||
// 如果左右的值相等,并且往下递归
|
||||
left.value == right.value && compare(left.left, right.right) && compare(left.right, right.left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 分别比较左子树和右子树
|
||||
compare(root.left, root.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 102.二叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -82,6 +82,26 @@ public:
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
# 递归法
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (cur == nullptr) return;
|
||||
if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>());
|
||||
result[depth].push_back(cur->val);
|
||||
order(cur->left, result, depth + 1);
|
||||
order(cur->right, result, depth + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> result;
|
||||
int depth = 0;
|
||||
order(root, result, depth);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python3代码:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -185,6 +205,36 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
102. 二叉树的递归遍历
|
||||
*/
|
||||
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
||||
arr := [][]int{}
|
||||
|
||||
depth := 0
|
||||
|
||||
var order func(root *TreeNode, depth int)
|
||||
|
||||
order = func(root *TreeNode, depth int) {
|
||||
if root == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(arr) == depth {
|
||||
arr = append(arr, []int{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
arr[depth] = append(arr[depth], root.Val)
|
||||
|
||||
order(root.Left, depth+1)
|
||||
order(root.Right, depth+1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
order(root, depth)
|
||||
|
||||
return arr
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
@@ -298,13 +348,68 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def levelOrder(root: TreeNode): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]() // 声明一个队列
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root) // 把根节点加入queue
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
val len = queue.size // 求出len的长度
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) { // 从0到当前队列长度的所有节点都加入到结果集
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
tmp.append(curNode.value)
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(tmp.toList)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn level_order(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut ans = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut stack = Vec::new();
|
||||
if root.is_none(){
|
||||
return ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
stack.push(root.unwrap());
|
||||
while stack.is_empty()!= true{
|
||||
let num = stack.len();
|
||||
let mut level = Vec::new();
|
||||
for _i in 0..num{
|
||||
let tmp = stack.remove(0);
|
||||
level.push(tmp.borrow_mut().val);
|
||||
if tmp.borrow_mut().left.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(tmp.borrow_mut().left.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tmp.borrow_mut().right.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(tmp.borrow_mut().right.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans.push(level);
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**此时我们就掌握了二叉树的层序遍历了,那么如下九道力扣上的题目,只需要修改模板的两三行代码(不能再多了),便可打倒!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 107.二叉树的层次遍历 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -528,9 +633,64 @@ func levelOrderBottom(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def levelOrderBottom(root: TreeNode): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
tmp.append(curNode.value)
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(tmp.toList)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最后翻转一下
|
||||
res.reverse.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn level_order(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut ans = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut stack = Vec::new();
|
||||
if root.is_none(){
|
||||
return ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
stack.push(root.unwrap());
|
||||
while stack.is_empty()!= true{
|
||||
let num = stack.len();
|
||||
let mut level = Vec::new();
|
||||
for _i in 0..num{
|
||||
let tmp = stack.remove(0);
|
||||
level.push(tmp.borrow_mut().val);
|
||||
if tmp.borrow_mut().left.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(tmp.borrow_mut().left.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tmp.borrow_mut().right.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(tmp.borrow_mut().right.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans.push(level);
|
||||
}
|
||||
ans
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 199.二叉树的右视图
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -750,9 +910,34 @@ func rightSideView(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 199.二叉树的右视图
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def rightSideView(root: TreeNode): List[Int] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
var curNode: TreeNode = null
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(curNode.value) // 把最后一个节点的值加入解集
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.toList // 最后需要把res转换为List,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 637.二叉树的层平均值
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -981,10 +1166,34 @@ func averageOfLevels(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Double] {
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 637.二叉树的层平均值
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def averageOfLevels(root: TreeNode): Array[Double] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Double]()
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
var sum = 0.0
|
||||
var len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
var curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
sum += curNode.value // 累加该层的值
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(sum / len) // 平均值即为sum/len
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.toArray // 最后需要转换为Array,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 429.N叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1225,9 +1434,37 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: Node?) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 429.N叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def levelOrder(root: Node): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root) // 根节点入队
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() // 存储每层节点
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
tmp.append(curNode.value) // 将该节点的值加入tmp
|
||||
// 循环遍历该节点的子节点,加入队列
|
||||
for (child <- curNode.children) {
|
||||
queue.enqueue(child)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(tmp.toList) // 将该层的节点放到结果集
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 515.在每个树行中找最大值
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
|
||||
|
||||
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1433,9 +1670,35 @@ func largestValues(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 515.在每个树行中找最大值
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def largestValues(root: TreeNode): List[Int] = {
|
||||
val res = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
var max = Int.MinValue // 初始化max为系统最小值
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
max = math.max(max, curNode.value) // 对比求解最大值
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.append(max) // 将最大值放入结果集
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1692,9 +1955,38 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
||||
def connect(root: Node): Node = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return root
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
val tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[Node]()
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
tmp.append(curNode)
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 处理next指针
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until tmp.size - 1) {
|
||||
tmp(i).next = tmp(i + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
tmp(tmp.size-1).next = null
|
||||
}
|
||||
root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1943,9 +2235,38 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
||||
def connect(root: Node): Node = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return root
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
val tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[Node]()
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
tmp.append(curNode)
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 处理next指针
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until tmp.size - 1) {
|
||||
tmp(i).next = tmp(i + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
tmp(tmp.size-1).next = null
|
||||
}
|
||||
root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2160,9 +2481,33 @@ func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.length
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 111.二叉树的最小深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2314,21 +2659,21 @@ JavaScript:
|
||||
var minDepth = function(root) {
|
||||
if (root === null) return 0;
|
||||
let queue = [root];
|
||||
let deepth = 0;
|
||||
let depth = 0;
|
||||
while (queue.length) {
|
||||
let n = queue.length;
|
||||
deepth++;
|
||||
depth++;
|
||||
for (let i=0; i<n; i++) {
|
||||
let node = queue.shift();
|
||||
// 如果左右节点都是null,则该节点深度最小
|
||||
// 如果左右节点都是null(在遇见的第一个leaf节点上),则该节点深度最小
|
||||
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
|
||||
return deepth;
|
||||
return depth;
|
||||
}
|
||||
node.left && queue.push(node.left);;
|
||||
node.right && queue.push (node.right);
|
||||
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return deepth;
|
||||
return depth;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2379,6 +2724,30 @@ func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 111.二叉树的最小深度
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def minDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
if (curNode.left == null && curNode.right == null) return depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 总结
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -192,11 +192,38 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
rust:
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn max_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
|
||||
if root.is_none(){
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let mut max_depth: i32 = 0;
|
||||
let mut stack = vec![root.unwrap()];
|
||||
while !stack.is_empty() {
|
||||
let num = stack.len();
|
||||
for _i in 0..num{
|
||||
let top = stack.remove(0);
|
||||
if top.borrow_mut().left.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().left.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if top.borrow_mut().right.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().right.take().unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
max_depth+=1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
max_depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
那么我们可以顺便解决一下n叉树的最大深度问题
|
||||
|
||||
# 559.n叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个 n 叉树,找到其最大深度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -267,14 +294,13 @@ class solution {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 递归法
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public int maxdepth(treenode root) {
|
||||
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
if (root == null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int leftdepth = maxdepth(root.left);
|
||||
int rightdepth = maxdepth(root.right);
|
||||
return math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth) + 1;
|
||||
|
||||
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
|
||||
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
|
||||
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -284,23 +310,23 @@ class solution {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public int maxdepth(treenode root) {
|
||||
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
if(root == null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
deque<treenode> deque = new linkedlist<>();
|
||||
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
deque.offer(root);
|
||||
int depth = 0;
|
||||
while (!deque.isempty()) {
|
||||
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
|
||||
int size = deque.size();
|
||||
depth++;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||||
treenode poll = deque.poll();
|
||||
if (poll.left != null) {
|
||||
deque.offer(poll.left);
|
||||
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
|
||||
if (node.left != null) {
|
||||
deque.offer(node.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (poll.right != null) {
|
||||
deque.offer(poll.right);
|
||||
if (node.right != null) {
|
||||
deque.offer(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -468,7 +494,7 @@ class solution:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## go
|
||||
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
@@ -521,6 +547,8 @@ func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
|
||||
|
||||
## javascript
|
||||
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var maxdepth = function(root) {
|
||||
if (root === null) return 0;
|
||||
@@ -568,6 +596,8 @@ var maxDepth = function(root) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 559.n叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
N叉树的最大深度 递归写法
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var maxDepth = function(root) {
|
||||
@@ -600,9 +630,9 @@ var maxDepth = function(root) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript:
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 二叉树的最大深度:
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
|
||||
@@ -645,7 +675,7 @@ function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> N叉树的最大深度
|
||||
### 559.n叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
|
||||
@@ -675,6 +705,8 @@ function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
二叉树最大深度递归
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
|
||||
@@ -731,7 +763,8 @@ int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
|
||||
|
||||
## Swift
|
||||
|
||||
>二叉树最大深度
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
// 递归 - 后序
|
||||
func maxDepth1(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
@@ -770,7 +803,8 @@ func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>N叉树最大深度
|
||||
### 559.n叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
func maxDepth(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
|
||||
@@ -806,5 +840,84 @@ func maxDepth1(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
### 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
def process(curNode: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (curNode == null) return 0
|
||||
// 递归左节点和右节点,返回最大的,最后+1
|
||||
math.max(process(curNode.left), process(curNode.right)) + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 调用递归方法,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
process(root)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
if (root == null) return depth
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth += 1 // 只要有层次就+=1
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 559.n叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
for (node <- root.children) {
|
||||
depth = math.max(depth, maxDepth(node))
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法: (层序遍历)
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
for (node <- curNode.children) queue.enqueue(node)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/)
|
||||
|
||||
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
|
||||
中序数组相对比较好切,找到切割点(后序数组的最后一个元素)在中序数组的位置,然后切割,如下代码中我坚持左闭右开的原则:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```C++
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 找到中序遍历的切割点
|
||||
int delimiterIndex;
|
||||
for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {
|
||||
@@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end() );
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// postorder 舍弃末尾元素,因为这个元素就是中间节点,已经用过了
|
||||
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -144,7 +144,7 @@ vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end
|
||||
|
||||
接下来可以递归了,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);
|
||||
root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -394,7 +394,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
# 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/)
|
||||
|
||||
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -584,35 +584,29 @@ tree2 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
Map<Integer, Integer> map; // 方便根据数值查找位置
|
||||
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
|
||||
return buildTree1(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
|
||||
map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
|
||||
map.put(inorder[i], i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
|
||||
}
|
||||
public TreeNode buildTree1(int[] inorder, int inLeft, int inRight,
|
||||
int[] postorder, int postLeft, int postRight) {
|
||||
// 没有元素了
|
||||
if (inRight - inLeft < 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
|
||||
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
|
||||
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 只有一个元素了
|
||||
if (inRight - inLeft == 1) {
|
||||
return new TreeNode(inorder[inLeft]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 后序数组postorder里最后一个即为根结点
|
||||
int rootVal = postorder[postRight - 1];
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
|
||||
int rootIndex = 0;
|
||||
// 根据根结点的值找到该值在中序数组inorder里的位置
|
||||
for (int i = inLeft; i < inRight; i++) {
|
||||
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
|
||||
rootIndex = i;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 根据rootIndex划分左右子树
|
||||
root.left = buildTree1(inorder, inLeft, rootIndex,
|
||||
postorder, postLeft, postLeft + (rootIndex - inLeft));
|
||||
root.right = buildTree1(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inRight,
|
||||
postorder, postLeft + (rootIndex - inLeft), postRight - 1);
|
||||
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]); // 找到后序遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
|
||||
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数
|
||||
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex,
|
||||
postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft);
|
||||
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd,
|
||||
postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -622,31 +616,29 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
|
||||
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
|
||||
return helper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public TreeNode helper(int[] preorder, int preLeft, int preRight,
|
||||
int[] inorder, int inLeft, int inRight) {
|
||||
// 递归终止条件
|
||||
if (inLeft > inRight || preLeft > preRight) return null;
|
||||
|
||||
// val 为前序遍历第一个的值,也即是根节点的值
|
||||
// idx 为根据根节点的值来找中序遍历的下标
|
||||
int idx = inLeft, val = preorder[preLeft];
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
|
||||
for (int i = inLeft; i <= inRight; i++) {
|
||||
if (inorder[i] == val) {
|
||||
idx = i;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
|
||||
map.put(inorder[i], i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据 idx 来递归找左右子树
|
||||
root.left = helper(preorder, preLeft + 1, preLeft + (idx - inLeft),
|
||||
inorder, inLeft, idx - 1);
|
||||
root.right = helper(preorder, preLeft + (idx - inLeft) + 1, preRight,
|
||||
inorder, idx + 1, inRight);
|
||||
return findNode(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length); // 前闭后开
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public TreeNode findNode(int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
|
||||
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
|
||||
if (preBegin >= preEnd || inBegin >= inEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); // 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
|
||||
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定前序数列的个数
|
||||
root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
|
||||
inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);
|
||||
root.right = findNode(preorder, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1, preEnd,
|
||||
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -790,7 +782,7 @@ func findRootIndex(target int,inorder []int) int{
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
|
||||
if (!preorder.length) return null;
|
||||
if (!inorder.length) return null;
|
||||
const rootVal = postorder.pop(); // 从后序遍历的数组中获取中间节点的值, 即数组最后一个值
|
||||
let rootIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootVal); // 获取中间节点在中序遍历中的下标
|
||||
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 创建中间节点
|
||||
@@ -1091,7 +1083,53 @@ class Solution_0106 {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def buildTree(inorder: Array[Int], postorder: Array[Int]): TreeNode = {
|
||||
// 1、如果长度为0,则直接返回null
|
||||
var len = inorder.size
|
||||
if (len == 0) return null
|
||||
// 2、后序数组的最后一个元素是当前根元素
|
||||
var rootValue = postorder(len - 1)
|
||||
var root: TreeNode = new TreeNode(rootValue, null, null)
|
||||
if (len == 1) return root // 如果数组只有一个节点,就直接返回
|
||||
// 3、在中序数组中找到切割点的索引
|
||||
var delimiterIndex: Int = inorder.indexOf(rootValue)
|
||||
// 4、切分数组往下迭代
|
||||
root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, delimiterIndex), postorder.slice(0, delimiterIndex))
|
||||
root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(delimiterIndex + 1, len), postorder.slice(delimiterIndex, len - 1))
|
||||
root // 返回root,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def buildTree(preorder: Array[Int], inorder: Array[Int]): TreeNode = {
|
||||
// 1、如果长度为0,直接返回空
|
||||
var len = inorder.size
|
||||
if (len == 0) return null
|
||||
// 2、前序数组的第一个元素是当前子树根节点
|
||||
var rootValue = preorder(0)
|
||||
var root = new TreeNode(rootValue, null, null)
|
||||
if (len == 1) return root // 如果数组元素只有一个,那么返回根节点
|
||||
// 3、在中序数组中,找到切割点
|
||||
var delimiterIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootValue)
|
||||
|
||||
// 4、切分数组往下迭代
|
||||
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1, delimiterIndex + 1), inorder.slice(0, delimiterIndex))
|
||||
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(delimiterIndex + 1, preorder.size), inorder.slice(delimiterIndex + 1, len))
|
||||
|
||||
root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -355,6 +355,7 @@ func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
递归
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {
|
||||
@@ -372,7 +373,44 @@ var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {
|
||||
return buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代
|
||||
```JavaScript
|
||||
var sortedArrayToBST = function(nums) {
|
||||
if(nums.length===0){
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let root=new TreeNode(0); //初始根节点
|
||||
let nodeQue=[root]; //放遍历的节点,并初始化
|
||||
let leftQue=[0]; //放左区间的下标,初始化
|
||||
let rightQue=[nums.length-1]; // 放右区间的下标
|
||||
|
||||
while(nodeQue.length){
|
||||
let curNode=nodeQue.pop();
|
||||
let left=leftQue.pop();
|
||||
let right=rightQue.pop();
|
||||
let mid=left+Math.floor((right-left)/2);
|
||||
|
||||
curNode.val=nums[mid]; //将下标为mid的元素给中间节点
|
||||
|
||||
// 处理左区间
|
||||
if(left<=mid-1){
|
||||
curNode.left=new TreeNode(0);
|
||||
nodeQue.push(curNode.left);
|
||||
leftQue.push(left);
|
||||
rightQue.push(mid-1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 处理右区间
|
||||
if(right>=mid+1){
|
||||
curNode.right=new TreeNode(0);
|
||||
nodeQue.push(curNode.right);
|
||||
leftQue.push(mid+1);
|
||||
rightQue.push(right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
@@ -410,5 +448,27 @@ struct TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(int* nums, int numsSize) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def sortedArrayToBST(nums: Array[Int]): TreeNode = {
|
||||
def buildTree(left: Int, right: Int): TreeNode = {
|
||||
if (left > right) return null // 当left大于right的时候,返回空
|
||||
// 最中间的节点是当前节点
|
||||
var mid = left + (right - left) / 2
|
||||
var curNode = new TreeNode(nums(mid))
|
||||
curNode.left = buildTree(left, mid - 1)
|
||||
curNode.right = buildTree(mid + 1, right)
|
||||
curNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
buildTree(0, nums.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 110.平衡二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是二叉搜索树了则返回-1
|
||||
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是平衡二叉树了则返回-1
|
||||
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
if (node == NULL) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@ int getDepth(TreeNode* cur) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后再用栈来模拟前序遍历,遍历每一个节点的时候,再去判断左右孩子的高度是否符合,代码如下:
|
||||
然后再用栈来模拟后序遍历,遍历每一个节点的时候,再去判断左右孩子的高度是否符合,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
|
||||
@@ -531,40 +531,26 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
|
||||
st = []
|
||||
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
st.append(root)
|
||||
while st:
|
||||
node = st.pop() #中
|
||||
if abs(self.getDepth(node.left) - self.getDepth(node.right)) > 1:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
if node.right:
|
||||
st.append(node.right) #右(空节点不入栈)
|
||||
if node.left:
|
||||
st.append(node.left) #左(空节点不入栈)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def getDepth(self, cur):
|
||||
st = []
|
||||
if cur:
|
||||
st.append(cur)
|
||||
depth = 0
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
while st:
|
||||
node = st.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
height_map = {}
|
||||
stack = [root]
|
||||
while stack:
|
||||
node = stack.pop()
|
||||
if node:
|
||||
st.append(node) #中
|
||||
st.append(None)
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
if node.right: st.append(node.right) #右
|
||||
if node.left: st.append(node.left) #左
|
||||
stack.append(node)
|
||||
stack.append(None)
|
||||
if node.left: stack.append(node.left)
|
||||
if node.right: stack.append(node.right)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
node = st.pop()
|
||||
depth -= 1
|
||||
result = max(result, depth)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
real_node = stack.pop()
|
||||
left, right = height_map.get(real_node.left, 0), height_map.get(real_node.right, 0)
|
||||
if abs(left - right) > 1:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
height_map[real_node] = 1 + max(left, right)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 111.二叉树的最小深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -372,7 +372,7 @@ var minDepth1 = function(root) {
|
||||
// 到叶子节点 返回 1
|
||||
if(!root.left && !root.right) return 1;
|
||||
// 只有右节点时 递归右节点
|
||||
if(!root.left) return 1 + minDepth(root.right);、
|
||||
if(!root.left) return 1 + minDepth(root.right);
|
||||
// 只有左节点时 递归左节点
|
||||
if(!root.right) return 1 + minDepth(root.left);
|
||||
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
|
||||
@@ -488,5 +488,110 @@ func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def minDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) return 1 + minDepth(root.right)
|
||||
if (root.left != null && root.right == null) return 1 + minDepth(root.left)
|
||||
// 如果两侧都不为空,则取最小值,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
1 + math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def minDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
var depth = 0
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
if (curNode.left == null && curNode.right == null) return depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
rust:
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn min_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
|
||||
return Solution::bfs(root)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
pub fn dfs(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32{
|
||||
if node.is_none(){
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let parent = node.unwrap();
|
||||
let left_child = parent.borrow_mut().left.take();
|
||||
let right_child = parent.borrow_mut().right.take();
|
||||
if left_child.is_none() && right_child.is_none(){
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let mut min_depth = i32::MAX;
|
||||
if left_child.is_some(){
|
||||
let left_depth = Solution::dfs(left_child);
|
||||
if left_depth <= min_depth{
|
||||
min_depth = left_depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if right_child.is_some(){
|
||||
let right_depth = Solution::dfs(right_child);
|
||||
if right_depth <= min_depth{
|
||||
min_depth = right_depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
min_depth + 1
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 迭代
|
||||
pub fn bfs(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32{
|
||||
let mut min_depth = 0;
|
||||
if node.is_none(){
|
||||
return min_depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
let mut stack = vec![node.unwrap()];
|
||||
while !stack.is_empty(){
|
||||
min_depth += 1;
|
||||
let num = stack.len();
|
||||
for _i in 0..num{
|
||||
let top = stack.remove(0);
|
||||
let left_child = top.borrow_mut().left.take();
|
||||
let right_child = top.borrow_mut().right.take();
|
||||
if left_child.is_none() && right_child.is_none(){
|
||||
return min_depth;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if left_child.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(left_child.unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if right_child.is_some(){
|
||||
stack.push(right_child.unwrap());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
min_depth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 112. 路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
# 113. 路径总和ii
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -300,7 +300,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
## java
|
||||
|
||||
lc112
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class solution {
|
||||
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
@@ -373,26 +373,26 @@ class solution {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class solution {
|
||||
public list<list<integer>> pathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
list<list<integer>> res = new arraylist<>();
|
||||
public List<List<Integer>> pathsum(TreeNode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
|
||||
|
||||
list<integer> path = new linkedlist<>();
|
||||
|
||||
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
preorderdfs(root, targetsum, res, path);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void preorderdfs(treenode root, int targetsum, list<list<integer>> res, list<integer> path) {
|
||||
public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {
|
||||
path.add(root.val);
|
||||
// 遇到了叶子节点
|
||||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
|
||||
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
|
||||
if (targetsum - root.val == 0) {
|
||||
res.add(new arraylist<>(path));
|
||||
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -436,7 +436,7 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
## python
|
||||
|
||||
0112.路径总和
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -488,7 +488,7 @@ class solution:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -545,7 +545,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
## go
|
||||
|
||||
112. 路径总和
|
||||
### 112. 路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
//递归法
|
||||
@@ -570,7 +570,7 @@ func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
113. 路径总和 II
|
||||
### 113. 路径总和 II
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
@@ -612,7 +612,7 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
|
||||
|
||||
## javascript
|
||||
|
||||
0112.路径总和
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
@@ -673,7 +673,7 @@ let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
@@ -768,7 +768,7 @@ let pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 0112.路径总和
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归法:**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -850,7 +850,7 @@ function hasPathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): boolean {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 0112.路径总和 ii
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和 ii
|
||||
|
||||
**递归法:**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -888,7 +888,7 @@ function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): number[][] {
|
||||
|
||||
## Swift
|
||||
|
||||
0112.路径总和
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -955,7 +955,7 @@ func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1006,7 +1006,210 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
> 0112.路径总和
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
||||
// 递归结束条件:若当前节点不存在,返回false
|
||||
if(!root)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
// 若当前节点为叶子节点,且targetSum-root的值为0。(当前路径上的节点值的和满足条件)返回true
|
||||
if(!root->right && !root->left && targetSum == root->val)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
// 查看左子树和右子树的所有节点是否满足条件
|
||||
return hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// 存储一个节点以及当前的和
|
||||
struct Pair {
|
||||
struct TreeNode* node;
|
||||
int sum;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
||||
struct Pair stack[1000];
|
||||
int stackTop = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 若root存在,则将节点和值封装成一个pair入栈
|
||||
if(root) {
|
||||
struct Pair newPair = {root, root->val};
|
||||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 当栈不为空时
|
||||
while(stackTop) {
|
||||
// 出栈栈顶元素
|
||||
struct Pair topPair = stack[--stackTop];
|
||||
// 若栈顶元素为叶子节点,且和为targetSum时,返回true
|
||||
if(!topPair.node->left && !topPair.node->right && topPair.sum == targetSum)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
// 若当前栈顶节点有左右孩子,计算和并入栈
|
||||
if(topPair.node->left) {
|
||||
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->left, topPair.sum + topPair.node->left->val};
|
||||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(topPair.node->right) {
|
||||
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->right, topPair.sum + topPair.node->right->val};
|
||||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
> 0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int** ret;
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int* colSize;
|
||||
int retTop;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
|
||||
void traversal(const struct TreeNode* const node, int count) {
|
||||
// 若当前节点为叶子节点
|
||||
if(!node->right && !node->left) {
|
||||
// 若当前path上的节点值总和等于targetSum。
|
||||
if(count == 0) {
|
||||
// 复制当前path
|
||||
int *curPath = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pathTop);
|
||||
memcpy(curPath, path, sizeof(int) * pathTop);
|
||||
// 记录当前path的长度为pathTop
|
||||
colSize[retTop] = pathTop;
|
||||
// 将当前path加入到ret数组中
|
||||
ret[retTop++] = curPath;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 若节点有左/右孩子
|
||||
if(node->left) {
|
||||
// 将左孩子的值加入path中
|
||||
path[pathTop++] = node->left->val;
|
||||
traversal(node->left, count - node->left->val);
|
||||
// 回溯
|
||||
pathTop--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(node->right) {
|
||||
// 将右孩子的值加入path中
|
||||
path[pathTop++] = node->right->val;
|
||||
traversal(node->right, count - node->right->val);
|
||||
// 回溯
|
||||
--pathTop;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||||
// 初始化数组
|
||||
ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 1000);
|
||||
path = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 1000);
|
||||
colSize = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
|
||||
retTop = pathTop = 0;
|
||||
*returnSize = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// 若根节点不存在,返回空的ret
|
||||
if(!root)
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
// 将根节点加入到path中
|
||||
path[pathTop++] = root->val;
|
||||
traversal(root, targetSum - root->val);
|
||||
|
||||
// 设置返回ret数组大小,以及其中每个一维数组元素的长度
|
||||
*returnSize = retTop;
|
||||
*returnColumnSizes = colSize;
|
||||
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归:**
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
|
||||
if(root == null) return false
|
||||
var res = false
|
||||
|
||||
def traversal(curNode: TreeNode, sum: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (res) return // 如果直接标记为true了,就没有往下递归的必要了
|
||||
if (curNode.left == null && curNode.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
|
||||
res = true
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 往下递归
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) traversal(curNode.left, sum + curNode.left.value)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) traversal(curNode.right, sum + curNode.right.value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
traversal(root, root.value)
|
||||
res // return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代:**
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return false
|
||||
val stack = mutable.Stack[(TreeNode, Int)]()
|
||||
stack.push((root, root.value)) // 将根节点元素放入stack
|
||||
while (!stack.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val curNode = stack.pop() // 取出栈顶元素
|
||||
// 如果遇到叶子节点,看当前的值是否等于targetSum,等于则返回true
|
||||
if (curNode._1.left == null && curNode._1.right == null && curNode._2 == targetSum) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (curNode._1.right != null) stack.push((curNode._1.right, curNode._2 + curNode._1.right.value))
|
||||
if (curNode._1.left != null) stack.push((curNode._1.left, curNode._2 + curNode._1.left.value))
|
||||
}
|
||||
false //如果没有返回true,即可返回false,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
|
||||
**递归:**
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||||
def pathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
val res = ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||||
val path = ListBuffer[Int]();
|
||||
|
||||
def traversal(cur: TreeNode, count: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null && count == 0) {
|
||||
res.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (cur.left != null) {
|
||||
path.append(cur.left.value)
|
||||
traversal(cur.left, count - cur.left.value)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (cur.right != null) {
|
||||
path.append(cur.right.value)
|
||||
traversal(cur.right, count - cur.right.value)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path.append(root.value)
|
||||
traversal(root, targetSum - root.value)
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 115.不同的子序列
|
||||
# 115.不同的子序列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/distinct-subsequences/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串 t ,计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -267,6 +267,36 @@ const numDistinct = (s, t) => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function numDistinct(s: string, t: string): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][j]: s前i个字符,t前j个字符,s子序列中t出现的个数
|
||||
dp[0][0]=1, 表示s前0个字符为'',t前0个字符为''
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const sLen: number = s.length,
|
||||
tLen: number = t.length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(sLen + 1).fill(0)
|
||||
.map(_ => new Array(tLen + 1).fill(0));
|
||||
for (let m = 0; m < sLen; m++) {
|
||||
dp[m][0] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= sLen; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j <= tLen; j++) {
|
||||
if (s[i - 1] === t[j - 1]) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[sLen][tLen];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -287,6 +287,79 @@ const connect = root => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
(注:命名空间‘Node’与typescript中内置类型冲突,这里改成了‘NodePro’)
|
||||
|
||||
> 递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
class NodePro {
|
||||
val: number
|
||||
left: NodePro | null
|
||||
right: NodePro | null
|
||||
next: NodePro | null
|
||||
constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
|
||||
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
|
||||
this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
|
||||
this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
|
||||
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
|
||||
if (root === null) return null;
|
||||
root.next = null;
|
||||
recur(root);
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
};
|
||||
function recur(node: NodePro): void {
|
||||
if (node.left === null || node.right === null) return;
|
||||
node.left.next = node.right;
|
||||
node.right.next = node.next && node.next.left;
|
||||
recur(node.left);
|
||||
recur(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 迭代法:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
class NodePro {
|
||||
val: number
|
||||
left: NodePro | null
|
||||
right: NodePro | null
|
||||
next: NodePro | null
|
||||
constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
|
||||
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
|
||||
this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
|
||||
this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
|
||||
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
|
||||
if (root === null) return null;
|
||||
const queue: NodePro[] = [];
|
||||
queue.push(root);
|
||||
while (queue.length > 0) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = queue.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
const curNode: NodePro = queue.shift()!;
|
||||
if (i === length - 1) {
|
||||
curNode.next = null;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
curNode.next = queue[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (curNode.left !== null) queue.push(curNode.left);
|
||||
if (curNode.right !== null) queue.push(curNode.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
|
||||
# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -311,7 +311,36 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
> 贪心法:
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
|
||||
low := math.MaxInt32
|
||||
rlt := 0
|
||||
for i := range prices{
|
||||
low = min(low, prices[i])
|
||||
rlt = max(rlt, prices[i]-low)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return rlt
|
||||
}
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b{
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a > b{
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划:版本一
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
|
||||
length:=len(prices)
|
||||
@@ -338,6 +367,29 @@ func max(a,b int)int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划:版本二
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
|
||||
dp := [2][2]int{}
|
||||
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
|
||||
dp[0][1] = 0
|
||||
for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++{
|
||||
dp[i%2][0] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][0], -prices[i])
|
||||
dp[i%2][1] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][1], dp[(i-1)%2][0]+prices[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return dp[(len(prices)-1)%2][1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a > b{
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划
|
||||
@@ -374,6 +426,46 @@ var maxProfit = function(prices) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 贪心法
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
if (prices.length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
let buy: number = prices[0];
|
||||
let profitMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
profitMax = Math.max(profitMax, prices[i] - buy);
|
||||
buy = Math.min(prices[i], buy);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return profitMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][0]: 第i天持有股票的最大现金
|
||||
dp[i][1]: 第i天不持有股票的最大现金
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length = prices.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = [];
|
||||
dp[0] = [-prices[0], 0];
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = [];
|
||||
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], -prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[length - 1][1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@
|
||||
本题首先要清楚两点:
|
||||
|
||||
* 只有一只股票!
|
||||
* 当前只有买股票或者买股票的操作
|
||||
* 当前只有买股票或者卖股票的操作
|
||||
|
||||
想获得利润至少要两天为一个交易单元。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -91,8 +91,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
### 动态规划
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -133,8 +133,9 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
### Java:
|
||||
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// 贪心思路
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
@@ -148,6 +149,7 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution { // 动态规划
|
||||
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
|
||||
@@ -169,8 +171,8 @@ class Solution { // 动态规划
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
### Python:
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +182,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python动态规划
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
@@ -194,7 +196,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return dp[-1][1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
### Go:
|
||||
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
//贪心算法
|
||||
@@ -231,7 +233,7 @@ func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Javascript:
|
||||
### Javascript:
|
||||
|
||||
贪心
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
@@ -264,12 +266,61 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return dp[prices.length -1][0];
|
||||
return dp[prices.length -1][1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
### TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
let resProfit: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
resProfit += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resProfit;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut result = 0;
|
||||
for i in 1..prices.len() {
|
||||
result += Self::max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let n = prices.len();
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; 2]; n];
|
||||
dp[0][0] -= prices[0];
|
||||
for i in 1..n {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = Self::max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Self::max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
Self::max(dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C:
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
@@ -284,5 +335,44 @@ int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
|
||||
|
||||
int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
|
||||
int dp[pricesSize][2];
|
||||
dp[0][0] = 0 - prices[0];
|
||||
dp[0][1] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
|
||||
// dp[i][0]为i-1天持股的钱数/在第i天用i-1天的钱买入的最大值。
|
||||
// 若i-1天持股,且第i天买入股票比i-1天持股时更亏,说明应在i-1天时持股
|
||||
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i]);
|
||||
//dp[i][1]为i-1天不持股钱数/在第i天卖出所持股票dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]的最大值
|
||||
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 返回在最后一天不持股时的钱数(将股票卖出后钱最大化)
|
||||
return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
贪心:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxProfit(prices: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var result = 0
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until prices.length) {
|
||||
if (prices(i) > prices(i - 1)) {
|
||||
result += prices(i) - prices(i - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
|
||||
# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return dp[prices.length -1][0];
|
||||
return dp[prices.length -1][1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 方法二:动态规划(滚动数组)
|
||||
@@ -295,6 +295,42 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][0]: 第i天持有股票
|
||||
dp[i][1]: 第i天不持有股票
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = prices.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0).map(_ => []);
|
||||
dp[0] = [-prices[0], 0];
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[length - 1][1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 贪心法
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
let resProfit: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
|
||||
resProfit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resProfit;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
|
||||
# 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
@@ -148,8 +148,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(n × 5)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(n × 5)
|
||||
|
||||
当然,大家可以看到力扣官方题解里的一种优化空间写法,我这里给出对应的C++版本:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -173,8 +173,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
大家会发现dp[2]利用的是当天的dp[1]。 但结果也是对的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -352,6 +352,36 @@ const maxProfit = prices => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 版本一
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][0]: 无操作;
|
||||
dp[i][1]: 第一次买入;
|
||||
dp[i][2]: 第一次卖出;
|
||||
dp[i][3]: 第二次买入;
|
||||
dp[i][4]: 第二次卖出;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = prices.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0)
|
||||
.map(_ => new Array(5).fill(0));
|
||||
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
|
||||
dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
|
||||
dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Math.max(dp[length - 1][2], dp[length - 1][4]);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
> 版本一:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 127. 单词接龙
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-ladder/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder/)
|
||||
|
||||
字典 wordList 中从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
|
||||
* 序列中第一个单词是 beginWord 。
|
||||
@@ -134,7 +134,29 @@ public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
|
||||
wordSet = set(wordList)
|
||||
if len(wordSet)== 0 or endWord not in wordSet:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
mapping = {beginWord:1}
|
||||
queue = deque([beginWord])
|
||||
while queue:
|
||||
word = queue.popleft()
|
||||
path = mapping[word]
|
||||
for i in range(len(word)):
|
||||
word_list = list(word)
|
||||
for j in range(26):
|
||||
word_list[i] = chr(ord('a')+j)
|
||||
newWord = "".join(word_list)
|
||||
if newWord == endWord:
|
||||
return path+1
|
||||
if newWord in wordSet and newWord not in mapping:
|
||||
mapping[newWord] = path+1
|
||||
queue.append(newWord)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,9 +3,12 @@
|
||||
<img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20210924105952.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -245,6 +248,29 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
|
||||
sum = 0
|
||||
travel(root, root.Val)
|
||||
return sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func travel(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int) {
|
||||
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
|
||||
sum += tmpSum
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if root.Left != nil {
|
||||
travel(root.Left, tmpSum*10+root.Left.Val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if root.Right != nil {
|
||||
travel(root.Right, tmpSum*10+root.Right.Val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
|
||||
@@ -289,7 +315,40 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||||
if (root === null) return 0;
|
||||
let resTotal: number = 0;
|
||||
const route: number[] = [];
|
||||
route.push(root.val);
|
||||
recur(root, route);
|
||||
return resTotal;
|
||||
function recur(node: TreeNode, route: number[]): void {
|
||||
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
|
||||
resTotal += listToSum(route);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node.left !== null) {
|
||||
route.push(node.left.val);
|
||||
recur(node.left, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
};
|
||||
if (node.right !== null) {
|
||||
route.push(node.right.val);
|
||||
recur(node.right, route);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
function listToSum(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
return Number(nums.join(''));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//sum记录总和
|
||||
int sum;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 131.分割回文串
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -206,6 +206,65 @@ public:
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 优化
|
||||
|
||||
上面的代码还存在一定的优化空间, 在于如何更高效的计算一个子字符串是否是回文字串。上述代码```isPalindrome```函数运用双指针的方法来判定对于一个字符串```s```, 给定起始下标和终止下标, 截取出的子字符串是否是回文字串。但是其中有一定的重复计算存在:
|
||||
|
||||
例如给定字符串```"abcde"```, 在已知```"bcd"```不是回文字串时, 不再需要去双指针操作```"abcde"```而可以直接判定它一定不是回文字串。
|
||||
|
||||
具体来说, 给定一个字符串`s`, 长度为```n```, 它成为回文字串的充分必要条件是```s[0] == s[n-1]```且```s[1:n-1]```是回文字串。
|
||||
|
||||
大家如果熟悉动态规划这种算法的话, 我们可以高效地事先一次性计算出, 针对一个字符串```s```, 它的任何子串是否是回文字串, 然后在我们的回溯函数中直接查询即可, 省去了双指针移动判定这一步骤.
|
||||
|
||||
具体参考代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
vector<vector<string>> result;
|
||||
vector<string> path; // 放已经回文的子串
|
||||
vector<vector<bool>> isPalindrome; // 放事先计算好的是否回文子串的结果
|
||||
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
|
||||
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
|
||||
if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
|
||||
result.push_back(path);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
|
||||
if (isPalindrome[startIndex][i]) { // 是回文子串
|
||||
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
|
||||
string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
|
||||
path.push_back(str);
|
||||
} else { // 不是回文,跳过
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
|
||||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在的子串
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void computePalindrome(const string& s) {
|
||||
// isPalindrome[i][j] 代表 s[i:j](双边包括)是否是回文字串
|
||||
isPalindrome.resize(s.size(), vector<bool>(s.size(), false)); // 根据字符串s, 刷新布尔矩阵的大小
|
||||
for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||||
// 需要倒序计算, 保证在i行时, i+1行已经计算好了
|
||||
for (int j = i; j < s.size(); j++) {
|
||||
if (j == i) {isPalindrome[i][j] = true;}
|
||||
else if (j - i == 1) {isPalindrome[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j]);}
|
||||
else {isPalindrome[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j] && isPalindrome[i+1][j-1]);}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
|
||||
result.clear();
|
||||
path.clear();
|
||||
computePalindrome(s);
|
||||
backtracking(s, 0);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 总结
|
||||
@@ -442,7 +501,7 @@ var partition = function(s) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(let j = i; j < len; j++) {
|
||||
if(!isPalindrome(s, i, j)) continue;
|
||||
path.push(s.substr(i, j - i + 1));
|
||||
path.push(s.slice(i, j + 1));
|
||||
backtracking(j + 1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -450,6 +509,43 @@ var partition = function(s) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function partition(s: string): string[][] {
|
||||
const res: string[][] = []
|
||||
const path: string[] = []
|
||||
const isHuiwen = (
|
||||
str: string,
|
||||
startIndex: number,
|
||||
endIndex: number
|
||||
): boolean => {
|
||||
for (; startIndex < endIndex; startIndex++, endIndex--) {
|
||||
if (str[startIndex] !== str[endIndex]) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
const rec = (str: string, index: number): void => {
|
||||
if (index >= str.length) {
|
||||
res.push([...path])
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = index; i < str.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (!isHuiwen(str, index, i)) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
path.push(str.substring(index, i + 1))
|
||||
rec(str, i + 1)
|
||||
path.pop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
rec(s, 0)
|
||||
return res
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -589,7 +685,8 @@ func partition(_ s: String) -> [[String]] {
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
**回溯+函数判断回文串**
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn partition(s: String) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
|
||||
let mut ret = vec![];
|
||||
@@ -639,5 +736,84 @@ impl Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
**回溯+动态规划预处理判断回文串**
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn backtracking(is_palindrome: &Vec<Vec<bool>>, result: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>, path: &mut Vec<String>, s: &Vec<char>, start_index: usize) {
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
if start_index >= len {
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in start_index..len {
|
||||
if is_palindrome[start_index][i] { path.push(s[start_index..=i].iter().collect::<String>()); } else { continue; }
|
||||
Self::backtracking(is_palindrome, result, path, s, i + 1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn partition(s: String) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let s = s.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>();
|
||||
let len: usize = s.len();
|
||||
// 使用动态规划预先打表
|
||||
// 当且仅当其为空串(i>j),或其长度为1(i=j),或者首尾字符相同且(s[i+1..j−1])时为回文串
|
||||
let mut is_palindrome = vec![vec![true; len]; len];
|
||||
for i in (0..len).rev() {
|
||||
for j in (i + 1)..len {
|
||||
is_palindrome[i][j] = s[i] == s[j] && is_palindrome[i + 1][j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&is_palindrome, &mut result, &mut path, &s, 0);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
||||
def partition(s: String): List[List[String]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[String]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断字符串是否回文
|
||||
def isPalindrome(start: Int, end: Int): Boolean = {
|
||||
var (left, right) = (start, end)
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
if (s(left) != s(right)) return false
|
||||
left += 1
|
||||
right -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 回溯算法
|
||||
def backtracking(startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (startIndex >= s.size) {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 添加循环守卫,如果当前分割是回文子串则进入回溯
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex until s.size if isPalindrome(startIndex, i)) {
|
||||
path.append(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1))
|
||||
backtracking(i + 1)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(0)
|
||||
result.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 132. 分割回文串 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -206,6 +206,55 @@ public:
|
||||
## Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
public int minCut(String s) {
|
||||
if(null == s || "".equals(s)){
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int len = s.length();
|
||||
// 1.
|
||||
// 记录子串[i..j]是否是回文串
|
||||
boolean[][] isPalindromic = new boolean[len][len];
|
||||
// 从下到上,从左到右
|
||||
for(int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--){
|
||||
for(int j = i; j < len; j++){
|
||||
if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){
|
||||
if(j - i <= 1){
|
||||
isPalindromic[i][j] = true;
|
||||
} else{
|
||||
isPalindromic[i][j] = isPalindromic[i + 1][j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else{
|
||||
isPalindromic[i][j] = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 2.
|
||||
// dp[i] 表示[0..i]的最小分割次数
|
||||
int[] dp = new int[len];
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
|
||||
//初始考虑最坏的情况。 1个字符分割0次, len个字符分割 len - 1次
|
||||
dp[i] = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++){
|
||||
if(isPalindromic[0][i]){
|
||||
// s[0..i]是回文了,那 dp[i] = 0, 一次也不用分割
|
||||
dp[i] = 0;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
|
||||
// 按文中的思路,不清楚就拿 "ababa" 为例,先写出 isPalindromic 数组,再进行求解
|
||||
if(isPalindromic[j + 1][i]){
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[len - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
@@ -240,6 +289,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 134. 加油站
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gas-station/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/gas-station/)
|
||||
|
||||
在一条环路上有 N 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -77,10 +77,9 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
C++暴力解法在leetcode上提交也可以过。
|
||||
|
||||
## 贪心算法(方法一)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -235,10 +234,34 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
return index;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 解法1
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
n = len(gas)
|
||||
cur_sum = 0
|
||||
min_sum = float('inf')
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(n):
|
||||
cur_sum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||||
min_sum = min(min_sum, cur_sum)
|
||||
|
||||
if cur_sum < 0: return -1
|
||||
if min_sum >= 0: return 0
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
|
||||
min_sum += gas[j] - cost[j]
|
||||
if min_sum >= 0:
|
||||
return j
|
||||
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 解法2
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
start = 0
|
||||
@@ -340,7 +363,102 @@ var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
**暴力法:**
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function canCompleteCircuit(gas: number[], cost: number[]): number {
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = gas.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let curSum: number = 0;
|
||||
let index: number = i;
|
||||
while (curSum >= 0 && index < i + length) {
|
||||
let tempIndex: number = index % length;
|
||||
curSum += gas[tempIndex] - cost[tempIndex];
|
||||
index++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (index === i + length && curSum >= 0) return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**解法二:**
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function canCompleteCircuit(gas: number[], cost: number[]): number {
|
||||
let total: number = 0;
|
||||
let curGas: number = 0;
|
||||
let tempDiff: number = 0;
|
||||
let resIndex: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = gas.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
tempDiff = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
total += tempDiff;
|
||||
curGas += tempDiff;
|
||||
if (curGas < 0) {
|
||||
resIndex = i + 1;
|
||||
curGas = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (total < 0) return -1;
|
||||
return resIndex;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法:方法一
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn can_complete_circuit(gas: Vec<i32>, cost: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut cur_sum = 0;
|
||||
let mut min = i32::MAX;
|
||||
for i in 0..gas.len() {
|
||||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
cur_sum += rest;
|
||||
if cur_sum < min { min = cur_sum; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cur_sum < 0 { return -1; }
|
||||
if min > 0 { return 0; }
|
||||
for i in (0..gas.len()).rev() {
|
||||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
min += rest;
|
||||
if min >= 0 { return i as i32; }
|
||||
}
|
||||
-1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法:方法二
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn can_complete_circuit(gas: Vec<i32>, cost: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut cur_sum = 0;
|
||||
let mut total_sum = 0;
|
||||
let mut start = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..gas.len() {
|
||||
cur_sum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
total_sum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
if cur_sum < 0 {
|
||||
start = i + 1;
|
||||
cur_sum = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if total_sum < 0 { return -1; }
|
||||
start as i32
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法:方法一
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int canCompleteCircuit(int* gas, int gasSize, int* cost, int costSize){
|
||||
int curSum = 0;
|
||||
@@ -370,5 +488,104 @@ int canCompleteCircuit(int* gas, int gasSize, int* cost, int costSize){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法:方法二
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int canCompleteCircuit(int* gas, int gasSize, int* cost, int costSize){
|
||||
int curSum = 0;
|
||||
int totalSum = 0;
|
||||
int start = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < gasSize; ++i) {
|
||||
// 当前i站中加油量与耗油量的差
|
||||
int diff = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||||
|
||||
curSum += diff;
|
||||
totalSum += diff;
|
||||
|
||||
// 若0到i的加油量都为负,则开始位置应为i+1
|
||||
if(curSum < 0) {
|
||||
curSum = 0;
|
||||
// 当i + 1 == gasSize时,totalSum < 0(此时i为gasSize - 1),油车不可能返回原点
|
||||
start = i + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 若总和小于0,加油车无论如何都无法返回原点。返回-1
|
||||
if(totalSum < 0)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
return start;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
暴力解法:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
for (i <- cost.indices) {
|
||||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||||
var index = (i + 1) % cost.length // index为i的下一个节点
|
||||
while (rest > 0 && i != index) {
|
||||
rest += (gas(index) - cost(index))
|
||||
index = (index + 1) % cost.length
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (rest >= 0 && index == i) return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
-1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法,方法一:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var curSum = 0
|
||||
var min = Int.MaxValue
|
||||
for (i <- gas.indices) {
|
||||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||||
curSum += rest
|
||||
min = math.min(min, curSum)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (curSum < 0) return -1 // 情况1: gas的总和小于cost的总和,不可能到达终点
|
||||
if (min >= 0) return 0 // 情况2: 最小值>=0,从0号出发可以直接到达
|
||||
// 情况3: min为负值,从后向前看,能把min填平的节点就是出发节点
|
||||
for (i <- gas.length - 1 to 0 by -1) {
|
||||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||||
min += rest
|
||||
if (min >= 0) return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
-1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
贪心算法,方法二:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var curSum = 0
|
||||
var totalSum = 0
|
||||
var start = 0
|
||||
for (i <- gas.indices) {
|
||||
curSum += (gas(i) - cost(i))
|
||||
totalSum += (gas(i) - cost(i))
|
||||
if (curSum < 0) {
|
||||
start = i + 1 // 起始位置更新
|
||||
curSum = 0 // curSum从0开始
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (totalSum < 0) return -1 // 说明怎么走不可能跑一圈
|
||||
start
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 135. 分发糖果
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/candy/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/candy/)
|
||||
|
||||
老师想给孩子们分发糖果,有 N 个孩子站成了一条直线,老师会根据每个孩子的表现,预先给他们评分。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -126,11 +126,11 @@ public:
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
分两个阶段
|
||||
/**
|
||||
分两个阶段
|
||||
1、起点下标1 从左往右,只要 右边 比 左边 大,右边的糖果=左边 + 1
|
||||
2、起点下标 ratings.length - 2 从右往左, 只要左边 比 右边 大,此时 左边的糖果应该 取本身的糖果数(符合比它左边大) 和 右边糖果数 + 1 二者的最大值,这样才符合 它比它左边的大,也比它右边大
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def candy(self, ratings: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
@@ -213,6 +213,25 @@ func findMax(num1 int ,num2 int) int{
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn candy(ratings: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut candies = vec![1i32; ratings.len()];
|
||||
for i in 1..ratings.len() {
|
||||
if ratings[i - 1] < ratings[i] {
|
||||
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i in (0..ratings.len()-1).rev() {
|
||||
if ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1] {
|
||||
candies[i] = candies[i].max(candies[i + 1] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
candies.iter().sum()
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript:
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var candy = function(ratings) {
|
||||
@@ -229,7 +248,7 @@ var candy = function(ratings) {
|
||||
candys[i] = Math.max(candys[i], candys[i + 1] + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
let count = candys.reduce((a, b) => {
|
||||
return a + b
|
||||
})
|
||||
@@ -239,5 +258,98 @@ var candy = function(ratings) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
```c
|
||||
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
|
||||
|
||||
int *initCandyArr(int size) {
|
||||
int *candyArr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < size; ++i)
|
||||
candyArr[i] = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
return candyArr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int candy(int* ratings, int ratingsSize){
|
||||
// 初始化数组,每个小孩开始至少有一颗糖
|
||||
int *candyArr = initCandyArr(ratingsSize);
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
// 先判断右边是否比左边评分高。若是,右边孩子的糖果为左边孩子+1(candyArr[i] = candyArr[i - 1] + 1)
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < ratingsSize; ++i) {
|
||||
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1])
|
||||
candyArr[i] = candyArr[i - 1] + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 再判断左边评分是否比右边高。
|
||||
// 若是,左边孩子糖果为右边孩子糖果+1/自己所持糖果最大值。(若糖果已经比右孩子+1多,则不需要更多糖果)
|
||||
// 举例:ratings为[1, 2, 3, 1]。此时评分为3的孩子在判断右边比左边大后为3,虽然它比最末尾的1(ratings[3])大,但是candyArr[3]为1。所以不必更新candyArr[2]
|
||||
for(i = ratingsSize - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
|
||||
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1])
|
||||
candyArr[i] = max(candyArr[i], candyArr[i + 1] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 求出糖果之和
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < ratingsSize; ++i) {
|
||||
result += candyArr[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function candy(ratings: number[]): number {
|
||||
const candies: number[] = [];
|
||||
candies[0] = 1;
|
||||
// 保证右边高分孩子一定比左边低分孩子发更多的糖果
|
||||
for (let i = 1, length = ratings.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) {
|
||||
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
candies[i] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 保证左边高分孩子一定比右边低分孩子发更多的糖果
|
||||
for (let i = ratings.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||||
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) {
|
||||
candies[i] = Math.max(candies[i], candies[i + 1] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return candies.reduce((pre, cur) => pre + cur);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def candy(ratings: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var candyVec = new Array[Int](ratings.length)
|
||||
for (i <- candyVec.indices) candyVec(i) = 1
|
||||
// 从前向后
|
||||
for (i <- 1 until candyVec.length) {
|
||||
if (ratings(i) > ratings(i - 1)) {
|
||||
candyVec(i) = candyVec(i - 1) + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 从后向前
|
||||
for (i <- (candyVec.length - 2) to 0 by -1) {
|
||||
if (ratings(i) > ratings(i + 1)) {
|
||||
candyVec(i) = math.max(candyVec(i), candyVec(i + 1) + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
candyVec.sum // 求和
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 139.单词拆分
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-break/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词的列表 wordDict,判定 s 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -207,7 +207,7 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^3),因为substr返回子串的副本是$O(n)$的复杂度(这里的n是substring的长度)
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^3),因为substr返回子串的副本是O(n)的复杂度(这里的n是substring的长度)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -345,6 +345,48 @@ const wordBreak = (s, wordDict) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 动态规划
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function wordBreak(s: string, wordDict: string[]): boolean {
|
||||
const dp: boolean[] = new Array(s.length + 1).fill(false);
|
||||
dp[0] = true;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= s.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
|
||||
const tempStr: string = s.slice(j, i);
|
||||
if (wordDict.includes(tempStr) && dp[j] === true) {
|
||||
dp[i] = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[s.length];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 记忆化回溯
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function wordBreak(s: string, wordDict: string[]): boolean {
|
||||
// 只需要记忆结果为false的情况
|
||||
const memory: boolean[] = [];
|
||||
return backTracking(s, wordDict, 0, memory);
|
||||
function backTracking(s: string, wordDict: string[], startIndex: number, memory: boolean[]): boolean {
|
||||
if (startIndex >= s.length) return true;
|
||||
if (memory[startIndex] === false) return false;
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex + 1, length = s.length; i <= length; i++) {
|
||||
const str: string = s.slice(startIndex, i);
|
||||
if (wordDict.includes(str) && backTracking(s, wordDict, i, memory))
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
memory[startIndex] = false;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 141. 环形链表
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/submissions/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
|
||||
|
||||
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
|
||||
@@ -103,9 +105,24 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func hasCycle(head *ListNode) bool {
|
||||
if head==nil{
|
||||
return false
|
||||
} //空链表一定不会有环
|
||||
fast:=head
|
||||
slow:=head //快慢指针
|
||||
for fast.Next!=nil&&fast.Next.Next!=nil{
|
||||
fast=fast.Next.Next
|
||||
slow=slow.Next
|
||||
if fast==slow{
|
||||
return true //快慢指针相遇则有环
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
@@ -124,6 +141,23 @@ var hasCycle = function(head) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
let slowNode: ListNode | null = head,
|
||||
fastNode: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
while (fastNode !== null && fastNode.next !== null) {
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode!.next;
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
|
||||
if (slowNode === fastNode) return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 142.环形链表II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
题意:
|
||||
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
|
||||
@@ -24,6 +24,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法公开课:[把环形链表讲清楚!| LeetCode:142.环形链表II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1if4y1d7ob),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目,不仅考察对链表的操作,而且还需要一些数学运算。
|
||||
|
||||
主要考察两知识点:
|
||||
@@ -301,13 +304,13 @@ function detectCycle(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let slowNode: ListNode | null = head,
|
||||
fastNode: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
while (fastNode !== null && fastNode.next !== null) {
|
||||
slowNode = (slowNode as ListNode).next;
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode!.next;
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
|
||||
if (slowNode === fastNode) {
|
||||
slowNode = head;
|
||||
while (slowNode !== fastNode) {
|
||||
slowNode = (slowNode as ListNode).next;
|
||||
fastNode = (fastNode as ListNode).next;
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode!.next;
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode!.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return slowNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -370,7 +373,31 @@ ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def detectCycle(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
var fast = head // 快指针
|
||||
var slow = head // 慢指针
|
||||
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next // 快指针一次走两步
|
||||
slow = slow.next // 慢指针一次走一步
|
||||
// 如果相遇,fast快指针回到头
|
||||
if (fast == slow) {
|
||||
fast = head
|
||||
// 两个指针一步一步的走,第一次相遇的节点必是入环节点
|
||||
while (fast != slow) {
|
||||
fast = fast.next
|
||||
slow = slow.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fast
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果fast指向空值,必然无环返回null
|
||||
null
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 143.重排链表
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reorder-list/submissions/)
|
||||
|
||||
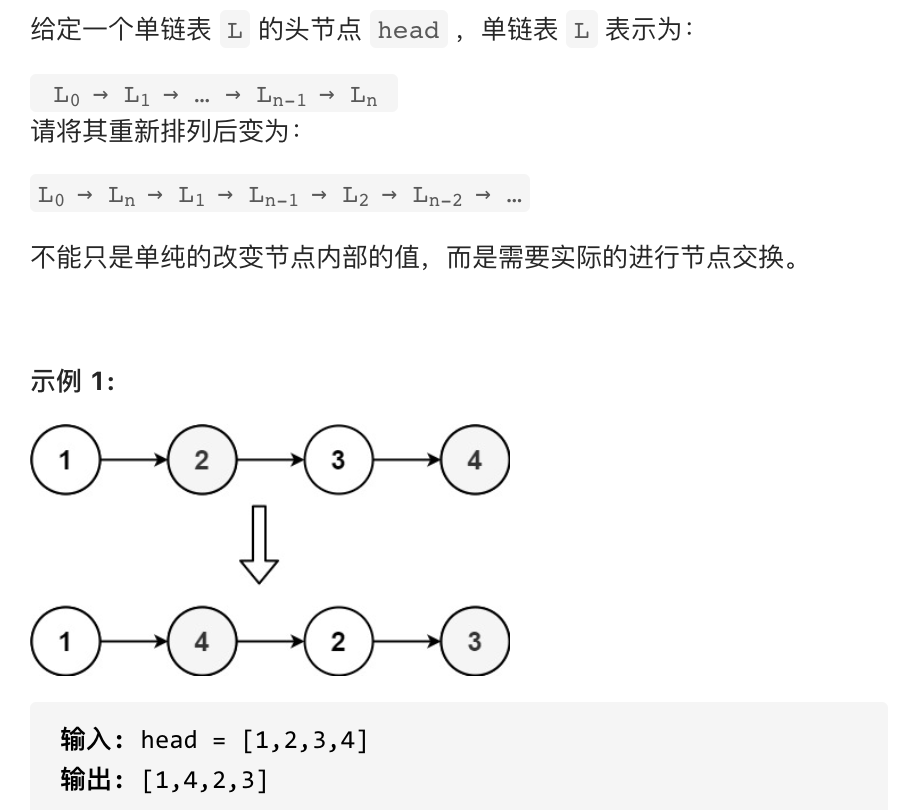
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
@@ -336,7 +338,33 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return pre
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
# 方法三 分割链表
|
||||
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
|
||||
var slow=head
|
||||
var fast=head
|
||||
for fast!=nil&&fast.Next!=nil{
|
||||
slow=slow.Next
|
||||
fast=fast.Next.Next
|
||||
} //双指针将链表分为左右两部分
|
||||
var right =new(ListNode)
|
||||
for slow!=nil{
|
||||
temp:=slow.Next
|
||||
slow.Next=right.Next
|
||||
right.Next=slow
|
||||
slow=temp
|
||||
} //翻转链表右半部分
|
||||
right=right.Next //right为反转后得右半部分
|
||||
h:=head
|
||||
for right.Next!=nil{
|
||||
temp:=right.Next
|
||||
right.Next=h.Next
|
||||
h.Next=right
|
||||
h=h.Next.Next
|
||||
right=temp
|
||||
} //将左右两部分重新组合
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
@@ -439,7 +467,81 @@ var reorderList = function(head, s = [], tmp) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 辅助数组法:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function reorderList(head: ListNode | null): void {
|
||||
if (head === null) return;
|
||||
const helperArr: ListNode[] = [];
|
||||
let curNode: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
while (curNode !== null) {
|
||||
helperArr.push(curNode);
|
||||
curNode = curNode.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let node: ListNode = head;
|
||||
let left: number = 1,
|
||||
right: number = helperArr.length - 1;
|
||||
let count: number = 0;
|
||||
while (left <= right) {
|
||||
if (count % 2 === 0) {
|
||||
node.next = helperArr[right--];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
node.next = helperArr[left++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
node = node.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
node.next = null;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 分割链表法:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function reorderList(head: ListNode | null): void {
|
||||
if (head === null || head.next === null) return;
|
||||
let fastNode: ListNode = head,
|
||||
slowNode: ListNode = head;
|
||||
while (fastNode.next !== null && fastNode.next.next !== null) {
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let head1: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
// 反转后半部分链表
|
||||
let head2: ListNode | null = reverseList(slowNode.next);
|
||||
// 分割链表
|
||||
slowNode.next = null;
|
||||
/**
|
||||
直接在head1链表上进行插入
|
||||
head1 链表长度一定大于或等于head2,
|
||||
因此在下面的循环中,只要head2不为null, head1 一定不为null
|
||||
*/
|
||||
while (head2 !== null) {
|
||||
const tempNode1: ListNode | null = head1!.next,
|
||||
tempNode2: ListNode | null = head2.next;
|
||||
head1!.next = head2;
|
||||
head2.next = tempNode1;
|
||||
head1 = tempNode1;
|
||||
head2 = tempNode2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let curNode: ListNode | null = head,
|
||||
preNode: ListNode | null = null;
|
||||
while (curNode !== null) {
|
||||
const tempNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next;
|
||||
curNode.next = preNode;
|
||||
preNode = curNode;
|
||||
curNode = tempNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return preNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
方法三:反转链表
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//翻转链表
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
|
||||
|
||||
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -65,6 +65,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[栈的最后表演! | LeetCode:150. 逆波兰表达式求值](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1kd4y1o7on),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
在上一篇文章中[1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](https://programmercarl.com/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.html)提到了 递归就是用栈来实现的。
|
||||
|
||||
所以**栈与递归之间在某种程度上是可以转换的!** 这一点我们在后续讲解二叉树的时候,会更详细的讲解到。
|
||||
@@ -109,7 +111,7 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 题外话
|
||||
## 题外话
|
||||
|
||||
我们习惯看到的表达式都是中缀表达式,因为符合我们的习惯,但是中缀表达式对于计算机来说就不是很友好了。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,7 +130,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 其他语言版本
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
java:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -136,19 +138,19 @@ java:
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
|
||||
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList();
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; ++i) {
|
||||
if ("+".equals(tokens[i])) { // leetcode 内置jdk的问题,不能使用==判断字符串是否相等
|
||||
for (String s : tokens) {
|
||||
if ("+".equals(s)) { // leetcode 内置jdk的问题,不能使用==判断字符串是否相等
|
||||
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop()); // 注意 - 和/ 需要特殊处理
|
||||
} else if ("-".equals(tokens[i])) {
|
||||
} else if ("-".equals(s)) {
|
||||
stack.push(-stack.pop() + stack.pop());
|
||||
} else if ("*".equals(tokens[i])) {
|
||||
} else if ("*".equals(s)) {
|
||||
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
|
||||
} else if ("/".equals(tokens[i])) {
|
||||
} else if ("/".equals(s)) {
|
||||
int temp1 = stack.pop();
|
||||
int temp2 = stack.pop();
|
||||
stack.push(temp2 / temp1);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(tokens[i]));
|
||||
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(s));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return stack.pop();
|
||||
@@ -326,5 +328,94 @@ func evalRPN(_ tokens: [String]) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public int EvalRPN(string[] tokens) {
|
||||
int num;
|
||||
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
|
||||
foreach(string s in tokens){
|
||||
if(int.TryParse(s, out num)){
|
||||
stack.Push(num);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
int num1 = stack.Pop();
|
||||
int num2 = stack.Pop();
|
||||
switch (s)
|
||||
{
|
||||
case "+":
|
||||
stack.Push(num1 + num2);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case "-":
|
||||
stack.Push(num2 - num1);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case "*":
|
||||
stack.Push(num1 * num2);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case "/":
|
||||
stack.Push(num2 / num1);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return stack.Pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
function evalRPN($tokens) {
|
||||
$st = new SplStack();
|
||||
for($i = 0;$i<count($tokens);$i++){
|
||||
// 是数字直接入栈
|
||||
if(is_numeric($tokens[$i])){
|
||||
$st->push($tokens[$i]);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
// 是符号进行运算
|
||||
$num1 = $st->pop();
|
||||
$num2 = $st->pop();
|
||||
if ($tokens[$i] == "+") $st->push($num2 + $num1);
|
||||
if ($tokens[$i] == "-") $st->push($num2 - $num1);
|
||||
if ($tokens[$i] == "*") $st->push($num2 * $num1);
|
||||
// 注意处理小数部分
|
||||
if ($tokens[$i] == "/") $st->push(intval($num2 / $num1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $st->pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def evalRPN(tokens: Array[String]): Int = {
|
||||
val stack = mutable.Stack[Int]() // 定义栈
|
||||
// 抽取运算操作,需要传递x,y,和一个函数
|
||||
def operator(x: Int, y: Int, f: (Int, Int) => Int): Int = f(x, y)
|
||||
for (token <- tokens) {
|
||||
// 模式匹配,匹配不同的操作符做什么样的运算
|
||||
token match {
|
||||
// 最后一个参数 _+_,代表x+y,遵循Scala的函数至简原则,以下运算同理
|
||||
case "+" => stack.push(operator(stack.pop(), stack.pop(), _ + _))
|
||||
case "-" => stack.push(operator(stack.pop(), stack.pop(), -_ + _))
|
||||
case "*" => stack.push(operator(stack.pop(), stack.pop(), _ * _))
|
||||
case "/" => {
|
||||
var pop1 = stack.pop()
|
||||
var pop2 = stack.pop()
|
||||
stack.push(operator(pop2, pop1, _ / _))
|
||||
}
|
||||
case _ => stack.push(token.toInt) // 不是运算符就入栈
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最后返回栈顶,不需要加return关键字
|
||||
stack.pop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 151.翻转字符串里的单词
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个字符串,逐个翻转字符串中的每个单词。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,8 +31,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
**这道题目可以说是综合考察了字符串的多种操作。**
|
||||
针对本题,我录制了视频讲解:[字符串复杂操作拿捏了! | LeetCode:151.翻转字符串里的单词](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uT41177fX),结合本题解一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
**这道题目可以说是综合考察了字符串的多种操作。**
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学会使用split库函数,分隔单词,然后定义一个新的string字符串,最后再把单词倒序相加,那么这道题题目就是一道水题了,失去了它的意义。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,19 +80,16 @@ void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {
|
||||
|
||||
逻辑很简单,从前向后遍历,遇到空格了就erase。
|
||||
|
||||
如果不仔细琢磨一下erase的时间复杂读,还以为以上的代码是$O(n)$的时间复杂度呢。
|
||||
如果不仔细琢磨一下erase的时间复杂度,还以为以上的代码是O(n)的时间复杂度呢。
|
||||
|
||||
想一下真正的时间复杂度是多少,一个erase本来就是O(n)的操作,erase实现原理题目:[数组:就移除个元素很难么?](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html),最优的算法来移除元素也要O(n)。
|
||||
想一下真正的时间复杂度是多少,一个erase本来就是O(n)的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
erase操作上面还套了一个for循环,那么以上代码移除冗余空格的代码时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
|
||||
|
||||
那么使用双指针法来去移除空格,最后resize(重新设置)一下字符串的大小,就可以做到O(n)的时间复杂度。
|
||||
|
||||
如果对这个操作比较生疏了,可以再看一下这篇文章:[数组:就移除个元素很难么?](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html)是如何移除元素的。
|
||||
|
||||
那么使用双指针来移除冗余空格代码如下: fastIndex走的快,slowIndex走的慢,最后slowIndex就标记着移除多余空格后新字符串的长度。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
//版本一
|
||||
void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {
|
||||
int slowIndex = 0, fastIndex = 0; // 定义快指针,慢指针
|
||||
// 去掉字符串前面的空格
|
||||
@@ -121,13 +119,37 @@ void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {
|
||||
1. leetcode上的测试集里,字符串的长度不够长,如果足够长,性能差距会非常明显。
|
||||
2. leetcode的测程序耗时不是很准确的。
|
||||
|
||||
版本一的代码是比较如何一般思考过程,就是 先移除字符串钱的空格,在移除中间的,在移除后面部分。
|
||||
|
||||
不过其实还可以优化,这部分和[27.移除元素](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html)的逻辑是一样一样的,本题是移除空格,而 27.移除元素 就是移除元素。
|
||||
|
||||
所以代码可以写的很精简,大家可以看 如下 代码 removeExtraSpaces 函数的实现:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 版本二
|
||||
void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {//去除所有空格并在相邻单词之间添加空格, 快慢指针。
|
||||
int slow = 0; //整体思想参考https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) { //
|
||||
if (s[i] != ' ') { //遇到非空格就处理,即删除所有空格。
|
||||
if (slow != 0) s[slow++] = ' '; //手动控制空格,给单词之间添加空格。slow != 0说明不是第一个单词,需要在单词前添加空格。
|
||||
while (i < s.size() && s[i] != ' ') { //补上该单词,遇到空格说明单词结束。
|
||||
s[slow++] = s[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.resize(slow); //slow的大小即为去除多余空格后的大小。
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果以上代码看不懂,建议先把 [27.移除元素](https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html)这道题目做了,或者看视频讲解:[数组中移除元素并不容易!LeetCode:27. 移除元素](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12A4y1Z7LP) 。
|
||||
|
||||
此时我们已经实现了removeExtraSpaces函数来移除冗余空格。
|
||||
|
||||
还做实现反转字符串的功能,支持反转字符串子区间,这个实现我们分别在[344.反转字符串](https://programmercarl.com/0344.反转字符串.html)和[541.反转字符串II](https://programmercarl.com/0541.反转字符串II.html)里已经讲过了。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 反转字符串s中左闭又闭的区间[start, end]
|
||||
void reverse(string& s, int start, int end) {
|
||||
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
|
||||
@@ -136,93 +158,45 @@ void reverse(string& s, int start, int end) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
本题C++整体代码
|
||||
|
||||
整体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 版本一
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// 反转字符串s中左闭又闭的区间[start, end]
|
||||
void reverse(string& s, int start, int end) {
|
||||
void reverse(string& s, int start, int end){ //翻转,区间写法:左闭又闭 []
|
||||
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
|
||||
swap(s[i], s[j]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 移除冗余空格:使用双指针(快慢指针法)O(n)的算法
|
||||
void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {
|
||||
int slowIndex = 0, fastIndex = 0; // 定义快指针,慢指针
|
||||
// 去掉字符串前面的空格
|
||||
while (s.size() > 0 && fastIndex < s.size() && s[fastIndex] == ' ') {
|
||||
fastIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (; fastIndex < s.size(); fastIndex++) {
|
||||
// 去掉字符串中间部分的冗余空格
|
||||
if (fastIndex - 1 > 0
|
||||
&& s[fastIndex - 1] == s[fastIndex]
|
||||
&& s[fastIndex] == ' ') {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s[slowIndex++] = s[fastIndex];
|
||||
void removeExtraSpaces(string& s) {//去除所有空格并在相邻单词之间添加空格, 快慢指针。
|
||||
int slow = 0; //整体思想参考https://programmercarl.com/0027.移除元素.html
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) { //
|
||||
if (s[i] != ' ') { //遇到非空格就处理,即删除所有空格。
|
||||
if (slow != 0) s[slow++] = ' '; //手动控制空格,给单词之间添加空格。slow != 0说明不是第一个单词,需要在单词前添加空格。
|
||||
while (i < s.size() && s[i] != ' ') { //补上该单词,遇到空格说明单词结束。
|
||||
s[slow++] = s[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (slowIndex - 1 > 0 && s[slowIndex - 1] == ' ') { // 去掉字符串末尾的空格
|
||||
s.resize(slowIndex - 1);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.resize(slowIndex); // 重新设置字符串大小
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.resize(slow); //slow的大小即为去除多余空格后的大小。
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
string reverseWords(string s) {
|
||||
removeExtraSpaces(s); // 去掉冗余空格
|
||||
reverse(s, 0, s.size() - 1); // 将字符串全部反转
|
||||
int start = 0; // 反转的单词在字符串里起始位置
|
||||
int end = 0; // 反转的单词在字符串里终止位置
|
||||
bool entry = false; // 标记枚举字符串的过程中是否已经进入了单词区间
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 开始反转单词
|
||||
if (!entry) {
|
||||
start = i; // 确定单词起始位置
|
||||
entry = true; // 进入单词区间
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 单词后面有空格的情况,空格就是分词符
|
||||
if (entry && s[i] == ' ' && s[i - 1] != ' ') {
|
||||
end = i - 1; // 确定单词终止位置
|
||||
entry = false; // 结束单词区间
|
||||
reverse(s, start, end);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最后一个结尾单词之后没有空格的情况
|
||||
if (entry && (i == (s.size() - 1)) && s[i] != ' ' ) {
|
||||
end = i;// 确定单词终止位置
|
||||
entry = false; // 结束单词区间
|
||||
reverse(s, start, end);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 当然这里的主函数reverseWords写的有一些冗余的,可以精简一些,精简之后的主函数为:
|
||||
/* 主函数简单写法
|
||||
string reverseWords(string s) {
|
||||
removeExtraSpaces(s);
|
||||
removeExtraSpaces(s); //去除多余空格,保证单词之间之只有一个空格,且字符串首尾没空格。
|
||||
reverse(s, 0, s.size() - 1);
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
|
||||
int j = i;
|
||||
// 查找单词间的空格,翻转单词
|
||||
while(j < s.size() && s[j] != ' ') j++;
|
||||
reverse(s, i, j - 1);
|
||||
i = j;
|
||||
int start = 0; //removeExtraSpaces后保证第一个单词的开始下标一定是0。
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i <= s.size(); ++i) {
|
||||
if (i == s.size() || s[i] == ' ') { //到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
|
||||
reverse(s, start, i - 1); //翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
|
||||
start = i + 1; //更新下一个单词的开始下标start
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
效率:
|
||||
<img src='https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/151_翻转字符串里的单词.png' width=600> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -721,10 +695,164 @@ func reverseWord(_ s: inout [Character]) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def reverseWords(s: String): String = {
|
||||
var sb = removeSpace(s) // 移除多余的空格
|
||||
reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length - 1) // 翻转字符串
|
||||
reverseEachWord(sb)
|
||||
sb.mkString
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 移除多余的空格
|
||||
def removeSpace(s: String): Array[Char] = {
|
||||
var start = 0
|
||||
var end = s.length - 1
|
||||
// 移除字符串前面的空格
|
||||
while (start < s.length && s(start) == ' ') start += 1
|
||||
// 移除字符串后面的空格
|
||||
while (end >= 0 && s(end) == ' ') end -= 1
|
||||
var sb = "" // String
|
||||
// 当start小于等于end的时候,执行添加操作
|
||||
while (start <= end) {
|
||||
var c = s(start)
|
||||
// 当前字符不等于空,sb的最后一个字符不等于空的时候添加到sb
|
||||
if (c != ' ' || sb(sb.length - 1) != ' ') {
|
||||
sb ++= c.toString
|
||||
}
|
||||
start += 1 // 指针向右移动
|
||||
}
|
||||
sb.toArray
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 翻转字符串
|
||||
def reverseString(s: Array[Char], start: Int, end: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
var (left, right) = (start, end)
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
var tmp = s(left)
|
||||
s(left) = s(right)
|
||||
s(right) = tmp
|
||||
left += 1
|
||||
right -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 翻转每个单词
|
||||
def reverseEachWord(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
|
||||
var i = 0
|
||||
while (i < s.length) {
|
||||
var j = i + 1
|
||||
// 向后迭代寻找每个单词的坐标
|
||||
while (j < s.length && s(j) != ' ') j += 1
|
||||
reverseString(s, i, j - 1) // 翻转每个单词
|
||||
i = j + 1 // i往后更新
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
function reverseWords($s) {
|
||||
$this->removeExtraSpaces($s);
|
||||
$this->reverseString($s, 0, strlen($s)-1);
|
||||
// 将每个单词反转
|
||||
$start = 0;
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i <= strlen($s); $i++) {
|
||||
// 到达空格或者串尾,说明一个单词结束。进行翻转。
|
||||
if ($i == strlen($s) || $s[$i] == ' ') {
|
||||
// 翻转,注意是左闭右闭 []的翻转。
|
||||
$this->reverseString($s, $start, $i-1);
|
||||
// +1: 单词与单词直接有个空格
|
||||
$start = $i + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $s;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 移除多余空格
|
||||
function removeExtraSpaces(&$s){
|
||||
$slow = 0;
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($s); $i++) {
|
||||
if ($s[$i] != ' ') {
|
||||
if ($slow != 0){
|
||||
$s[$slow++] = ' ';
|
||||
}
|
||||
while ($i < strlen($s) && $s[$i] != ' ') {
|
||||
$s[$slow++] = $s[$i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 移动覆盖处理,丢弃多余的脏数据。
|
||||
$s = substr($s,0,$slow);
|
||||
return ;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 翻转字符串
|
||||
function reverseString(&$s, $start, $end) {
|
||||
for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
|
||||
$tmp = $s[$i];
|
||||
$s[$i] = $s[$j];
|
||||
$s[$j] = $tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
// 根据C++版本二思路进行实现
|
||||
// 函数名根据Rust编译器建议由驼峰命名法改为蛇形命名法
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn reverse(s: &mut Vec<char>, mut begin: usize, mut end: usize){
|
||||
while begin < end {
|
||||
let temp = s[begin];
|
||||
s[begin] = s[end];
|
||||
s[end] = temp;
|
||||
begin += 1;
|
||||
end -= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn remove_extra_spaces(s: &mut Vec<char>) {
|
||||
let mut slow: usize = 0;
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
// 注意这里不能用for循环,不然在里面那个while循环中对i的递增会失效
|
||||
let mut i: usize = 0;
|
||||
while i < len {
|
||||
if !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
|
||||
if slow != 0 {
|
||||
s[slow] = ' ';
|
||||
slow += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
while i < len && !s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
|
||||
s[slow] = s[i];
|
||||
slow += 1;
|
||||
i += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.resize(slow, ' ');
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn reverse_words(s: String) -> String {
|
||||
let mut s = s.chars().collect::<Vec<char>>();
|
||||
Self::remove_extra_spaces(&mut s);
|
||||
let len = s.len();
|
||||
Self::reverse(&mut s, 0, len - 1);
|
||||
let mut start = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..=len {
|
||||
if i == len || s[i].is_ascii_whitespace() {
|
||||
Self::reverse(&mut s, start, i - 1);
|
||||
start = i + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.iter().collect::<String>()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV
|
||||
# 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -409,5 +409,27 @@ var maxProfit = function(k, prices) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(k: number, prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = prices.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0)
|
||||
.map(_ => new Array(k * 2 + 1).fill(0));
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
|
||||
dp[0][i * 2 - 1] = -prices[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j < 2 * k + 1; j++) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1] + Math.pow(-1, j) * prices[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[length - 1][2 * k];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 189. 旋转数组
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-array/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,将数组中的元素向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
|
||||
|
||||
进阶:
|
||||
@@ -124,6 +126,19 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func rotate(nums []int, k int) {
|
||||
l:=len(nums)
|
||||
index:=l-k%l
|
||||
reverse(nums)
|
||||
reverse(nums[:l-index])
|
||||
reverse(nums[l-index:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
func reverse(nums []int){
|
||||
l:=len(nums)
|
||||
for i:=0;i<l/2;i++{
|
||||
nums[i],nums[l-1-i]=nums[l-1-i],nums[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
@@ -147,6 +162,27 @@ var rotate = function (nums, k) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function rotate(nums: number[], k: number): void {
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
k %= length;
|
||||
reverseByRange(nums, 0, length - 1);
|
||||
reverseByRange(nums, 0, k - 1);
|
||||
reverseByRange(nums, k, length - 1);
|
||||
};
|
||||
function reverseByRange(nums: number[], left: number, right: number): void {
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
const temp = nums[left];
|
||||
nums[left] = nums[right];
|
||||
nums[right] = temp;
|
||||
left++;
|
||||
right--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 198.打家劫舍
|
||||
# 198.打家劫舍
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber/)
|
||||
|
||||
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -189,6 +189,29 @@ const rob = nums => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function rob(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]: 前i个房屋能偷到的最大金额
|
||||
dp[0]: nums[0];
|
||||
dp[1]: max(nums[0], nums[1]);
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+nums[i]);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
if (length === 1) return nums[0];
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
dp[0] = nums[0];
|
||||
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
|
||||
for (let i = 2; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[length - 1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
249
problems/0200.岛屿数量.md
Normal file
249
problems/0200.岛屿数量.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,249 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 200. 岛屿数量
|
||||
|
||||
[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-islands/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
* m == grid.length
|
||||
* n == grid[i].length
|
||||
* 1 <= m, n <= 300
|
||||
* grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
注意题目中每座岛屿只能由**水平方向和/或竖直方向上**相邻的陆地连接形成。
|
||||
|
||||
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
|
||||
|
||||
本题思路,是用遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
|
||||
|
||||
在遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
那么如果把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
|
||||
|
||||
### 深度优先搜索
|
||||
|
||||
以下代码使用dfs实现,如果对dfs不太了解的话,建议先看这篇题解:[797.所有可能的路径](https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-paths-from-source-to-target/solution/by-carlsun-2-66pf/),
|
||||
|
||||
C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 版本一
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||||
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
|
||||
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
|
||||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
|
||||
visited[i][j] = true;
|
||||
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
很多录友可能有疑惑,为什么 以上代码中的dfs函数,没有终止条件呢? 感觉递归没有终止很危险。
|
||||
|
||||
其实终止条件 就写在了,调用dfs的地方,如果遇到不合法的方向,直接不会去调用dfs。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,也可以这么写:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
// 版本二
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||||
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||||
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == '0') return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
|
||||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
|
||||
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
|
||||
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里大家应该能看出区别了,无疑就是版本一中 调用dfs 的条件,放在了 版本二 的 终止条件位置上。
|
||||
|
||||
**版本一的写法**是 :下一个节点是否能合法已经判断完了,只要调用dfs就是可以合法的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
**版本二的写法**是:不管节点是否合法,上来就dfs,然后在终止条件的地方进行判断,不合法再return。
|
||||
|
||||
**理论上来讲,版本一的效率更高一些**,因为避免了 没有意义的递归调用,在调用dfs之前,就做合法性判断。 但从写法来说,可能版本二 更利于理解一些。(不过其实都差不太多)
|
||||
|
||||
很多同学看了同一道题目,都是dfs,写法却不一样,有时候有终止条件,有时候连终止条件都没有,其实这就是根本原因,两种写法而已。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 广度优先搜索
|
||||
|
||||
不少同学用广搜做这道题目的时候,超时了。 这里有一个广搜中很重要的细节:
|
||||
|
||||
根本原因是**只要 加入队列就代表 走过,就需要标记,而不是从队列拿出来的时候再去标记走过**。
|
||||
|
||||
很多同学可能感觉这有区别吗?
|
||||
|
||||
如果从队列拿出节点,再去标记这个节点走过,就会发生下图所示的结果,会导致很多节点重复加入队列。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
超时写法 (从队列中取出节点再标记)
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||||
que.push({x, y});
|
||||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||||
visited[curx][cury] = true; // 从队列中取出在标记走过
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
加入队列 就代表走过,立刻标记,正确写法:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||||
que.push({x, y});
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以上两个版本其实,其实只有细微区别,就是 `visited[x][y] = true;` 放在的地方,着去取决于我们对 代码中队列的定义,队列中的节点就表示已经走过的节点。 **所以只要加入队列,理解标记该节点走过**。
|
||||
|
||||
本题完整广搜代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||||
que.push({x, y});
|
||||
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
|
||||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
|
||||
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
|
||||
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
|
||||
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
其实本题是 dfs,bfs 模板题,但正是因为是模板题,所以大家或者一些题解把重要的细节都很忽略了,我这里把大家没注意的但以后会踩的坑 都给列出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 第202题. 快乐数
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/)
|
||||
|
||||
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -315,5 +315,115 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn get_sum(mut n: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut sum = 0;
|
||||
while n > 0 {
|
||||
sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
|
||||
n /= 10;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn is_happy(n: i32) -> bool {
|
||||
let mut n = n;
|
||||
let mut set = HashSet::new();
|
||||
loop {
|
||||
let sum = Self::get_sum(n);
|
||||
if sum == 1 {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if set.contains(&sum) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
} else { set.insert(sum); }
|
||||
n = sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
```C
|
||||
typedef struct HashNodeTag {
|
||||
int key; /* num */
|
||||
struct HashNodeTag *next;
|
||||
}HashNode;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calcualte the hash key */
|
||||
static inline int hash(int key, int size) {
|
||||
int index = key % size;
|
||||
return (index > 0) ? (index) : (-index);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the sum of the squares of its digits*/
|
||||
static inline int calcSquareSum(int num) {
|
||||
unsigned int sum = 0;
|
||||
while(num > 0) {
|
||||
sum += (num % 10) * (num % 10);
|
||||
num = num/10;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
// 引入mutable
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def isHappy(n: Int): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 存放每次计算后的结果
|
||||
val set: mutable.HashSet[Int] = new mutable.HashSet[Int]()
|
||||
var tmp = n // 因为形参是不可变量,所以需要找到一个临时变量
|
||||
// 开始进入循环
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
val sum = getSum(tmp) // 获取这个数每个值的平方和
|
||||
if (sum == 1) return true // 如果最终等于 1,则返回true
|
||||
// 如果set里面已经有这个值了,说明进入无限循环,可以返回false,否则添加这个值到set
|
||||
if (set.contains(sum)) return false
|
||||
else set.add(sum)
|
||||
tmp = sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终需要返回值,直接返回个false
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def getSum(n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var sum = 0
|
||||
var tmp = n
|
||||
while (tmp != 0) {
|
||||
sum += (tmp % 10) * (tmp % 10)
|
||||
tmp = tmp / 10
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
private int getSum(int n) {
|
||||
int sum = 0;
|
||||
//每位数的换算
|
||||
while (n > 0) {
|
||||
sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
|
||||
n /= 10;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
public bool IsHappy(int n) {
|
||||
HashSet <int> set = new HashSet<int>();
|
||||
while(n != 1 && !set.Contains(n)) { //判断避免循环
|
||||
set.Add(n);
|
||||
n = getSum(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n == 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 203.移除链表元素
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/)
|
||||
|
||||
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,6 +28,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
为了方便大家理解,我特意录制了视频:[链表基础操作| LeetCode:203.移除链表元素](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18B4y1s7R9),结合视频在看本题解,事半功倍。
|
||||
|
||||
这里以链表 1 4 2 4 来举例,移除元素4。
|
||||
|
||||
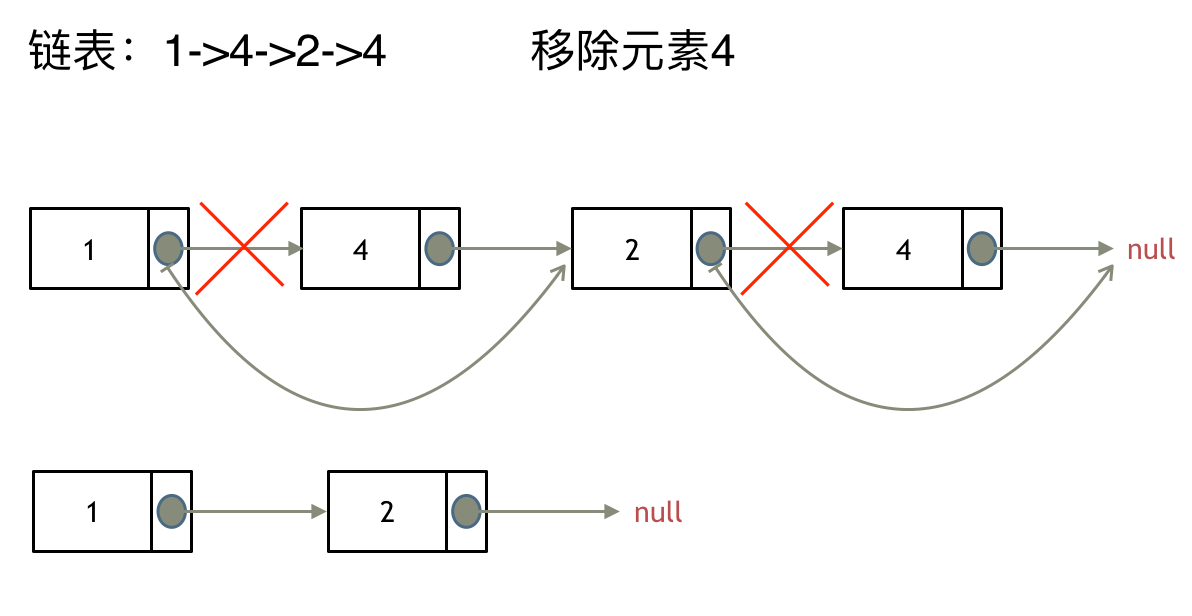
|
||||
@@ -145,6 +147,38 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
C:
|
||||
用原来的链表操作:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
|
||||
struct ListNode* temp;
|
||||
// 当头结点存在并且头结点的值等于val时
|
||||
while(head && head->val == val) {
|
||||
temp = head;
|
||||
// 将新的头结点设置为head->next并删除原来的头结点
|
||||
head = head->next;
|
||||
free(temp);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct ListNode *cur = head;
|
||||
// 当cur存在并且cur->next存在时
|
||||
// 此解法需要判断cur存在因为cur指向head。若head本身为NULL或者原链表中元素都为val的话,cur也会为NULL
|
||||
while(cur && (temp = cur->next)) {
|
||||
// 若cur->next的值等于val
|
||||
if(temp->val == val) {
|
||||
// 将cur->next设置为cur->next->next并删除cur->next
|
||||
cur->next = temp->next;
|
||||
free(temp);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 若cur->next不等于val,则将cur后移一位
|
||||
else
|
||||
cur = cur->next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 返回头结点
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
设置一个虚拟头结点:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
@@ -234,6 +268,27 @@ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 不添加虚拟节点and pre Node方式
|
||||
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
|
||||
* @param head
|
||||
* @param val
|
||||
* @return
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
|
||||
while(head!=null && head.val==val){
|
||||
head = head.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ListNode curr = head;
|
||||
while(curr!=null){
|
||||
while(curr.next!=null && curr.next.val == val){
|
||||
curr.next = curr.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
curr = curr.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
@@ -330,7 +385,8 @@ function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null {
|
||||
if (cur.val === val) {
|
||||
pre.next = cur.next;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pre = pre.next;
|
||||
//此处不加类型断言时:编译器会认为pre类型为ListNode, pre.next类型为ListNode | null
|
||||
pre = pre.next as ListNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
cur = cur.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -342,18 +398,18 @@ function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null {
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
|
||||
let pre: ListNode = dummyHead, cur: ListNode | null = dummyHead.next;
|
||||
// 删除非头部节点
|
||||
// 添加虚拟节点
|
||||
const data = new ListNode(0, head);
|
||||
let pre = data, cur = data.next;
|
||||
while (cur) {
|
||||
if (cur.val === val) {
|
||||
pre.next = cur.next;
|
||||
pre.next = cur.next
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pre = cur;
|
||||
}
|
||||
cur = cur.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return head.next;
|
||||
return data.next;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -432,20 +488,86 @@ RUST:
|
||||
// }
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn remove_elements(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, val: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
|
||||
let mut head = head;
|
||||
let mut dummy_head = ListNode::new(0);
|
||||
let mut cur = &mut dummy_head;
|
||||
while let Some(mut node) = head {
|
||||
head = std::mem::replace(&mut node.next, None);
|
||||
if node.val != val {
|
||||
cur.next = Some(node);
|
||||
let mut dummyHead = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
|
||||
dummyHead.next = head;
|
||||
let mut cur = dummyHead.as_mut();
|
||||
// 使用take()替换std::men::replace(&mut node.next, None)达到相同的效果,并且更普遍易读
|
||||
while let Some(nxt) = cur.next.take() {
|
||||
if nxt.val == val {
|
||||
cur.next = nxt.next;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
cur.next = Some(nxt);
|
||||
cur = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dummy_head.next
|
||||
dummyHead.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* class ListNode(_x: Int = 0, _next: ListNode = null) {
|
||||
* var next: ListNode = _next
|
||||
* var x: Int = _x
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def removeElements(head: ListNode, `val`: Int): ListNode = {
|
||||
if (head == null) return head
|
||||
var dummy = new ListNode(-1, head) // 定义虚拟头节点
|
||||
var cur = head // cur 表示当前节点
|
||||
var pre = dummy // pre 表示cur前一个节点
|
||||
while (cur != null) {
|
||||
if (cur.x == `val`) {
|
||||
// 相等,就删除那么cur的前一个节点pre执行cur的下一个
|
||||
pre.next = cur.next
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// 不相等,pre就等于当前cur节点
|
||||
pre = cur
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 向下迭代
|
||||
cur = cur.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终返回dummy的下一个,就是链表的头
|
||||
dummy.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Example:
|
||||
* var li = ListNode(5)
|
||||
* var v = li.`val`
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
|
||||
* var next: ListNode? = null
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
fun removeElements(head: ListNode?, `val`: Int): ListNode? {
|
||||
// 使用虚拟节点,令该节点指向head
|
||||
var dummyNode = ListNode(-1)
|
||||
dummyNode.next = head
|
||||
// 使用cur遍历链表各个节点
|
||||
var cur = dummyNode
|
||||
// 判断下个节点是否为空
|
||||
while (cur.next != null) {
|
||||
// 符合条件,移除节点
|
||||
if (cur.next.`val` == `val`) {
|
||||
cur.next = cur.next.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 不符合条件,遍历下一节点
|
||||
else {
|
||||
cur = cur.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 注意:返回的不是虚拟节点
|
||||
return dummyNode.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 205. 同构字符串
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/isomorphic-strings/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个字符串 s 和 t,判断它们是否是同构的。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -156,6 +156,28 @@ var isIsomorphic = function(s, t) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isIsomorphic(s: string, t: string): boolean {
|
||||
const helperMap1: Map<string, string> = new Map();
|
||||
const helperMap2: Map<string, string> = new Map();
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = s.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let temp1: string | undefined = helperMap1.get(s[i]);
|
||||
let temp2: string | undefined = helperMap2.get(t[i]);
|
||||
if (temp1 === undefined && temp2 === undefined) {
|
||||
helperMap1.set(s[i], t[i]);
|
||||
helperMap2.set(t[i], s[i]);
|
||||
} else if (temp1 !== t[i] || temp2 !== s[i]) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 206.反转链表
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
|
||||
|
||||
题意:反转一个单链表。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,6 +19,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
本题我录制了B站视频,[帮你拿下反转链表 | LeetCode:206.反转链表](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nB4y1i7eL),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
如果再定义一个新的链表,实现链表元素的反转,其实这是对内存空间的浪费。
|
||||
|
||||
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:
|
||||
@@ -29,7 +31,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
那么接下来看一看是如何反转的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:
|
||||
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:(纠正:动画应该是先移动pre,在移动cur)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@@ -406,6 +408,7 @@ def reverse(pre, cur)
|
||||
reverse(cur, tem) # 通过递归实现双指针法中的更新操作
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
```Kotlin
|
||||
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
|
||||
@@ -420,6 +423,41 @@ fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
|
||||
return pre
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Example:
|
||||
* var li = ListNode(5)
|
||||
* var v = li.`val`
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
|
||||
* var next: ListNode? = null
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
|
||||
// temp用来存储临时的节点
|
||||
var temp: ListNode?
|
||||
// cur用来遍历链表
|
||||
var cur: ListNode? = head
|
||||
// pre用来作为链表反转的工具
|
||||
// pre是比pre前一位的节点
|
||||
var pre: ListNode? = null
|
||||
while (cur != null) {
|
||||
// 临时存储原本cur的下一个节点
|
||||
temp = cur.next
|
||||
// 使cur下一节点地址为它之前的
|
||||
cur.next = pre
|
||||
// 之后随着cur的遍历移动pre
|
||||
pre = cur;
|
||||
// 移动cur遍历链表各个节点
|
||||
cur = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 由于开头使用pre为null,所以cur等于链表本身长度+1,
|
||||
// 此时pre在cur前一位,所以此时pre为头节点
|
||||
return pre;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Swift:
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
@@ -497,5 +535,58 @@ struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// 双指针法:
|
||||
function reverseList($head) {
|
||||
$cur = $head;
|
||||
$pre = NULL;
|
||||
while($cur){
|
||||
$temp = $cur->next;
|
||||
$cur->next = $pre;
|
||||
$pre = $cur;
|
||||
$cur = $temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $pre;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
双指针法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def reverseList(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
var pre: ListNode = null
|
||||
var cur = head
|
||||
while (cur != null) {
|
||||
var tmp = cur.next
|
||||
cur.next = pre
|
||||
pre = cur
|
||||
cur = tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
pre
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def reverseList(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
reverse(null, head)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def reverse(pre: ListNode, cur: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
if (cur == null) {
|
||||
return pre // 如果当前cur为空,则返回pre
|
||||
}
|
||||
val tmp: ListNode = cur.next
|
||||
cur.next = pre
|
||||
reverse(cur, tmp) // 此时cur成为前一个节点,tmp是当前节点
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,9 +5,9 @@
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 209.长度最小的子数组
|
||||
# 209.长度最小的子数组
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 s ,找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的 连续 子数组,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,10 +17,13 @@
|
||||
输出:2
|
||||
解释:子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的子数组。
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
为了易于大家理解,我特意录制了B站视频[拿下滑动窗口! | LeetCode 209 长度最小的子数组](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tZ4y1q7XE),结合视频看本题解,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
## 暴力解法
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目暴力解法当然是 两个for循环,然后不断的寻找符合条件的子序列,时间复杂度很明显是O(n^2)。
|
||||
这道题目暴力解法当然是 两个for循环,然后不断的寻找符合条件的子序列,时间复杂度很明显是O(n^2)。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,8 +50,10 @@ public:
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
|
||||
空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
后面力扣更新了数据,暴力解法已经超时了。
|
||||
|
||||
## 滑动窗口
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,6 +61,20 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
所谓滑动窗口,**就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们要想的结果**。
|
||||
|
||||
在暴力解法中,是一个for循环滑动窗口的起始位置,一个for循环为滑动窗口的终止位置,用两个for循环 完成了一个不断搜索区间的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
那么滑动窗口如何用一个for循环来完成这个操作呢。
|
||||
|
||||
首先要思考 如果用一个for循环,那么应该表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,还是终止位置。
|
||||
|
||||
如果只用一个for循环来表示 滑动窗口的起始位置,那么如何遍历剩下的终止位置?
|
||||
|
||||
此时难免再次陷入 暴力解法的怪圈。
|
||||
|
||||
所以 只用一个for循环,那么这个循环的索引,一定是表示 滑动窗口的终止位置。
|
||||
|
||||
那么问题来了, 滑动窗口的起始位置如何移动呢?
|
||||
|
||||
这里还是以题目中的示例来举例,s=7, 数组是 2,3,1,2,4,3,来看一下查找的过程:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -74,7 +93,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
窗口的起始位置如何移动:如果当前窗口的值大于s了,窗口就要向前移动了(也就是该缩小了)。
|
||||
|
||||
窗口的结束位置如何移动:窗口的结束位置就是遍历数组的指针,窗口的起始位置设置为数组的起始位置就可以了。
|
||||
窗口的结束位置如何移动:窗口的结束位置就是遍历数组的指针,也就是for循环里的索引。
|
||||
|
||||
解题的关键在于 窗口的起始位置如何移动,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -107,17 +126,17 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
**一些录友会疑惑为什么时间复杂度是O(n)**。
|
||||
|
||||
不要以为for里放一个while就以为是O(n^2)啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是 2 × n 也就是O(n)。
|
||||
不要以为for里放一个while就以为是O(n^2)啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是 2 × n 也就是O(n)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 相关题目推荐
|
||||
|
||||
* [904.水果成篮](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fruit-into-baskets/)
|
||||
* [76.最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
|
||||
* [904.水果成篮](https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/)
|
||||
* [76.最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -162,8 +181,27 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
index += 1
|
||||
return 0 if res==float("inf") else res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python3
|
||||
#滑动窗口
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def minSubArrayLen(self, target: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
if nums is None or len(nums)==0:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
lenf=len(nums)+1
|
||||
total=0
|
||||
i=j=0
|
||||
while (j<len(nums)):
|
||||
total=total+nums[j]
|
||||
j+=1
|
||||
while (total>=target):
|
||||
lenf=min(lenf,j-i)
|
||||
total=total-nums[i]
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
if lenf==len(nums)+1:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return lenf
|
||||
```
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func minSubArrayLen(target int, nums []int) int {
|
||||
@@ -198,7 +236,7 @@ JavaScript:
|
||||
var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) {
|
||||
// 长度计算一次
|
||||
const len = nums.length;
|
||||
let l = r = sum = 0,
|
||||
let l = r = sum = 0,
|
||||
res = len + 1; // 子数组最大不会超过自身
|
||||
while(r < len) {
|
||||
sum += nums[r++];
|
||||
@@ -260,12 +298,12 @@ Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn min_sub_array_len(target: i32, nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
pub fn min_sub_array_len(target: i32, nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let (mut result, mut subLength): (i32, i32) = (i32::MAX, 0);
|
||||
let (mut sum, mut i) = (0, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (pos, val) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
|
||||
sum += val;
|
||||
sum += val;
|
||||
while sum >= target {
|
||||
subLength = (pos - i + 1) as i32;
|
||||
if result > subLength {
|
||||
@@ -364,7 +402,7 @@ int minSubArrayLen(int target, int* nums, int numsSize){
|
||||
int minLength = INT_MAX;
|
||||
int sum = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int left = 0, right = 0;
|
||||
int left = 0, right = 0;
|
||||
//右边界向右扩展
|
||||
for(; right < numsSize; ++right) {
|
||||
sum += nums[right];
|
||||
@@ -380,5 +418,127 @@ int minSubArrayLen(int target, int* nums, int numsSize){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
fun minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
|
||||
var start = 0
|
||||
var end = 0
|
||||
var ret = Int.MAX_VALUE
|
||||
var count = 0
|
||||
while (end < nums.size) {
|
||||
count += nums[end]
|
||||
while (count >= target) {
|
||||
ret = if (ret > (end - start + 1)) end - start + 1 else ret
|
||||
count -= nums[start++]
|
||||
}
|
||||
end++
|
||||
}
|
||||
return if (ret == Int.MAX_VALUE) 0 else ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
滑动窗口
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
fun minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
|
||||
// 左边界 和 右边界
|
||||
var left: Int = 0
|
||||
var right: Int = 0
|
||||
// sum 用来记录和
|
||||
var sum: Int = 0
|
||||
// result记录一个固定值,便于判断是否存在的这样的数组
|
||||
var result: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE
|
||||
// subLenth记录长度
|
||||
var subLength = Int.MAX_VALUE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while (right < nums.size) {
|
||||
// 从数组首元素开始逐次求和
|
||||
sum += nums[right++]
|
||||
// 判断
|
||||
while (sum >= target) {
|
||||
var temp = right - left
|
||||
// 每次和上一次比较求出最小数组长度
|
||||
subLength = if (subLength > temp) temp else subLength
|
||||
// sum减少,左边界右移
|
||||
sum -= nums[left++]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果subLength为初始值,则说明长度为0,否则返回subLength
|
||||
return if(subLength == result) 0 else subLength
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
滑动窗口:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
var result = Int.MaxValue // 返回结果,默认最大值
|
||||
var left = 0 // 慢指针,当sum>=target,向右移动
|
||||
var sum = 0 // 窗口值的总和
|
||||
for (right <- 0 until nums.length) {
|
||||
sum += nums(right)
|
||||
while (sum >= target) {
|
||||
result = math.min(result, right - left + 1) // 产生新结果
|
||||
sum -= nums(left) // 左指针移动,窗口总和减去左指针的值
|
||||
left += 1 // 左指针向右移动
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 相当于三元运算符,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
if (result == Int.MaxValue) 0 else result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
暴力解法:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def minSubArrayLen(target: Int, nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||||
import scala.util.control.Breaks
|
||||
var res = Int.MaxValue
|
||||
var subLength = 0
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until nums.length) {
|
||||
var sum = 0
|
||||
Breaks.breakable(
|
||||
for (j <- i until nums.length) {
|
||||
sum += nums(j)
|
||||
if (sum >= target) {
|
||||
subLength = j - i + 1
|
||||
res = math.min(subLength, res)
|
||||
Breaks.break()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 相当于三元运算符
|
||||
if (res == Int.MaxValue) 0 else res
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int MinSubArrayLen(int s, int[] nums) {
|
||||
int n = nums.Length;
|
||||
int ans = int.MaxValue;
|
||||
int start = 0, end = 0;
|
||||
int sum = 0;
|
||||
while (end < n) {
|
||||
sum += nums[end];
|
||||
while (sum >= s)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ans = Math.Min(ans, end - start + 1);
|
||||
sum -= nums[start];
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
end++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ans == int.MaxValue ? 0 : ans;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 213.打家劫舍II
|
||||
# 213.打家劫舍II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-ii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋,每间房内都藏有一定的现金。这个地方所有的房屋都 围成一圈 ,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的。同时,相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警 。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -165,7 +165,30 @@ const robRange = (nums, start, end) => {
|
||||
return dp[end]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function rob(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
if (length === 0) return 0;
|
||||
if (length === 1) return nums[0];
|
||||
return Math.max(robRange(nums, 0, length - 2),
|
||||
robRange(nums, 1, length - 1));
|
||||
};
|
||||
function robRange(nums: number[], start: number, end: number): number {
|
||||
if (start === end) return nums[start];
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
dp[start] = nums[start];
|
||||
dp[start + 1] = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]);
|
||||
for (let i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[end];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 打家劫舍Ⅱ 动态规划
|
||||
// 时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 216.组合总和III
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/)
|
||||
|
||||
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
# 总结
|
||||
|
||||
开篇就介绍了本题与[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)的区别,相对来说加了元素总和的限制,如果做完[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)再做本题在合适不过。
|
||||
开篇就介绍了本题与[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)的区别,相对来说加了元素总和的限制,如果做完[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)再做本题在合适不过。
|
||||
|
||||
分析完区别,依然把问题抽象为树形结构,按照回溯三部曲进行讲解,最后给出剪枝的优化。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -360,42 +360,86 @@ func backTree(n,k,startIndex int,track *[]int,result *[][]int){
|
||||
## javaScript
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// 等差数列
|
||||
var maxV = k => k * (9 + 10 - k) / 2;
|
||||
var minV = k => k * (1 + k) / 2;
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number} k
|
||||
* @param {number} n
|
||||
* @return {number[][]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
var combinationSum3 = function(k, n) {
|
||||
if (k > 9 || k < 1) return [];
|
||||
// if (n > maxV(k) || n < minV(k)) return [];
|
||||
// if (n === maxV(k)) return [Array.from({length: k}).map((v, i) => 9 - i)];
|
||||
// if (n === minV(k)) return [Array.from({length: k}).map((v, i) => i + 1)];
|
||||
|
||||
const res = [], path = [];
|
||||
backtracking(k, n, 1, 0);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
function backtracking(k, n, i, sum){
|
||||
const len = path.length;
|
||||
if (len > k || sum > n) return;
|
||||
if (maxV(k - len) < n - sum) return;
|
||||
if (minV(k - len) > n - sum) return;
|
||||
|
||||
if(len === k && sum == n) {
|
||||
res.push(Array.from(path));
|
||||
const backtrack = (start) => {
|
||||
const l = path.length;
|
||||
if (l === k) {
|
||||
const sum = path.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
|
||||
if (sum === n) {
|
||||
res.push([...path]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const min = Math.min(n - sum, 9 + len - k + 1);
|
||||
|
||||
for(let a = i; a <= min; a++) {
|
||||
path.push(a);
|
||||
sum += a;
|
||||
backtracking(k, n, a + 1, sum);
|
||||
for (let i = start; i <= 9 - (k - l) + 1; i++) {
|
||||
path.push(i);
|
||||
backtrack(i + 1);
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
sum -= a;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
let res = [], path = [];
|
||||
backtrack(1);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function combinationSum3(k: number, n: number): number[][] {
|
||||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||||
function backTracking(k: number, n: number, sum: number, startIndex: number, tempArr: number[]): void {
|
||||
if (sum > n) return;
|
||||
if (tempArr.length === k) {
|
||||
if (sum === n) {
|
||||
resArr.push(tempArr.slice());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (k - tempArr.length) + 1; i++) {
|
||||
tempArr.push(i);
|
||||
backTracking(k, n, sum + i, i + 1, tempArr);
|
||||
tempArr.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
backTracking(k, n, 0, 1, []);
|
||||
return resArr;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path:&mut Vec<i32>, targetSum:i32, k: i32, mut sum: i32, startIndex: i32) {
|
||||
let len = path.len() as i32;
|
||||
if len == k {
|
||||
if sum == targetSum {
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i in startIndex..=9 {
|
||||
sum += i;
|
||||
path.push(i);
|
||||
Self::backtracking(result, path, targetSum, k, sum, i+1);
|
||||
sum -= i;
|
||||
path.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn combination_sum3(k: i32, n: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||||
let mut result: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
|
||||
let mut path: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
|
||||
Self::backtracking(&mut result, &mut path, n, k, 0, 1);
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
@@ -487,5 +531,35 @@ func combinationSum3(_ count: Int, _ targetSum: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def combinationSum3(k: Int, n: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(k: Int, n: Int, sum: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (sum > n) return // 剪枝,如果sum>目标和,就返回
|
||||
if (sum == n && path.size == k) {
|
||||
result.append(path.toList)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 剪枝
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to (9 - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
|
||||
path.append(i)
|
||||
backtracking(k, n, sum + i, i + 1)
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(k, n, 0, 1) // 调用递归方法
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回结果集的List形式
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
|
||||
|
||||
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -646,5 +646,68 @@ func countNodes(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if(root == null) return 0
|
||||
1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
层序遍历:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
var node = 0
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
node += 1
|
||||
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
node
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
利用完全二叉树性质:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def countNodes(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||||
var leftNode = root.left
|
||||
var rightNode = root.right
|
||||
// 向左向右往下探
|
||||
var leftDepth = 0
|
||||
while (leftNode != null) {
|
||||
leftDepth += 1
|
||||
leftNode = leftNode.left
|
||||
}
|
||||
var rightDepth = 0
|
||||
while (rightNode != null) {
|
||||
rightDepth += 1
|
||||
rightNode = rightNode.right
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果相等就是一个满二叉树
|
||||
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
|
||||
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果不相等就不是一个完全二叉树,继续向下递归
|
||||
countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 225. 用队列实现栈
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/)
|
||||
|
||||
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,6 +28,10 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法公开课:[队列的基本操作! | LeetCode:225. 用队列实现栈](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Fd4y1K7sm),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(这里要强调是单向队列)
|
||||
|
||||
有的同学可能疑惑这种题目有什么实际工程意义,**其实很多算法题目主要是对知识点的考察和教学意义远大于其工程实践的意义,所以面试题也是这样!**
|
||||
@@ -815,6 +819,203 @@ class MyStack {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
使用两个队列模拟栈:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
||||
class MyStack() {
|
||||
|
||||
val queue1 = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
|
||||
val queue2 = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def push(x: Int) {
|
||||
queue1.enqueue(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def pop(): Int = {
|
||||
var size = queue1.size
|
||||
// 将queue1中的每个元素都移动到queue2
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
|
||||
queue2.enqueue(queue1.dequeue())
|
||||
}
|
||||
var res = queue1.dequeue()
|
||||
// 再将queue2中的每个元素都移动到queue1
|
||||
while (!queue2.isEmpty) {
|
||||
queue1.enqueue(queue2.dequeue())
|
||||
}
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def top(): Int = {
|
||||
var size = queue1.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
|
||||
queue2.enqueue(queue1.dequeue())
|
||||
}
|
||||
var res = queue1.dequeue()
|
||||
while (!queue2.isEmpty) {
|
||||
queue1.enqueue(queue2.dequeue())
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终还需要把res送进queue1
|
||||
queue1.enqueue(res)
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def empty(): Boolean = {
|
||||
queue1.isEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
使用一个队列模拟:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
||||
class MyStack() {
|
||||
|
||||
val queue = new mutable.Queue[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
def push(x: Int) {
|
||||
queue.enqueue(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def pop(): Int = {
|
||||
var size = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until size - 1) {
|
||||
queue.enqueue(queue.head) // 把头添到队列最后
|
||||
queue.dequeue() // 再出队
|
||||
}
|
||||
queue.dequeue()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def top(): Int = {
|
||||
var size = queue.size
|
||||
var res = 0
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until size) {
|
||||
queue.enqueue(queue.head) // 把头添到队列最后
|
||||
res = queue.dequeue() // 再出队
|
||||
}
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def empty(): Boolean = {
|
||||
queue.isEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class MyStack {
|
||||
Queue<int> queue1;
|
||||
Queue<int> queue2;
|
||||
public MyStack() {
|
||||
queue1 = new Queue<int>();
|
||||
queue2 = new Queue<int>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void Push(int x) {
|
||||
queue2.Enqueue(x);
|
||||
while(queue1.Count != 0){
|
||||
queue2.Enqueue(queue1.Dequeue());
|
||||
}
|
||||
Queue<int> queueTemp;
|
||||
queueTemp = queue1;
|
||||
queue1 = queue2;
|
||||
queue2 = queueTemp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int Pop() {
|
||||
return queue1.Count > 0 ? queue1.Dequeue() : -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int Top() {
|
||||
return queue1.Count > 0 ? queue1.Peek() : -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public bool Empty() {
|
||||
return queue1.Count == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP
|
||||
> 双对列
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// SplQueue 类通过使用一个双向链表来提供队列的主要功能。(PHP 5 >= 5.3.0, PHP 7, PHP 8)
|
||||
// https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splqueue.php
|
||||
class MyStack {
|
||||
public $queueMain; // 保存数据
|
||||
public $queueTmp; // 辅助作用
|
||||
|
||||
function __construct() {
|
||||
$this->queueMain=new SplQueue();
|
||||
$this->queueTmp=new SplQueue();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// queueMain: 1,2,3 <= add
|
||||
function push($x) {
|
||||
$this->queueMain->enqueue($x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function pop() {
|
||||
$qmSize = $this->queueMain->Count();
|
||||
$qmSize --;
|
||||
// queueMain: 3,2,1 => pop =>2,1 => add => 2,1 :queueTmp
|
||||
while($qmSize --){
|
||||
$this->queueTmp->enqueue($this->queueMain->dequeue());
|
||||
}
|
||||
// queueMain: 3
|
||||
$val = $this->queueMain->dequeue();
|
||||
// queueMain <= queueTmp
|
||||
$this->queueMain = $this->queueTmp;
|
||||
// 清空queueTmp,下次使用
|
||||
$this->queueTmp = new SplQueue();
|
||||
return $val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function top() {
|
||||
// 底层是双链表实现:从双链表的末尾查看节点
|
||||
return $this->queueMain->top();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function empty() {
|
||||
return $this->queueMain->isEmpty();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
> 单对列
|
||||
```php
|
||||
class MyStack {
|
||||
public $queue;
|
||||
|
||||
function __construct() {
|
||||
$this->queue=new SplQueue();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function push($x) {
|
||||
$this->queue->enqueue($x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function pop() {
|
||||
$qmSize = $this->queue->Count();
|
||||
$qmSize --;
|
||||
//queue: 3,2,1 => pop =>2,1 => add => 2,1,3 :queue
|
||||
while($qmSize --){
|
||||
$this->queue->enqueue($this->queue->dequeue());
|
||||
}
|
||||
$val = $this->queue->dequeue();
|
||||
return $val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function top() {
|
||||
return $this->queue->top();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function empty() {
|
||||
return $this->queue->isEmpty();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 226.翻转二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
翻转一棵二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -368,9 +368,7 @@ func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
|
||||
if root ==nil{
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
temp:=root.Left
|
||||
root.Left=root.Right
|
||||
root.Right=temp
|
||||
root.Left,root.Right=root.Right,root.Left//交换
|
||||
|
||||
invertTree(root.Left)
|
||||
invertTree(root.Right)
|
||||
@@ -472,25 +470,14 @@ func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
|
||||
使用递归版本的前序遍历
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var invertTree = function(root) {
|
||||
//1. 首先使用递归版本的前序遍历实现二叉树翻转
|
||||
//交换节点函数
|
||||
const inverNode=function(left,right){
|
||||
let temp=left;
|
||||
left=right;
|
||||
right=temp;
|
||||
//需要重新给root赋值一下
|
||||
root.left=left;
|
||||
root.right=right;
|
||||
// 终止条件
|
||||
if (!root) {
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//确定递归函数的参数和返回值inverTree=function(root)
|
||||
//确定终止条件
|
||||
if(root===null){
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//确定节点处理逻辑 交换
|
||||
inverNode(root.left,root.right);
|
||||
invertTree(root.left);
|
||||
invertTree(root.right);
|
||||
// 交换左右节点
|
||||
const rightNode = root.right;
|
||||
root.right = invertTree(root.left);
|
||||
root.left = invertTree(rightNode);
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -820,5 +807,53 @@ func invertTree(_ root: TreeNode?) -> TreeNode? {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
深度优先遍历(前序遍历):
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def invertTree(root: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return root
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
def process(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
|
||||
if (node == null) return
|
||||
// 翻转节点
|
||||
val curNode = node.left
|
||||
node.left = node.right
|
||||
node.right = curNode
|
||||
process(node.left)
|
||||
process(node.right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
process(root)
|
||||
root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
广度优先遍历(层序遍历):
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
def invertTree(root: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||||
if (root == null) return root
|
||||
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
|
||||
queue.enqueue(root)
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
|
||||
val len = queue.size
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until len) {
|
||||
var curNode = queue.dequeue()
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
|
||||
// 翻转
|
||||
var tmpNode = curNode.left
|
||||
curNode.left = curNode.right
|
||||
curNode.right = tmpNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 232.用栈实现队列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
|
||||
|
||||
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -38,6 +38,9 @@ queue.empty(); // 返回 false
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法公开课:[栈的基本操作! | LeetCode:232.用栈实现队列](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nY4y1w7VC),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。
|
||||
|
||||
使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈**一个输入栈,一个输出栈**,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
|
||||
@@ -111,7 +114,7 @@ public:
|
||||
|
||||
## 拓展
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出peek()的实现,直接复用了pop()。
|
||||
可以看出peek()的实现,直接复用了pop(), 要不然,对stOut判空的逻辑又要重写一遍。
|
||||
|
||||
再多说一些代码开发上的习惯问题,在工业级别代码开发中,最忌讳的就是 实现一个类似的函数,直接把代码粘过来改一改就完事了。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -170,14 +173,6 @@ class MyQueue {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||||
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
|
||||
* obj.push(x);
|
||||
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
|
||||
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
|
||||
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
|
||||
*/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -275,15 +270,11 @@ func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
|
||||
|
||||
/** Get the front element. */
|
||||
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
|
||||
for len(this.stack) != 0 {
|
||||
val := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
|
||||
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
|
||||
this.back = append(this.back, val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(this.back) == 0 {
|
||||
val := this.Pop()
|
||||
if val == 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
val := this.back[len(this.back)-1]
|
||||
this.back = append(this.back, val)
|
||||
return val
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -500,5 +491,136 @@ void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public class MyQueue {
|
||||
Stack<int> inStack;
|
||||
Stack<int> outStack;
|
||||
|
||||
public MyQueue() {
|
||||
inStack = new Stack<int>();// 负责进栈
|
||||
outStack = new Stack<int>();// 负责出栈
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void Push(int x) {
|
||||
inStack.Push(x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int Pop() {
|
||||
dumpstackIn();
|
||||
return outStack.Pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int Peek() {
|
||||
dumpstackIn();
|
||||
return outStack.Peek();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public bool Empty() {
|
||||
return inStack.Count == 0 && outStack.Count == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 处理方法:
|
||||
// 如果outStack为空,那么将inStack中的元素全部放到outStack中
|
||||
private void dumpstackIn(){
|
||||
if (outStack.Count != 0) return;
|
||||
while(inStack.Count != 0){
|
||||
outStack.Push(inStack.Pop());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// SplStack 类通过使用一个双向链表来提供栈的主要功能。[PHP 5 >= 5.3.0, PHP 7, PHP 8]
|
||||
// https://www.php.net/manual/zh/class.splstack.php
|
||||
class MyQueue {
|
||||
// 双栈模拟队列:In栈存储数据;Out栈辅助处理
|
||||
private $stackIn;
|
||||
private $stackOut;
|
||||
|
||||
function __construct() {
|
||||
$this->stackIn = new SplStack();
|
||||
$this->stackOut = new SplStack();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// In: 1 2 3 <= push
|
||||
function push($x) {
|
||||
$this->stackIn->push($x);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function pop() {
|
||||
$this->peek();
|
||||
return $this->stackOut->pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function peek() {
|
||||
if($this->stackOut->isEmpty()){
|
||||
$this->shift();
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $this->stackOut->top();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function empty() {
|
||||
return $this->stackOut->isEmpty() && $this->stackIn->isEmpty();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 如果Out栈为空,把In栈数据压入Out栈
|
||||
// In: 1 2 3 => pop push => 1 2 3 :Out
|
||||
private function shift(){
|
||||
while(!$this->stackIn->isEmpty()){
|
||||
$this->stackOut->push($this->stackIn->pop());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
class MyQueue() {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
val stackIn = mutable.Stack[Int]() // 负责出栈
|
||||
val stackOut = mutable.Stack[Int]() // 负责入栈
|
||||
|
||||
// 添加元素
|
||||
def push(x: Int) {
|
||||
stackIn.push(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 复用代码,如果stackOut为空就把stackIn的所有元素都压入StackOut
|
||||
def dumpStackIn(): Unit = {
|
||||
if (!stackOut.isEmpty) return
|
||||
while (!stackIn.isEmpty) {
|
||||
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 弹出元素
|
||||
def pop(): Int = {
|
||||
dumpStackIn()
|
||||
stackOut.pop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取队头
|
||||
def peek(): Int = {
|
||||
dumpStackIn()
|
||||
val res: Int = stackOut.pop()
|
||||
stackOut.push(res)
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断是否为空
|
||||
def empty(): Boolean = {
|
||||
stackIn.isEmpty && stackOut.isEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 234.回文链表
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
|
||||
|
||||
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -218,65 +218,115 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#数组模拟
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
|
||||
length = 0
|
||||
tmp = head
|
||||
while tmp: #求链表长度
|
||||
length += 1
|
||||
tmp = tmp.next
|
||||
|
||||
result = [0] * length
|
||||
tmp = head
|
||||
index = 0
|
||||
while tmp: #链表元素加入数组
|
||||
result[index] = tmp.val
|
||||
index += 1
|
||||
tmp = tmp.next
|
||||
|
||||
i, j = 0, length - 1
|
||||
while i < j: # 判断回文
|
||||
if result[i] != result[j]:
|
||||
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
|
||||
list=[]
|
||||
while head:
|
||||
list.append(head.val)
|
||||
head=head.next
|
||||
l,r=0, len(list)-1
|
||||
while l<=r:
|
||||
if list[l]!=list[r]:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
j -= 1
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
l+=1
|
||||
r-=1
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
#反转后半部分链表
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
|
||||
if head == None or head.next == None:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
slow, fast = head, head
|
||||
while fast and fast.next:
|
||||
pre = slow
|
||||
slow = slow.next
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next
|
||||
|
||||
pre.next = None # 分割链表
|
||||
cur1 = head # 前半部分
|
||||
cur2 = self.reverseList(slow) # 反转后半部分,总链表长度如果是奇数,cur2比cur1多一个节点
|
||||
while cur1:
|
||||
if cur1.val != cur2.val:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
cur1 = cur1.next
|
||||
cur2 = cur2.next
|
||||
return True
|
||||
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
|
||||
fast = slow = head
|
||||
|
||||
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
|
||||
cur = head
|
||||
pre = None
|
||||
while(cur!=None):
|
||||
temp = cur.next # 保存一下cur的下一个节点
|
||||
cur.next = pre # 反转
|
||||
pre = cur
|
||||
cur = temp
|
||||
return pre
|
||||
# find mid point which including (first) mid point into the first half linked list
|
||||
while fast and fast.next:
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next
|
||||
slow = slow.next
|
||||
node = None
|
||||
|
||||
# reverse second half linked list
|
||||
while slow:
|
||||
slow.next, slow, node = node, slow.next, slow
|
||||
|
||||
# compare reversed and original half; must maintain reversed linked list is shorter than 1st half
|
||||
while node:
|
||||
if node.val != head.val:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
node = node.next
|
||||
head = head.next
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* type ListNode struct {
|
||||
* Val int
|
||||
* Next *ListNode
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
//方法一,使用数组
|
||||
func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool{
|
||||
//计算切片长度,避免切片频繁扩容
|
||||
cur,ln:=head,0
|
||||
for cur!=nil{
|
||||
ln++
|
||||
cur=cur.Next
|
||||
}
|
||||
nums:=make([]int,ln)
|
||||
index:=0
|
||||
for head!=nil{
|
||||
nums[index]=head.Val
|
||||
index++
|
||||
head=head.Next
|
||||
}
|
||||
//比较回文切片
|
||||
for i,j:=0,ln-1;i<=j;i,j=i+1,j-1{
|
||||
if nums[i]!=nums[j]{return false}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 方法二,快慢指针
|
||||
func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool {
|
||||
if head==nil&&head.Next==nil{return true}
|
||||
//慢指针,找到链表中间分位置,作为分割
|
||||
slow:=head
|
||||
fast:=head
|
||||
//记录慢指针的前一个节点,用来分割链表
|
||||
pre:=head
|
||||
for fast!=nil && fast.Next!=nil{
|
||||
pre=slow
|
||||
slow=slow.Next
|
||||
fast=fast.Next.Next
|
||||
}
|
||||
//分割链表
|
||||
pre.Next=nil
|
||||
//前半部分
|
||||
cur1:=head
|
||||
//反转后半部分,总链表长度如果是奇数,cur2比cur1多一个节点
|
||||
cur2:=ReverseList(slow)
|
||||
|
||||
//开始两个链表的比较
|
||||
for cur1!=nil{
|
||||
if cur1.Val!=cur2.Val{return false}
|
||||
cur1=cur1.Next
|
||||
cur2=cur2.Next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
//反转链表
|
||||
func ReverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode{
|
||||
var pre *ListNode
|
||||
cur:=head
|
||||
for cur!=nil{
|
||||
tmp:=cur.Next
|
||||
cur.Next=pre
|
||||
pre=cur
|
||||
cur=tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pre
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
@@ -319,6 +369,63 @@ var isPalindrome = function(head) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 数组模拟
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isPalindrome(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
const helperArr: number[] = [];
|
||||
let curNode: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
while (curNode !== null) {
|
||||
helperArr.push(curNode.val);
|
||||
curNode = curNode.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let left: number = 0,
|
||||
right: number = helperArr.length - 1;
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
if (helperArr[left++] !== helperArr[right--]) return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 反转后半部分链表
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function isPalindrome(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
if (head === null || head.next === null) return true;
|
||||
let fastNode: ListNode | null = head,
|
||||
slowNode: ListNode = head,
|
||||
preNode: ListNode = head;
|
||||
while (fastNode !== null && fastNode.next !== null) {
|
||||
preNode = slowNode;
|
||||
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
|
||||
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
preNode.next = null;
|
||||
let cur1: ListNode | null = head;
|
||||
let cur2: ListNode | null = reverseList(slowNode);
|
||||
while (cur1 !== null) {
|
||||
if (cur1.val !== cur2!.val) return false;
|
||||
cur1 = cur1.next;
|
||||
cur2 = cur2!.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let curNode: ListNode | null = head,
|
||||
preNode: ListNode | null = null;
|
||||
while (curNode !== null) {
|
||||
let tempNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next;
|
||||
curNode.next = preNode;
|
||||
preNode = curNode;
|
||||
curNode = tempNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return preNode;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -381,7 +381,36 @@ function lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode | null, p: TreeNode | null, q: Tree
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||||
// scala中每个关键字都有其返回值,于是可以不写return
|
||||
if (root.value > p.value && root.value > q.value) lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
|
||||
else if (root.value < p.value && root.value < q.value) lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
|
||||
else root
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||||
var curNode = root // 因为root是不可变量,所以要赋值给curNode一个可变量
|
||||
while(curNode != null){
|
||||
if(curNode.value > p.value && curNode.value > q.value) curNode = curNode.left
|
||||
else if(curNode.value < p.value && curNode.value < q.value) curNode = curNode.right
|
||||
else return curNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
null
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -343,7 +343,25 @@ function lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode | null, p: TreeNode | null, q: Tree
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode): TreeNode = {
|
||||
// 递归结束条件
|
||||
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
|
||||
return root
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
|
||||
var right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
|
||||
|
||||
if (left != null && right != null) return root
|
||||
if (left == null) return right
|
||||
left
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 239. 滑动窗口最大值
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,11 +32,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[单调队列正式登场!| LeetCode:239. 滑动窗口最大值](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XS4y1p7qj),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
|
||||
|
||||
这是使用单调队列的经典题目。
|
||||
|
||||
难点是如何求一个区间里的最大值呢? (这好像是废话),暴力一下不就得了。
|
||||
|
||||
暴力方法,遍历一遍的过程中每次从窗口中在找到最大的数值,这样很明显是$O(n × k)$的算法。
|
||||
暴力方法,遍历一遍的过程中每次从窗口中在找到最大的数值,这样很明显是O(n × k)的算法。
|
||||
|
||||
有的同学可能会想用一个大顶堆(优先级队列)来存放这个窗口里的k个数字,这样就可以知道最大的最大值是多少了, **但是问题是这个窗口是移动的,而大顶堆每次只能弹出最大值,我们无法移除其他数值,这样就造成大顶堆维护的不是滑动窗口里面的数值了。所以不能用大顶堆。**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -183,13 +185,13 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在来看一下时间复杂度,使用单调队列的时间复杂度是 $O(n)$。
|
||||
在来看一下时间复杂度,使用单调队列的时间复杂度是 O(n)。
|
||||
|
||||
有的同学可能想了,在队列中 push元素的过程中,还有pop操作呢,感觉不是纯粹的$O(n)$。
|
||||
有的同学可能想了,在队列中 push元素的过程中,还有pop操作呢,感觉不是纯粹的O(n)。
|
||||
|
||||
其实,大家可以自己观察一下单调队列的实现,nums 中的每个元素最多也就被 push_back 和 pop_back 各一次,没有任何多余操作,所以整体的复杂度还是 $O(n)$。
|
||||
其实,大家可以自己观察一下单调队列的实现,nums 中的每个元素最多也就被 push_back 和 pop_back 各一次,没有任何多余操作,所以整体的复杂度还是 O(n)。
|
||||
|
||||
空间复杂度因为我们定义一个辅助队列,所以是$O(k)$。
|
||||
空间复杂度因为我们定义一个辅助队列,所以是O(k)。
|
||||
|
||||
# 扩展
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -630,6 +632,172 @@ func maxSlidingWindow(_ nums: [Int], _ k: Int) -> [Int] {
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def maxSlidingWindow(nums: Array[Int], k: Int): Array[Int] = {
|
||||
var len = nums.length - k + 1 // 滑动窗口长度
|
||||
var res: Array[Int] = new Array[Int](len) // 声明存储结果的数组
|
||||
var index = 0 // 结果数组指针
|
||||
val queue: MyQueue = new MyQueue // 自定义队列
|
||||
// 将前k个添加到queue
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until k) {
|
||||
queue.add(nums(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
res(index) = queue.peek // 第一个滑动窗口的最大值
|
||||
index += 1
|
||||
for (i <- k until nums.length) {
|
||||
queue.poll(nums(i - k)) // 首先移除第i-k个元素
|
||||
queue.add(nums(i)) // 添加当前数字到队列
|
||||
res(index) = queue.peek() // 赋值
|
||||
index+=1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 最终返回res,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class MyQueue {
|
||||
var queue = ArrayBuffer[Int]()
|
||||
|
||||
// 移除元素,如果传递进来的跟队头相等,那么移除
|
||||
def poll(value: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (!queue.isEmpty && queue.head == value) {
|
||||
queue.remove(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 添加元素,当队尾大于当前元素就删除
|
||||
def add(value: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty && value > queue.last) {
|
||||
queue.remove(queue.length - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
queue.append(value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def peek(): Int = queue.head
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param Integer[] $nums
|
||||
* @param Integer $k
|
||||
* @return Integer[]
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function maxSlidingWindow($nums, $k) {
|
||||
$myQueue = new MyQueue();
|
||||
// 先将前k的元素放进队列
|
||||
for ($i = 0; $i < $k; $i++) {
|
||||
$myQueue->push($nums[$i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
$result = [];
|
||||
$result[] = $myQueue->max(); // result 记录前k的元素的最大值
|
||||
|
||||
for ($i = $k; $i < count($nums); $i++) {
|
||||
$myQueue->pop($nums[$i - $k]); // 滑动窗口移除最前面元素
|
||||
$myQueue->push($nums[$i]); // 滑动窗口前加入最后面的元素
|
||||
$result[]= $myQueue->max(); // 记录对应的最大值
|
||||
}
|
||||
return $result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 单调对列构建
|
||||
class MyQueue{
|
||||
private $queue;
|
||||
|
||||
public function __construct(){
|
||||
$this->queue = new SplQueue(); //底层是双向链表实现。
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public function pop($v){
|
||||
// 判断当前对列是否为空
|
||||
// 比较当前要弹出的数值是否等于队列出口元素的数值,如果相等则弹出。
|
||||
// bottom 从链表前端查看元素, dequeue 从双向链表的开头移动一个节点
|
||||
if(!$this->queue->isEmpty() && $v == $this->queue->bottom()){
|
||||
$this->queue->dequeue(); //弹出队列
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public function push($v){
|
||||
// 判断当前对列是否为空
|
||||
// 如果push的数值大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列后端的数值弹出,直到push的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止。
|
||||
// 这样就保持了队列里的数值是单调从大到小的了。
|
||||
while (!$this->queue->isEmpty() && $v > $this->queue->top()) {
|
||||
$this->queue->pop(); // pop从链表末尾弹出一个元素,
|
||||
}
|
||||
$this->queue->enqueue($v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 查询当前队列里的最大值 直接返回队首
|
||||
public function max(){
|
||||
// bottom 从链表前端查看元素, top从链表末尾查看元素
|
||||
return $this->queue->bottom();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 辅助理解: 打印队列元素
|
||||
public function println(){
|
||||
// "迭代器移动到链表头部": 可理解为从头遍历链表元素做准备。
|
||||
// 【PHP中没有指针概念,所以就没说指针。从数据结构上理解,就是把指针指向链表头部】
|
||||
$this->queue->rewind();
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Println: ";
|
||||
while($this->queue->valid()){
|
||||
echo $this->queue->current()," -> ";
|
||||
$this->queue->next();
|
||||
}
|
||||
echo "\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
class myDequeue{
|
||||
private LinkedList<int> linkedList = new LinkedList<int>();
|
||||
|
||||
public void Enqueue(int n){
|
||||
while(linkedList.Count > 0 && linkedList.Last.Value < n){
|
||||
linkedList.RemoveLast();
|
||||
}
|
||||
linkedList.AddLast(n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int Max(){
|
||||
return linkedList.First.Value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public void Dequeue(int n){
|
||||
if(linkedList.First.Value == n){
|
||||
linkedList.RemoveFirst();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
myDequeue window = new myDequeue();
|
||||
List<int> res = new List<int>();
|
||||
|
||||
public int[] MaxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
|
||||
window.Enqueue(nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
res.Add(window.Max());
|
||||
for(int i = k; i < nums.Length; i++){
|
||||
window.Dequeue(nums[i-k]);
|
||||
window.Enqueue(nums[i]);
|
||||
res.Add(window.Max());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return res.ToArray();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 242.有效的字母异位词
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-anagram/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,6 +27,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
本题B站视频讲解版:[学透哈希表,数组使用有技巧!Leetcode:242.有效的字母异位词](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YG411p7BA)
|
||||
|
||||
先看暴力的解法,两层for循环,同时还要记录字符是否重复出现,很明显时间复杂度是 O(n^2)。
|
||||
|
||||
暴力的方法这里就不做介绍了,直接看一下有没有更优的方式。
|
||||
@@ -125,8 +127,6 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
if record[i] != 0:
|
||||
#record数组如果有的元素不为零0,说明字符串s和t 一定是谁多了字符或者谁少了字符。
|
||||
return False
|
||||
#如果有一个元素不为零,则可以判断字符串s和t不是字母异位词
|
||||
break
|
||||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -307,6 +307,52 @@ impl Solution {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def isAnagram(s: String, t: String): Boolean = {
|
||||
// 如果两个字符串的长度不等,直接返回false
|
||||
if (s.length != t.length) return false
|
||||
val record = new Array[Int](26) // 记录每个单词出现了多少次
|
||||
// 遍历字符串,对于s字符串单词对应的记录+=1,t字符串对应的记录-=1
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until s.length) {
|
||||
record(s(i) - 97) += 1
|
||||
record(t(i) - 97) -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果不等于则直接返回false
|
||||
for (i <- 0 until 26) {
|
||||
if (record(i) != 0) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果前面不返回false,说明匹配成功,返回true,return可以省略
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
C#:
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
public bool IsAnagram(string s, string t) {
|
||||
int sl=s.Length,tl=t.Length;
|
||||
if(sl!=tl) return false;
|
||||
int[] a = new int[26];
|
||||
for(int i = 0; i < sl; i++){
|
||||
a[s[i] - 'a']++;
|
||||
a[t[i] - 'a']--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
foreach (int i in a)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (i != 0)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 相关题目
|
||||
|
||||
* 383.赎金信
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 257. 二叉树的所有路径
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -702,5 +702,35 @@ func binaryTreePaths(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [String] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||||
def binaryTreePaths(root: TreeNode): List[String] = {
|
||||
val res = ListBuffer[String]()
|
||||
def traversal(curNode: TreeNode, path: ListBuffer[Int]): Unit = {
|
||||
path.append(curNode.value)
|
||||
if (curNode.left == null && curNode.right == null) {
|
||||
res.append(path.mkString("->")) // mkString函数: 将数组的所有值按照指定字符串拼接
|
||||
return // 处理完可以直接return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (curNode.left != null) {
|
||||
traversal(curNode.left, path)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (curNode.right != null) {
|
||||
traversal(curNode.right, path)
|
||||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
traversal(root, ListBuffer[Int]())
|
||||
res.toList
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 279.完全平方数
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/perfect-squares/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, ...)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -355,5 +355,24 @@ var numSquares2 = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function numSquares(n: number): number {
|
||||
const goodsNum: number = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(n));
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(Infinity);
|
||||
dp[0] = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i <= goodsNum; i++) {
|
||||
const tempVal: number = i * i;
|
||||
for (let j = tempVal; j <= n; j++) {
|
||||
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - tempVal] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 283. 移动零
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/move-zeroes/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -133,6 +133,27 @@ var moveZeroes = function(nums) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function moveZeroes(nums: number[]): void {
|
||||
const length: number = nums.length;
|
||||
let slowIndex: number = 0,
|
||||
fastIndex: number = 0;
|
||||
while (fastIndex < length) {
|
||||
if (nums[fastIndex] !== 0) {
|
||||
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex];
|
||||
};
|
||||
fastIndex++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (slowIndex < length) {
|
||||
nums[slowIndex++] = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 300.最长递增子序列
|
||||
# 300.最长递增子序列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
|
||||
|
||||
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -168,6 +168,56 @@ func lengthOfLIS(nums []int ) int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 动态规划求解
|
||||
func lengthOfLIS(nums []int) int {
|
||||
// dp数组的定义 dp[i]表示取第i个元素的时候,表示子序列的长度,其中包括 nums[i] 这个元素
|
||||
dp := make([]int, len(nums))
|
||||
|
||||
// 初始化,所有的元素都应该初始化为1
|
||||
for i := range dp {
|
||||
dp[i] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ans := dp[0]
|
||||
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < i; j++ {
|
||||
if nums[i] > nums[j] {
|
||||
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dp[i] > ans {
|
||||
ans = dp[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ans
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(x, y int) int {
|
||||
if x > y {
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
return y
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn length_of_lis(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![1; nums.len() + 1];
|
||||
let mut result = 1;
|
||||
for i in 1..nums.len() {
|
||||
for j in 0..i {
|
||||
if nums[j] < nums[i] {
|
||||
dp[i] = dp[i].max(dp[j] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = result.max(dp[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Javascript
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const lengthOfLIS = (nums) => {
|
||||
@@ -187,6 +237,27 @@ const lengthOfLIS = (nums) => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function lengthOfLIS(nums: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]: 前i个元素中,以nums[i]结尾,最长子序列的长度
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
|
||||
let resMax: number = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
|
||||
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return resMax;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
|
||||
# 309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-cooldown/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-cooldown/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,6 +44,8 @@ dp[i][j],第i天状态为j,所剩的最多现金为dp[i][j]。
|
||||
* 状态三:今天卖出了股票
|
||||
* 状态四:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
j的状态为:
|
||||
|
||||
* 0:状态一
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +59,7 @@ j的状态为:
|
||||
|
||||
**注意这里的每一个状态,例如状态一,是买入股票状态并不是说今天已经就买入股票,而是说保存买入股票的状态即:可能是前几天买入的,之后一直没操作,所以保持买入股票的状态**。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 确定递推公式
|
||||
1. 确定递推公式
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
达到买入股票状态(状态一)即:dp[i][0],有两个具体操作:
|
||||
@@ -214,8 +216,8 @@ class Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 2; i <= prices.length; i++) {
|
||||
/*
|
||||
dp[i][0] 第i天未持有股票收益;
|
||||
dp[i][1] 第i天持有股票收益;
|
||||
dp[i][0] 第i天持有股票收益;
|
||||
dp[i][1] 第i天不持有股票收益;
|
||||
情况一:第i天是冷静期,不能以dp[i-1][1]购买股票,所以以dp[i - 2][1]买股票,没问题
|
||||
情况二:第i天不是冷静期,理论上应该以dp[i-1][1]购买股票,但是第i天不是冷静期说明,第i-1天没有卖出股票,
|
||||
则dp[i-1][1]=dp[i-2][1],所以可以用dp[i-2][1]买股票,没问题
|
||||
@@ -325,6 +327,66 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
> 版本一,与本文思路一致
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][0]: 持股状态;
|
||||
dp[i][1]: 无股状态,当天为非冷冻期;
|
||||
dp[i][2]: 无股状态,当天卖出;
|
||||
dp[i][3]: 无股状态,当天为冷冻期;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = prices.length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0).map(_ => []);
|
||||
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
|
||||
dp[0][1] = dp[0][2] = dp[0][3] = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = Math.max(
|
||||
dp[i - 1][0],
|
||||
Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][3]) - prices[i]
|
||||
);
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][3]);
|
||||
dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
|
||||
dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2];
|
||||
}
|
||||
const lastEl: number[] = dp[length - 1];
|
||||
return Math.max(lastEl[1], lastEl[2], lastEl[3]);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 版本二,状态定义略有不同,可以帮助理解
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][0]: 持股状态,当天买入;
|
||||
dp[i][1]: 持股状态,当天未买入;
|
||||
dp[i][2]: 无股状态,当天卖出;
|
||||
dp[i][3]: 无股状态,当天未卖出;
|
||||
|
||||
买入有冷冻期限制,其实就是状态[0]只能由前一天的状态[3]得到;
|
||||
如果卖出有冷冻期限制,其实就是[2]由[1]得到。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = prices.length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0).map(_ => []);
|
||||
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
|
||||
dp[0][1] = -Infinity;
|
||||
dp[0][2] = dp[0][3] = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][3] - prices[i];
|
||||
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0]);
|
||||
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1]) + prices[i];
|
||||
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Math.max(dp[length - 1][2], dp[length - 1][3]);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 322. 零钱兑换
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/coin-change/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -220,7 +220,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
for j in range(coin, amount + 1):
|
||||
dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - coin] + 1)
|
||||
return dp[amount] if dp[amount] < amount + 1 else -1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def coinChange1(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int:
|
||||
'''版本二'''
|
||||
# 初始化
|
||||
@@ -302,6 +302,24 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn coin_change(coins: Vec<i32>, amount: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let amount = amount as usize;
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![i32::MAX; amount + 1];
|
||||
dp[0] = 0;
|
||||
for i in 0..coins.len() {
|
||||
for j in coins[i] as usize..=amount {
|
||||
if dp[j - coins[i] as usize] != i32::MAX {
|
||||
dp[j] = dp[j].min(dp[j - coins[i] as usize] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dp[amount] == i32::MAX { -1 } else { dp[amount] }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Javascript:
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const coinChange = (coins, amount) => {
|
||||
@@ -322,7 +340,21 @@ const coinChange = (coins, amount) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function coinChange(coins: number[], amount: number): number {
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(amount + 1).fill(Infinity);
|
||||
dp[0] = 0;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) {
|
||||
if (dp[j - coins[i]] === Infinity) continue;
|
||||
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[amount] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[amount];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 332.重新安排行程
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reconstruct-itinerary/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reconstruct-itinerary/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个机票的字符串二维数组 [from, to],子数组中的两个成员分别表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点,对该行程进行重新规划排序。所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -379,7 +379,7 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
return path
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### GO
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type pair struct {
|
||||
target string
|
||||
@@ -543,6 +543,50 @@ var findItinerary = function(tickets) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function findItinerary(tickets: string[][]): string[] {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
TicketsMap 实例:
|
||||
{ NRT: Map(1) { 'JFK' => 1 }, JFK: Map(2) { 'KUL' => 1, 'NRT' => 1 } }
|
||||
这里选择Map数据结构的原因是:与Object类型的一个主要差异是,Map实例会维护键值对的插入顺序。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
type TicketsMap = {
|
||||
[index: string]: Map<string, number>
|
||||
};
|
||||
tickets.sort((a, b) => {
|
||||
return a[1] < b[1] ? -1 : 1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
const ticketMap: TicketsMap = {};
|
||||
for (const [from, to] of tickets) {
|
||||
if (ticketMap[from] === undefined) {
|
||||
ticketMap[from] = new Map();
|
||||
}
|
||||
ticketMap[from].set(to, (ticketMap[from].get(to) || 0) + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
const resRoute = ['JFK'];
|
||||
backTracking(tickets.length, ticketMap, resRoute);
|
||||
return resRoute;
|
||||
function backTracking(ticketNum: number, ticketMap: TicketsMap, route: string[]): boolean {
|
||||
if (route.length === ticketNum + 1) return true;
|
||||
const targetMap = ticketMap[route[route.length - 1]];
|
||||
if (targetMap !== undefined) {
|
||||
for (const [to, count] of targetMap.entries()) {
|
||||
if (count > 0) {
|
||||
route.push(to);
|
||||
targetMap.set(to, count - 1);
|
||||
if (backTracking(ticketNum, ticketMap, route) === true) return true;
|
||||
targetMap.set(to, count);
|
||||
route.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
直接迭代tickets数组:
|
||||
@@ -663,5 +707,105 @@ for line in tickets {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
|
||||
// 先排序,然后找到第一条路径即可返回
|
||||
func findItinerary(tickets [][]string) []string {
|
||||
var path []string // 用来保存搜索的路径
|
||||
data := make(map[string]ticketSlice) // 用来保存tickets排序后的结果
|
||||
|
||||
var search func(airport string) bool
|
||||
search = func(airport string) bool {
|
||||
if len(path) == len(tickets) {
|
||||
path = append(path, airport)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
to := data[airport]
|
||||
for _, item := range to {
|
||||
if item.Count == 0 {
|
||||
// 已用完
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path = append(path, airport)
|
||||
item.Count--
|
||||
if search(item.To) { return true }
|
||||
item.Count++
|
||||
path = path[:len(path) - 1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 排序
|
||||
// 感觉这段代码有点啰嗦,不知道能不能简化一下
|
||||
tmp := make(map[string]map[string]int)
|
||||
for _, ticket := range tickets {
|
||||
if to, ok := tmp[ticket[0]]; ok {
|
||||
if _, ok2 := to[ticket[1]]; ok2 {
|
||||
to[ticket[1]]++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
to[ticket[1]] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
tmp[ticket[0]] = map[string]int{
|
||||
ticket[1]: 1,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for from, to := range tmp {
|
||||
var tmp ticketSlice
|
||||
for to, num := range to {
|
||||
tmp = append(tmp, &ticketStat{To: to, Count: num})
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Sort(tmp)
|
||||
data[from] = tmp
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
search("JFK")
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type ticketStat struct {
|
||||
To string
|
||||
Count int
|
||||
}
|
||||
type ticketSlice []*ticketStat
|
||||
|
||||
func (p ticketSlice) Len() int { return len(p) }
|
||||
func (p ticketSlice) Less(i, j int) bool { return strings.Compare(p[i].To, p[j].To) == -1 }
|
||||
func (p ticketSlice) Swap(i, j int) { p[i], p[j] = p[j], p[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
** 文中的Hashmap嵌套Hashmap的方法因为Rust的所有权问题暂时无法实现,此方法为删除哈希表中元素法 **
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
use std::collections::HashMap;
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(airport: String, targets: &mut HashMap<&String, Vec<&String>>, result: &mut Vec<String>) {
|
||||
while let Some(next_airport) = targets.get_mut(&airport).unwrap_or(&mut vec![]).pop() {
|
||||
Self::backtracking(next_airport.clone(), targets, result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
result.push(airport.clone());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pub fn find_itinerary(tickets: Vec<Vec<String>>) -> Vec<String> {
|
||||
let mut targets: HashMap<&String, Vec<&String>> = HashMap::new();
|
||||
let mut result = Vec::new();
|
||||
for t in 0..tickets.len() {
|
||||
targets.entry(&tickets[t][0]).or_default().push(&tickets[t][1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (_, target) in targets.iter_mut() {
|
||||
target.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a));
|
||||
}
|
||||
Self::backtracking("JFK".to_string(), &mut targets, &mut result);
|
||||
result.reverse();
|
||||
result
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,9 +5,9 @@
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 337.打家劫舍 III
|
||||
# 337.打家劫舍 III
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-iii/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/house-robber-iii/)
|
||||
|
||||
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋后,小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为“根”。 除了“根”之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫,房屋将自动报警。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -190,9 +190,9 @@ public:
|
||||
if (cur == NULL) return vector<int>{0, 0};
|
||||
vector<int> left = robTree(cur->left);
|
||||
vector<int> right = robTree(cur->right);
|
||||
// 偷cur
|
||||
int val1 = cur->val + left[0] + right[0];
|
||||
// 不偷cur
|
||||
// 偷cur,那么就不能偷左右节点。
|
||||
int val1 = cur->val + left[1] + right[1];
|
||||
// 不偷cur,那么可以偷也可以不偷左右节点,则取较大的情况
|
||||
int val2 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
|
||||
return {val2, val1};
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -353,18 +353,30 @@ class Solution:
|
||||
# self.left = left
|
||||
# self.right = right
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def rob(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
|
||||
result = self.rob_tree(root)
|
||||
return max(result[0], result[1])
|
||||
|
||||
def rob_tree(self, node):
|
||||
if node is None:
|
||||
return (0, 0) # (偷当前节点金额,不偷当前节点金额)
|
||||
left = self.rob_tree(node.left)
|
||||
right = self.rob_tree(node.right)
|
||||
val1 = node.val + left[1] + right[1] # 偷当前节点,不能偷子节点
|
||||
val2 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]) # 不偷当前节点,可偷可不偷子节点
|
||||
return (val1, val2)
|
||||
def rob(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
|
||||
# dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义:
|
||||
# 1. 下标为 0 记录 **不偷该节点** 所得到的的最大金钱
|
||||
# 2. 下标为 1 记录 **偷该节点** 所得到的的最大金钱
|
||||
dp = self.traversal(root)
|
||||
return max(dp)
|
||||
|
||||
# 要用后序遍历, 因为要通过递归函数的返回值来做下一步计算
|
||||
def traversal(self, node):
|
||||
|
||||
# 递归终止条件,就是遇到了空节点,那肯定是不偷的
|
||||
if not node:
|
||||
return (0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
left = self.traversal(node.left)
|
||||
right = self.traversal(node.right)
|
||||
|
||||
# 不偷当前节点, 偷子节点
|
||||
val_0 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1])
|
||||
|
||||
# 偷当前节点, 不偷子节点
|
||||
val_1 = node.val + left[0] + right[0]
|
||||
|
||||
return (val_0, val_1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
@@ -429,7 +441,50 @@ const rob = root => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
> 记忆化后序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
const memory: Map<TreeNode, number> = new Map();
|
||||
function rob(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||||
if (root === null) return 0;
|
||||
if (memory.has(root)) return memory.get(root);
|
||||
// 不取当前节点
|
||||
const res1: number = rob(root.left) + rob(root.right);
|
||||
// 取当前节点
|
||||
let res2: number = root.val;
|
||||
if (root.left !== null) res2 += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right);
|
||||
if (root.right !== null) res2 += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right);
|
||||
const res: number = Math.max(res1, res2);
|
||||
memory.set(root, res);
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 状态标记化后序遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function rob(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||||
return Math.max(...robNode(root));
|
||||
};
|
||||
// [0]-不偷当前节点能获得的最大金额; [1]-偷~~
|
||||
type MaxValueArr = [number, number];
|
||||
function robNode(node: TreeNode | null): MaxValueArr {
|
||||
if (node === null) return [0, 0];
|
||||
const leftArr: MaxValueArr = robNode(node.left);
|
||||
const rightArr: MaxValueArr = robNode(node.right);
|
||||
// 不偷
|
||||
const val1: number = Math.max(leftArr[0], leftArr[1]) +
|
||||
Math.max(rightArr[0], rightArr[1]);
|
||||
// 偷
|
||||
const val2: number = leftArr[0] + rightArr[0] + node.val;
|
||||
return [val1, val2];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 打家劫舍Ⅲ 动态规划
|
||||
// 时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(logn)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 343. 整数拆分
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/integer-break/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/integer-break/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个正整数 n,将其拆分为至少两个正整数的和,并使这些整数的乘积最大化。 返回你可以获得的最大乘积。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -119,8 +119,8 @@ public:
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
### 贪心
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ public:
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int integerBreak(int n) {
|
||||
@@ -259,6 +259,21 @@ func max(a,b int) int{
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub fn integer_break(n: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let n = n as usize;
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![0; n + 1];
|
||||
dp[2] = 1;
|
||||
for i in 3..=n {
|
||||
for j in 1..i-1 {
|
||||
dp[i] = dp[i].max((i - j) * j).max(dp[i - j] * j);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[n] as i32
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var integerBreak = function(n) {
|
||||
@@ -274,7 +289,54 @@ var integerBreak = function(n) {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
function integerBreak(n: number): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i]: i对应的最大乘积
|
||||
dp[2]: 1;
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: max(
|
||||
1 * dp[i - 1], 1 * (i - 1),
|
||||
2 * dp[i - 2], 2 * (i - 2),
|
||||
..., (i - 2) * dp[2], (i - 2) * 2
|
||||
);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
|
||||
dp[2] = 1;
|
||||
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j <= i - 2; j++) {
|
||||
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], j * dp[i - j], j * (i - j));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32{
|
||||
if a > b { a } else { b }
|
||||
}
|
||||
pub fn integer_break(n: i32) -> i32 {
|
||||
let n = n as usize;
|
||||
let mut dp = vec![0; n + 1];
|
||||
dp[2] = 1;
|
||||
for i in 3..=n {
|
||||
for j in 1..i - 1 {
|
||||
dp[i] = Self::max(dp[i], Self::max(((i - j) * j) as i32, dp[i - j] * j as i32));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp[n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//初始化DP数组
|
||||
int *initDP(int num) {
|
||||
@@ -309,5 +371,22 @@ int integerBreak(int n){
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def integerBreak(n: Int): Int = {
|
||||
var dp = new Array[Int](n + 1)
|
||||
dp(2) = 1
|
||||
for (i <- 3 to n) {
|
||||
for (j <- 1 until i - 1) {
|
||||
dp(i) = math.max(dp(i), math.max(j * (i - j), j * dp(i - j)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 344.反转字符串
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string/)
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string/)
|
||||
|
||||
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 char[] 的形式给出。
|
||||
|
||||
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 $O(1)$ 的额外空间解决这一问题。
|
||||
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以假设数组中的所有字符都是 ASCII 码表中的可打印字符。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -29,6 +29,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
针对本题,我录制了视频讲解:[字符串基础操作! | LeetCode:344.反转字符串](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fV4y17748),结合本题解一起看,事半功倍!
|
||||
|
||||
先说一说题外话:
|
||||
|
||||
对于这道题目一些同学直接用C++里的一个库函数 reverse,调一下直接完事了, 相信每一门编程语言都有这样的库函数。
|
||||
@@ -190,13 +192,13 @@ javaScript:
|
||||
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
var reverseString = function(s) {
|
||||
return s.reverse();
|
||||
//Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead.
|
||||
reverse(s)
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
var reverseString = function(s) {
|
||||
var reverse = function(s) {
|
||||
let l = -1, r = s.length;
|
||||
while(++l < --r) [s[l], s[r]] = [s[r], s[l]];
|
||||
return s;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -238,6 +240,22 @@ func reverseString(_ s: inout [Character]) {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rust:
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn reverse_string(s: &mut Vec<char>) {
|
||||
let (mut left, mut right) = (0, s.len()-1);
|
||||
while left < right {
|
||||
let temp = s[left];
|
||||
s[left] = s[right];
|
||||
s[right] = temp;
|
||||
left += 1;
|
||||
right -= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
void reverseString(char* s, int sSize){
|
||||
@@ -267,5 +285,51 @@ public class Solution
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// 双指针
|
||||
// 一:
|
||||
function reverseString(&$s) {
|
||||
$left = 0;
|
||||
$right = count($s)-1;
|
||||
while($left<$right){
|
||||
$temp = $s[$left];
|
||||
$s[$left] = $s[$right];
|
||||
$s[$right] = $temp;
|
||||
$left++;
|
||||
$right--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 二:
|
||||
function reverseString(&$s) {
|
||||
$this->reverse($s,0,count($s)-1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 按指定位置交换元素
|
||||
function reverse(&$s, $start, $end) {
|
||||
for ($i = $start, $j = $end; $i < $j; $i++, $j--) {
|
||||
$tmp = $s[$i];
|
||||
$s[$i] = $s[$j];
|
||||
$s[$j] = $tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def reverseString(s: Array[Char]): Unit = {
|
||||
var (left, right) = (0, s.length - 1)
|
||||
while (left < right) {
|
||||
var tmp = s(left)
|
||||
s(left) = s(right)
|
||||
s(right) = tmp
|
||||
left += 1
|
||||
right -= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user